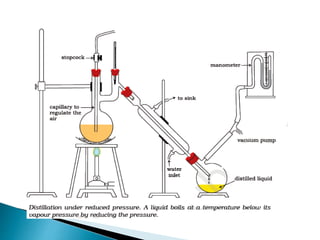
Vacuum distillation is a distillation technique performed under reduced pressure that allows compounds to boil and be separated at temperatures below their normal boiling points. This technique is useful for separating compounds with high boiling points over 200°C that may decompose if boiled at their normal temperature, or compounds that are otherwise difficult to distill. Under reduced pressure, the boiling point of compounds is lowered, facilitating separation based on differences in boiling points.