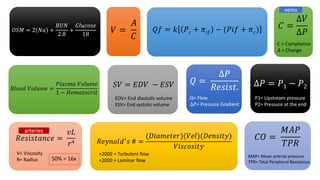
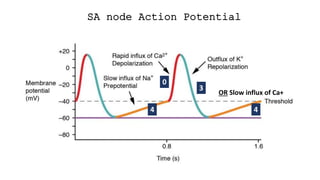
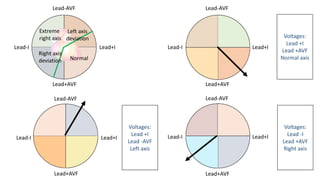
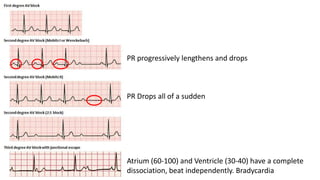
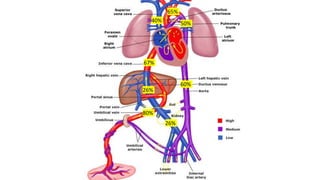
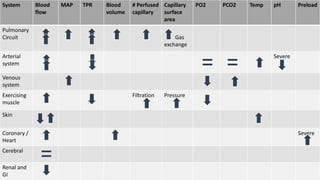
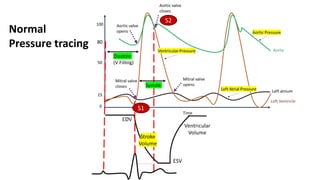
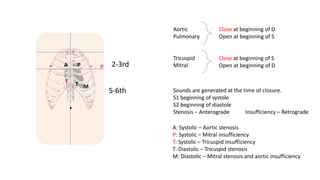
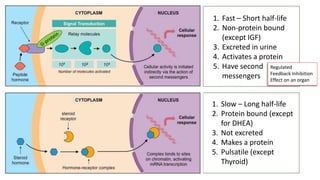
The document contains a comprehensive overview of various cardiovascular and respiratory mechanisms, including blood flow dynamics, pressures, and gas exchange principles. It discusses concepts such as cardiac output, stroke volume, and the effects of different factors on vascular resistance and compliance. Additionally, it covers renal function, hormonal influences on metabolism, and the physics behind capillary filtration and reabsorption.