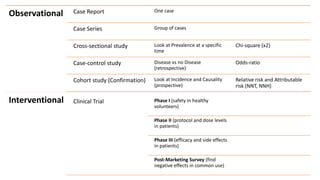
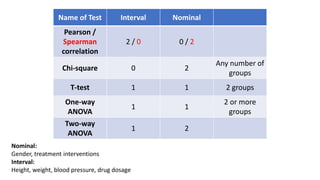
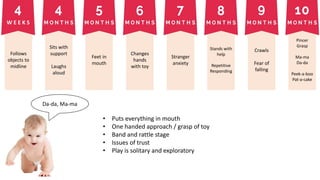
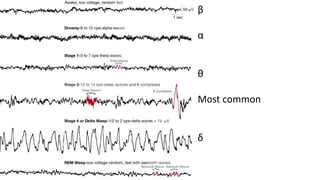
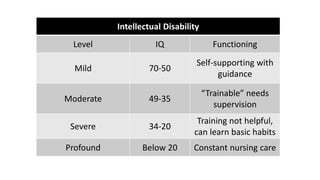
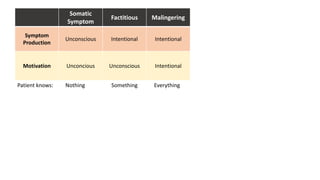
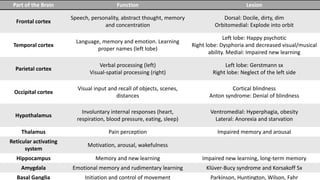
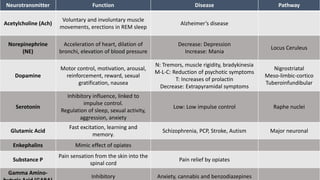
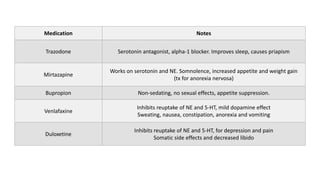
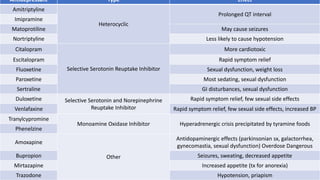
The document covers a wide range of topics related to mental health, medical statistics, treatments, and research methodologies. It includes discussions on different types of psychological disorders, their symptoms, medication treatments, risks, and research designs such as cohort and case-control studies. Additionally, it elaborates on various neurotransmitters and their functions, along with health insurance plans and their characteristics.