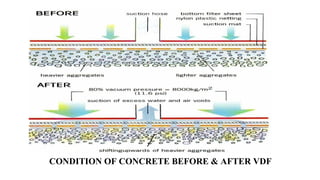
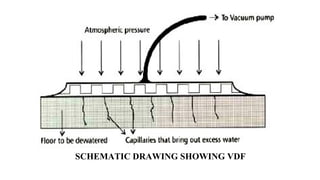
This document provides an overview of vacuum dewated flooring (VDF). VDF is a flooring technique that uses vacuum pressure to remove water from freshly laid concrete, resulting in a stronger and harder floor. The document defines VDF, outlines its benefits such as increased strength and wear resistance. It describes the VDF process which involves laying concrete, vibrating it, placing a suction mat to remove water, and finishing the surface. Equipment for VDF including screed vibrators, vacuum pumps, and power floats are also detailed. Advantages like early strength and reduced cracking are contrasted with disadvantages like higher initial costs. Applications of VDF in industrial, transportation, and hydraulic structures are listed. New dewatering