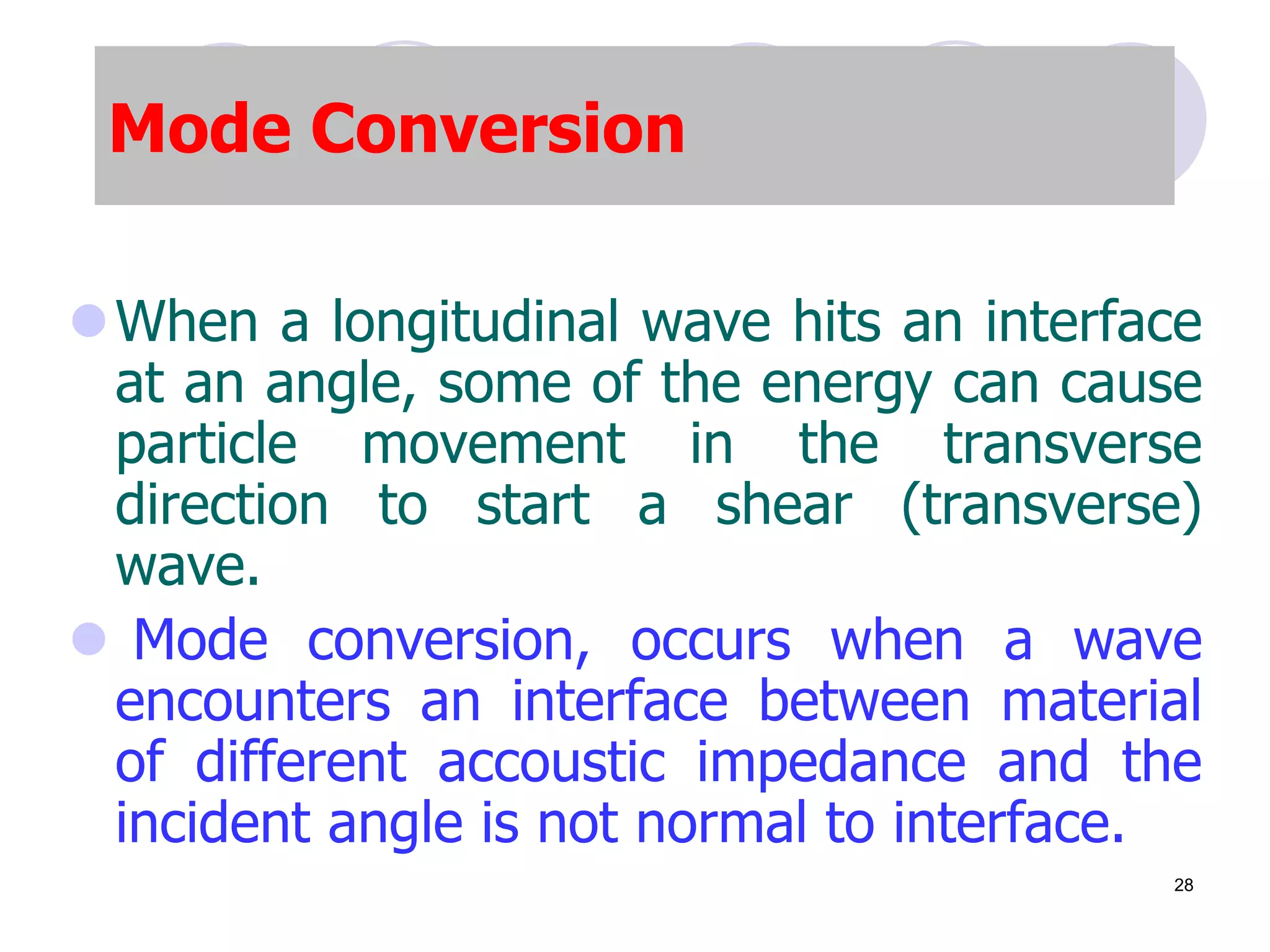
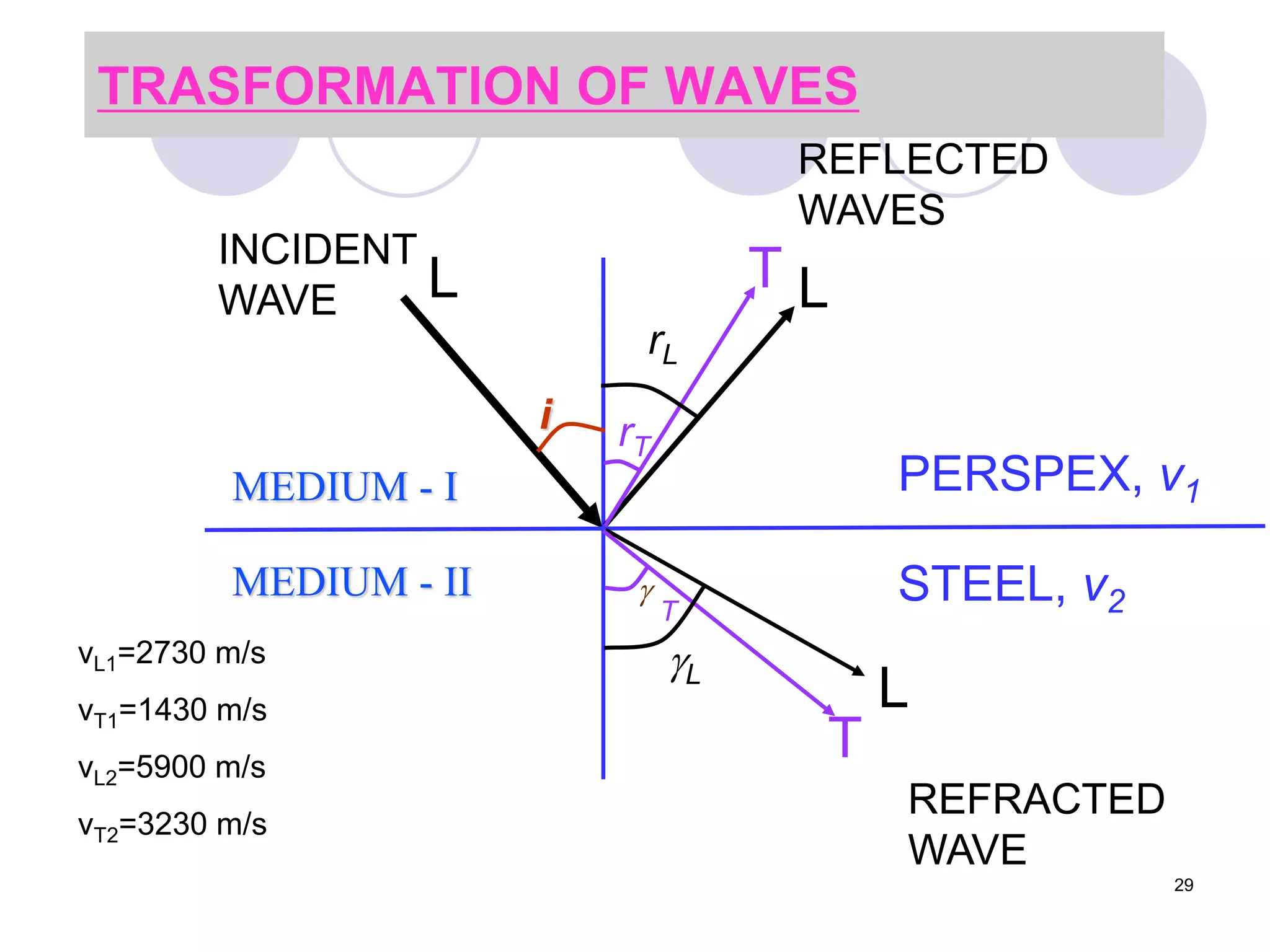
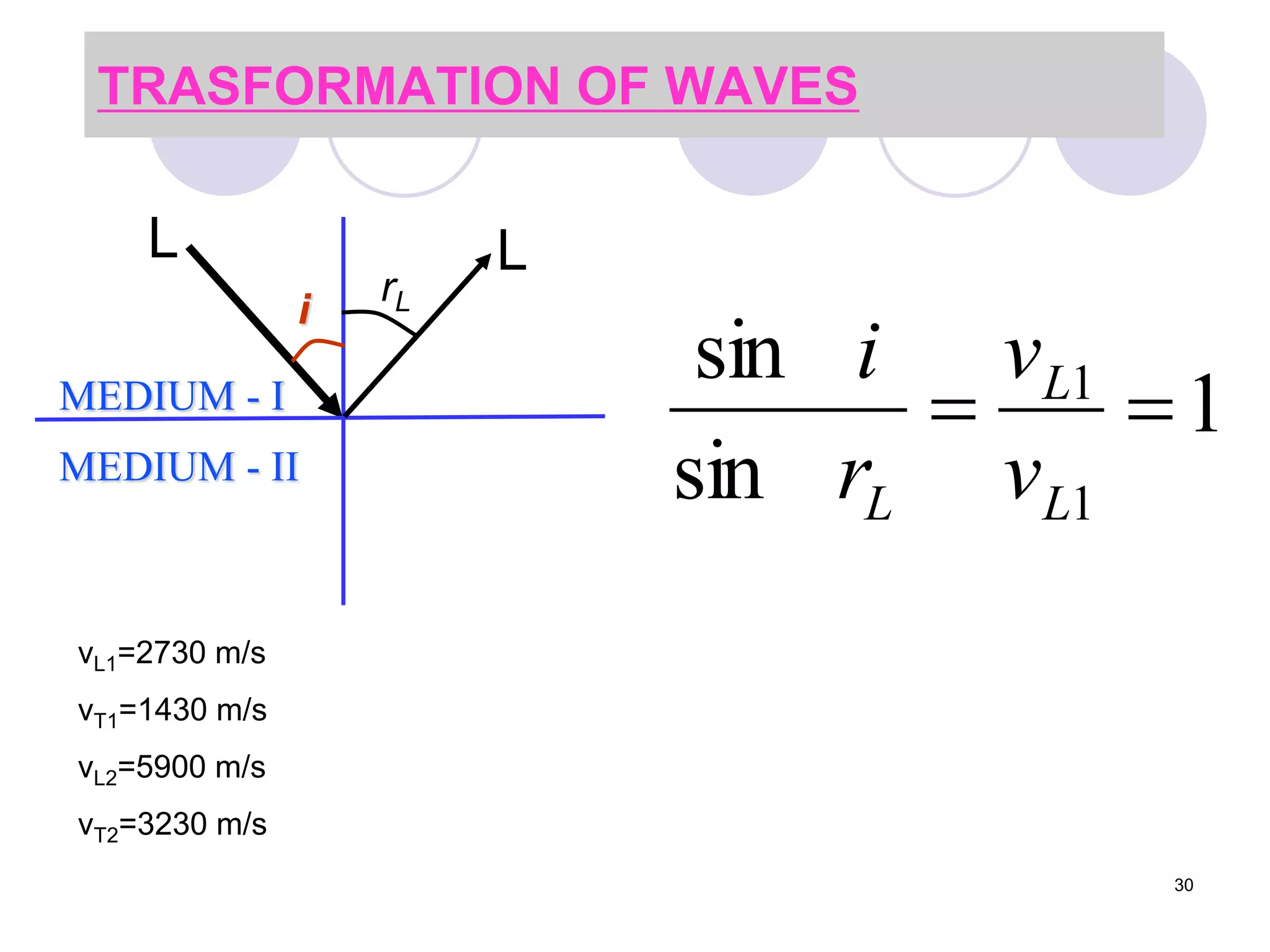
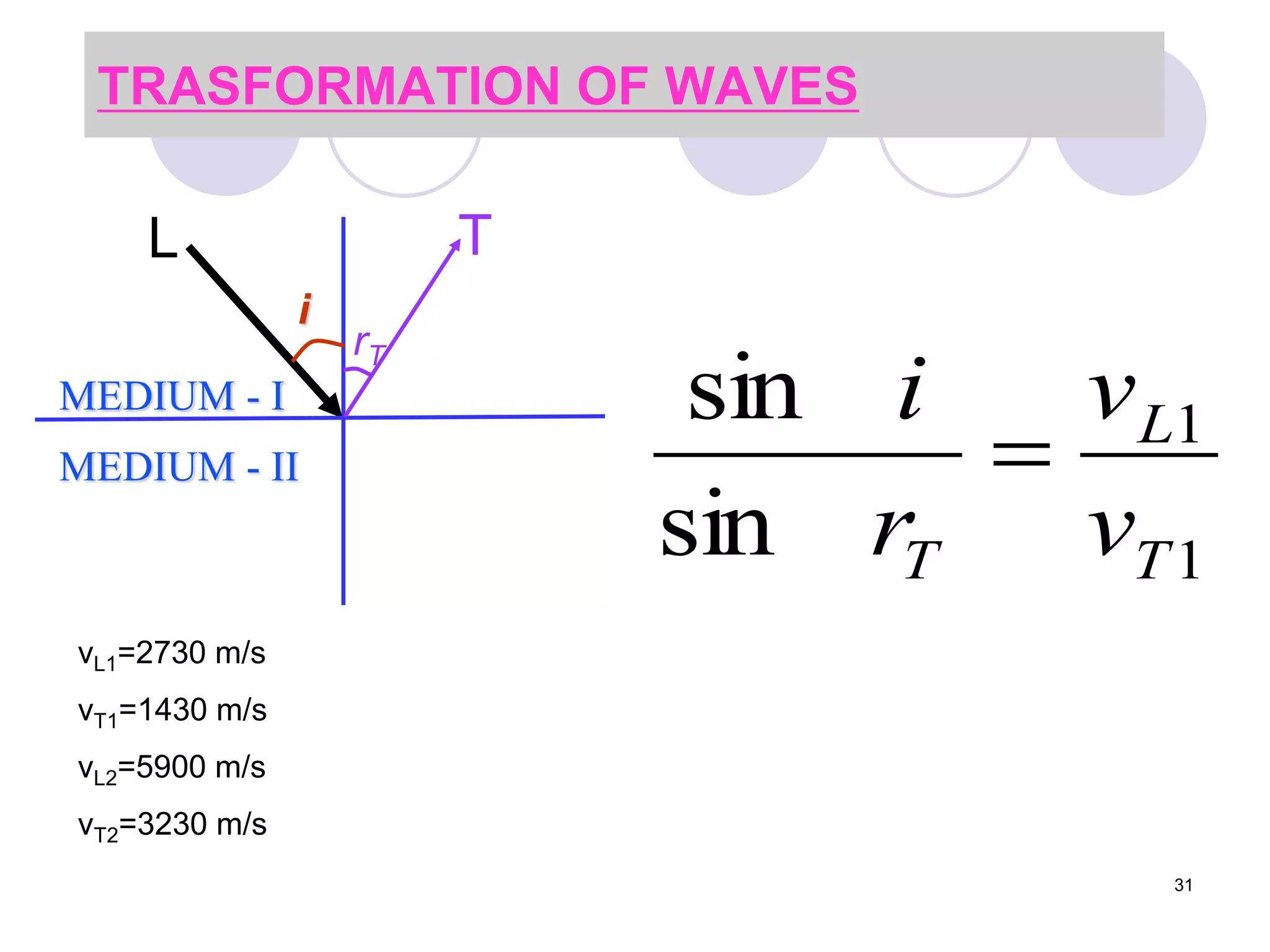
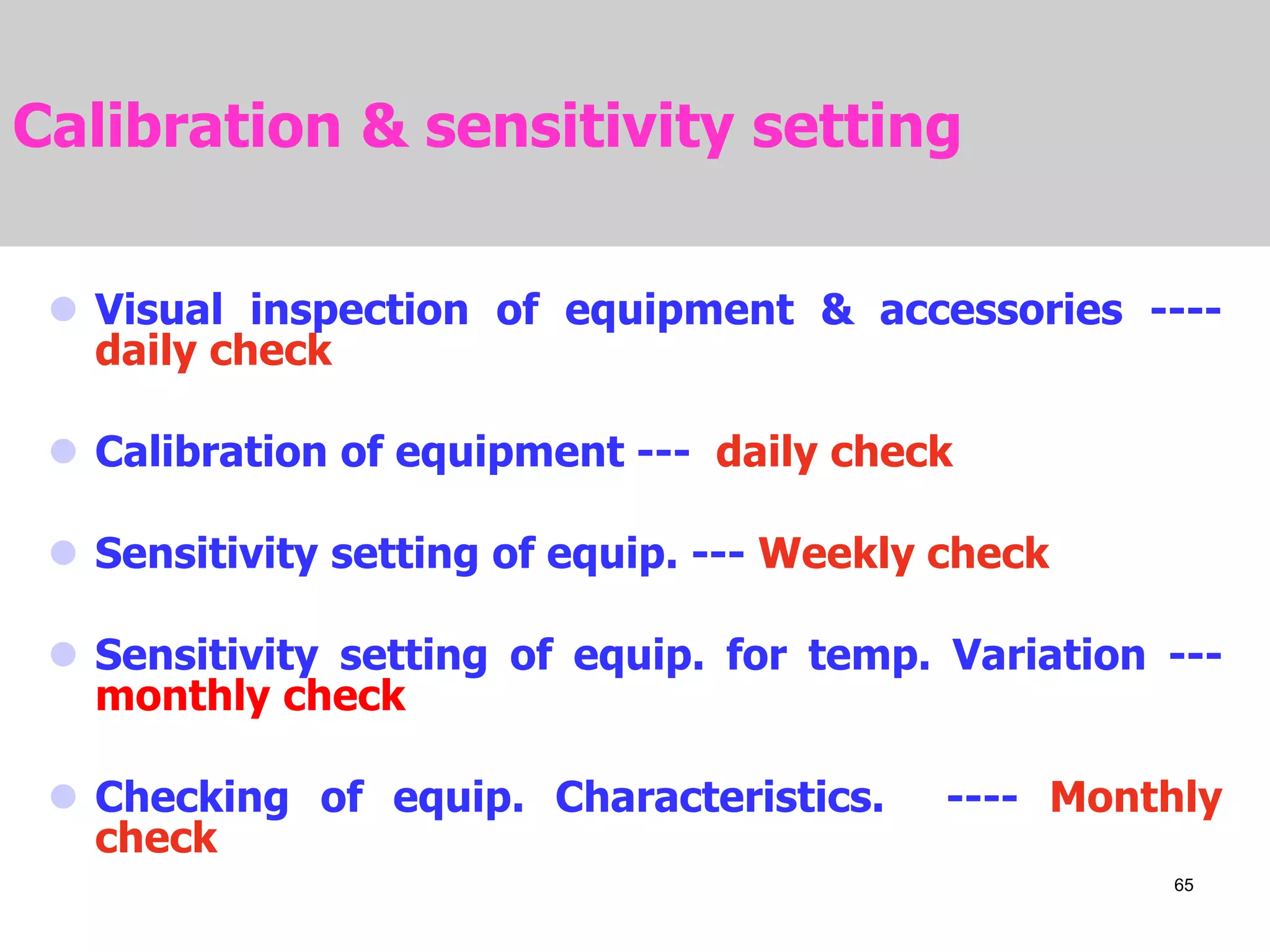
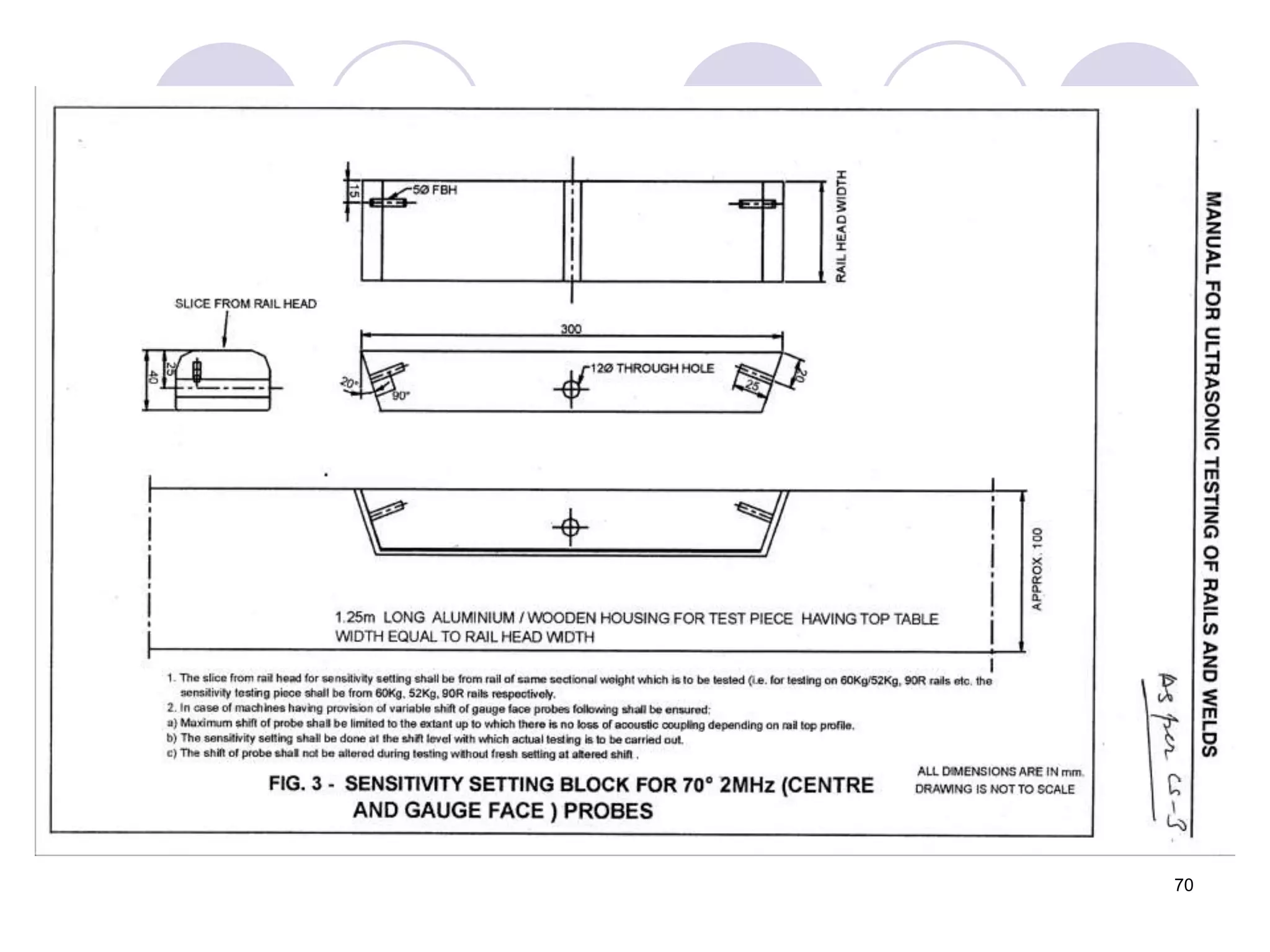
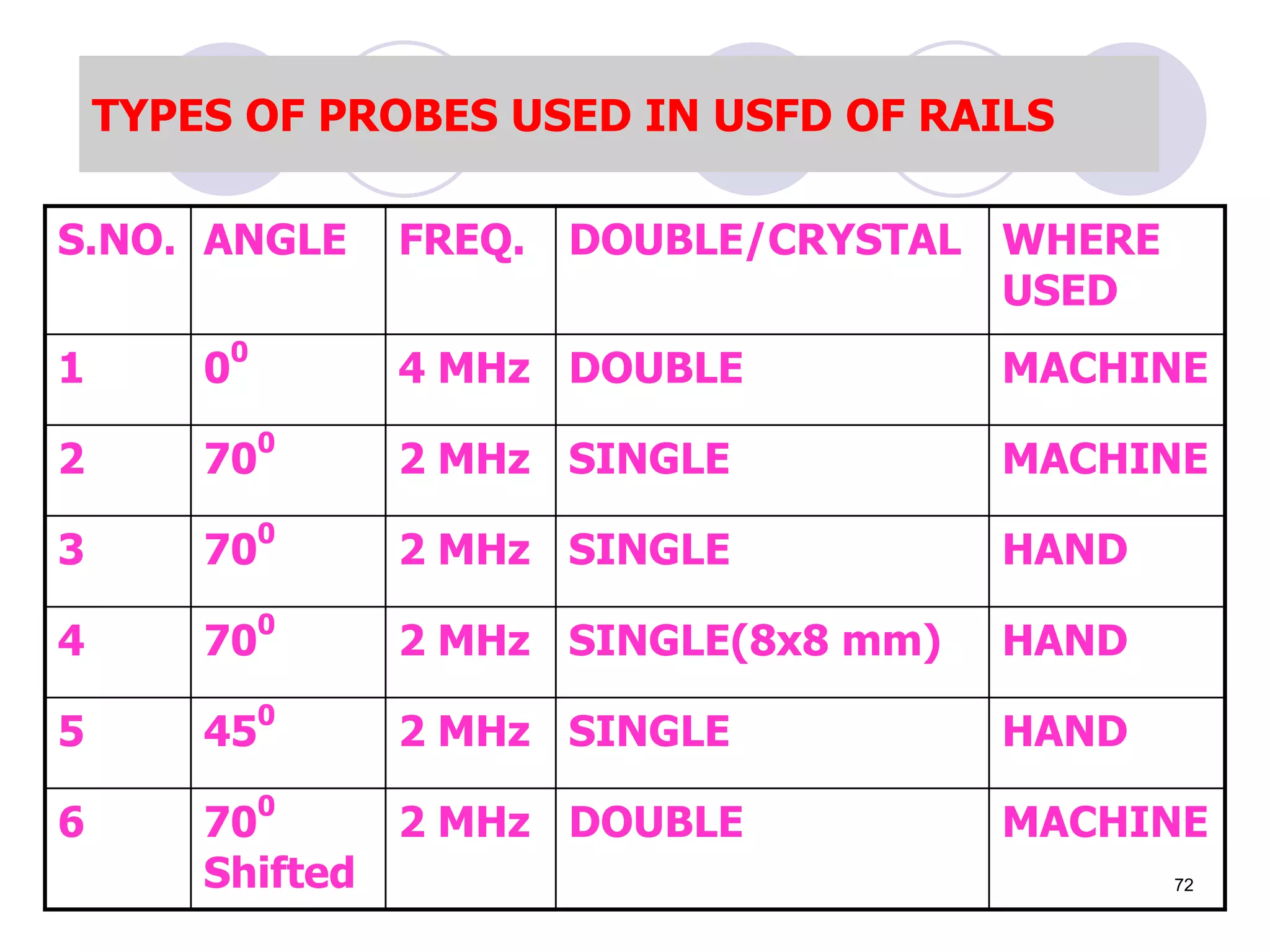
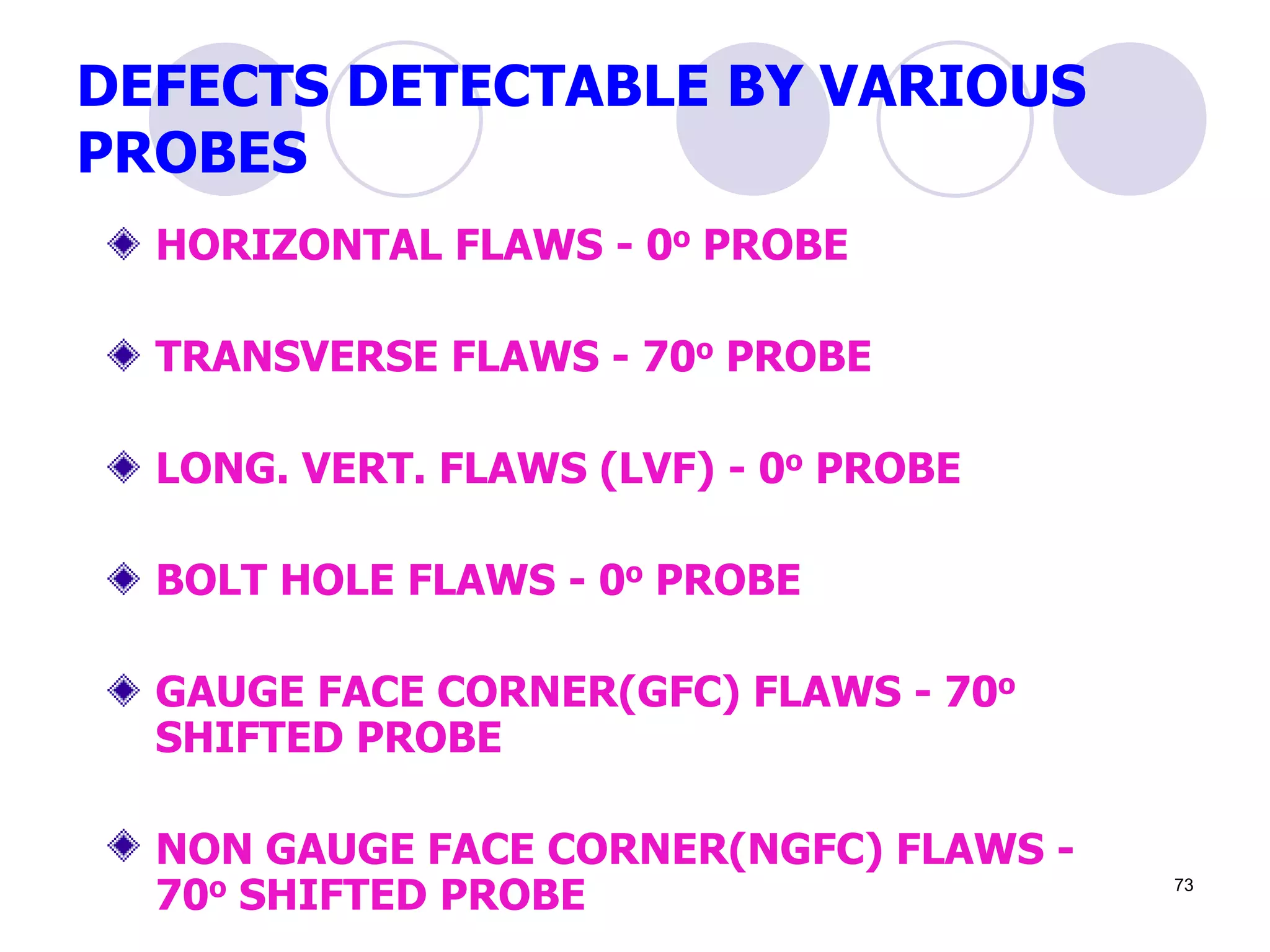
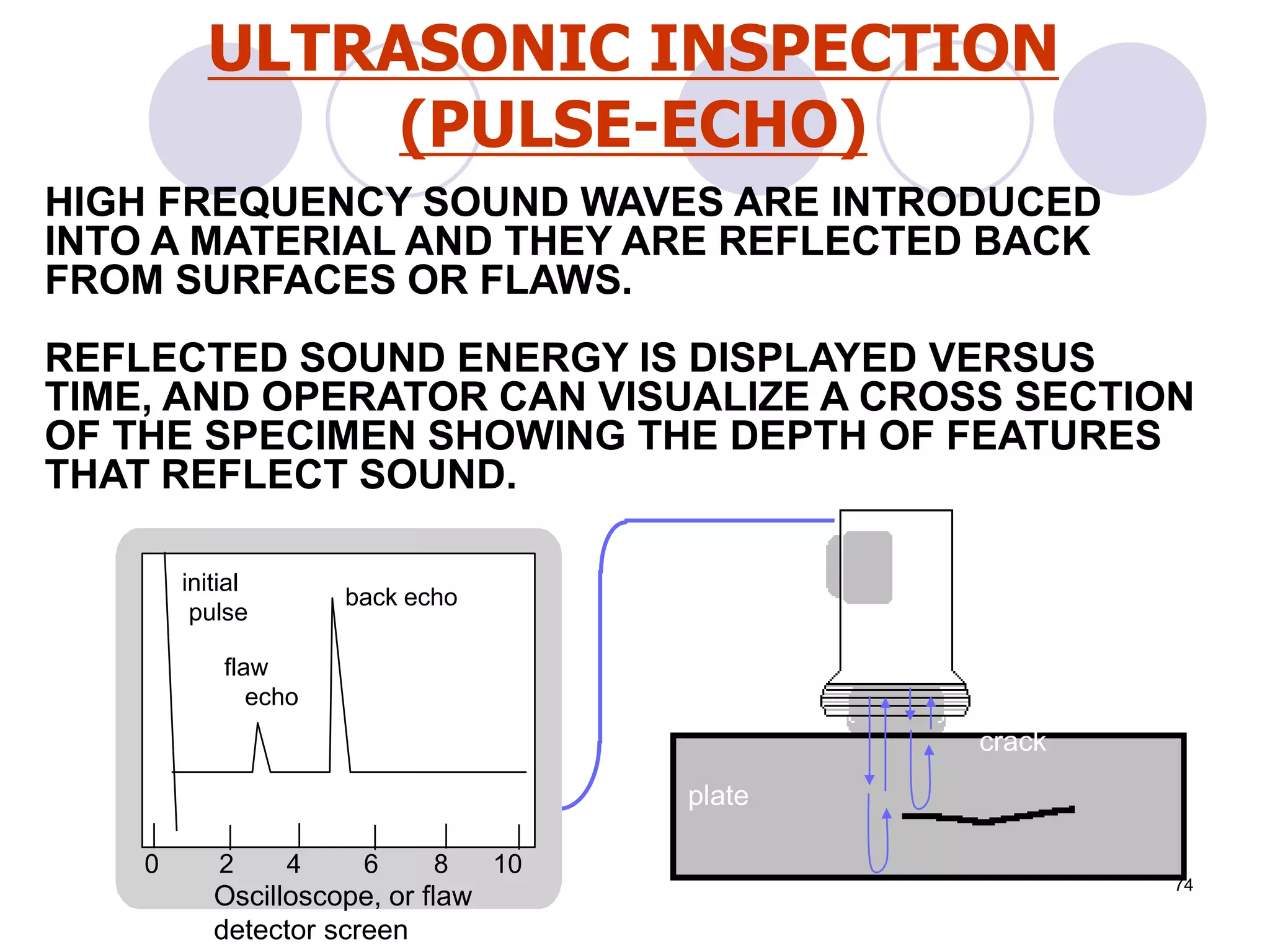
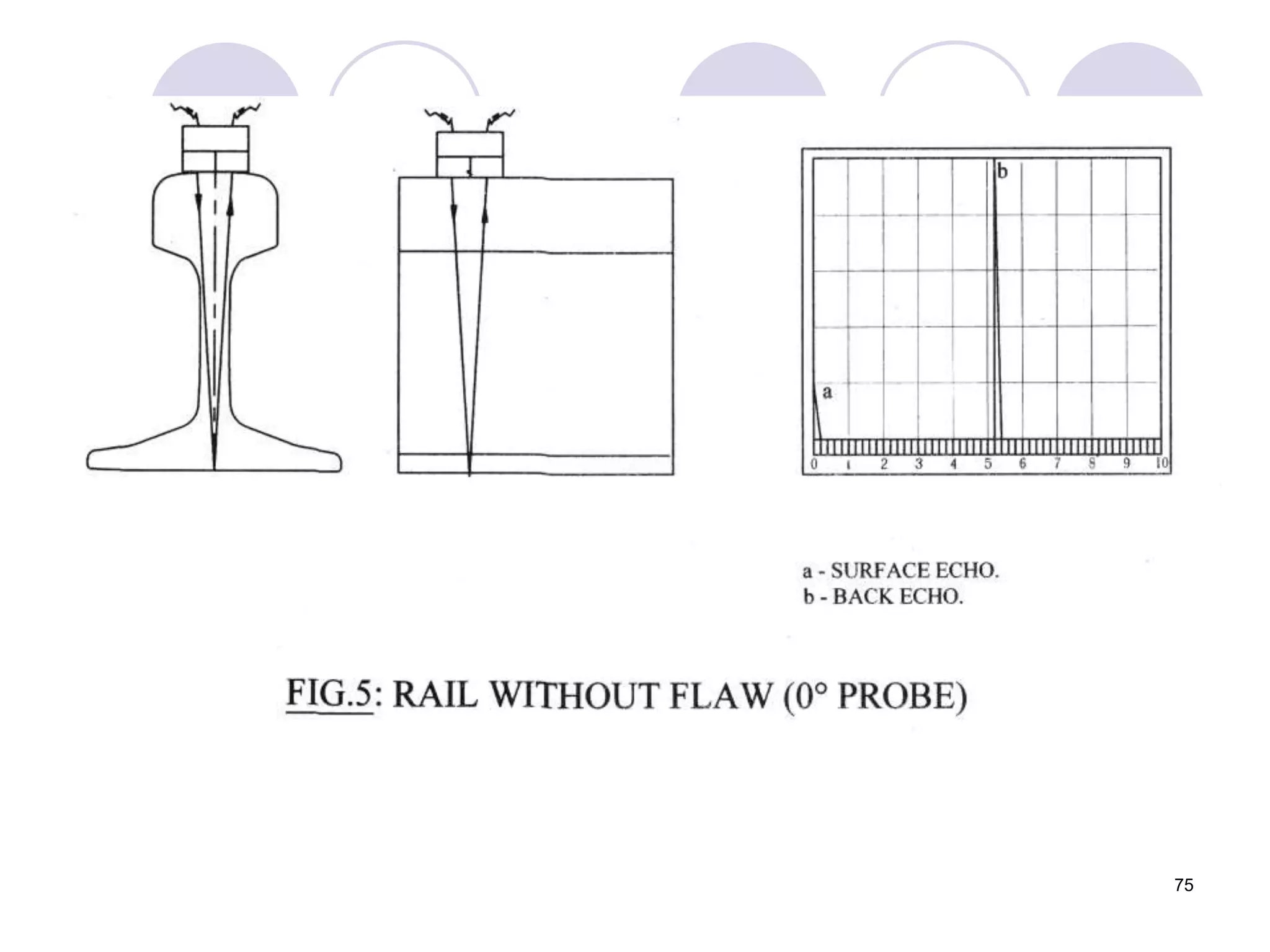
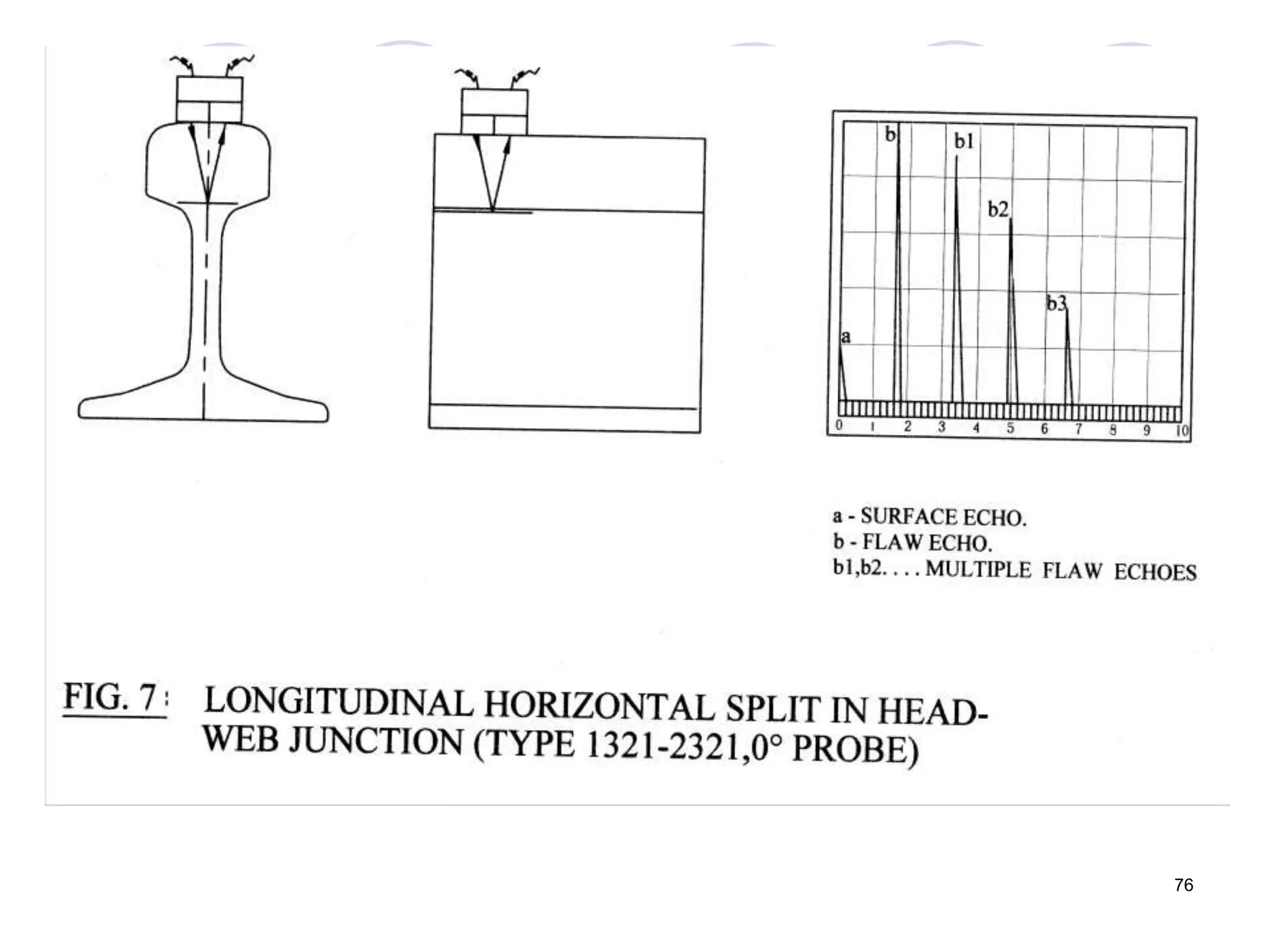
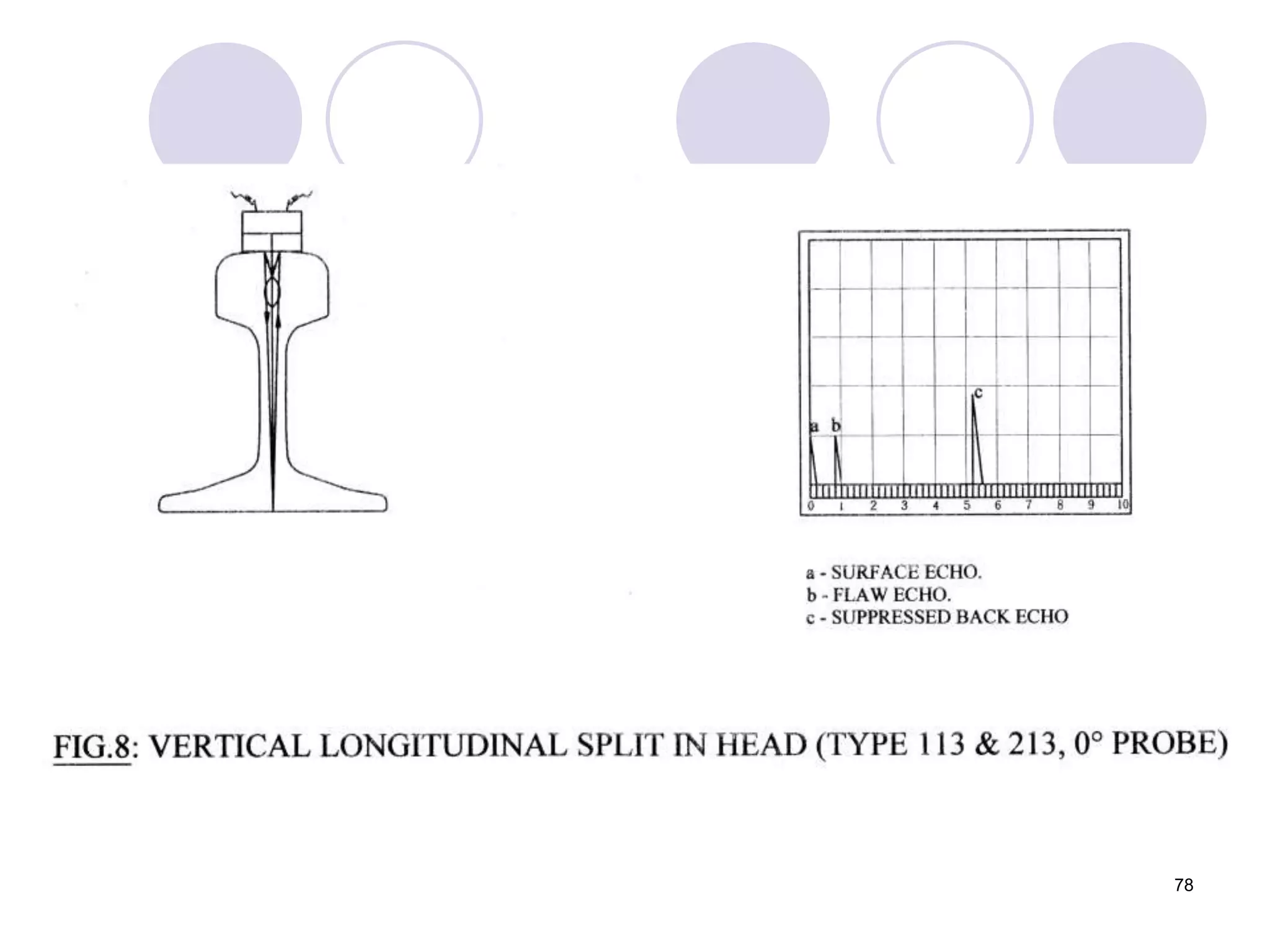
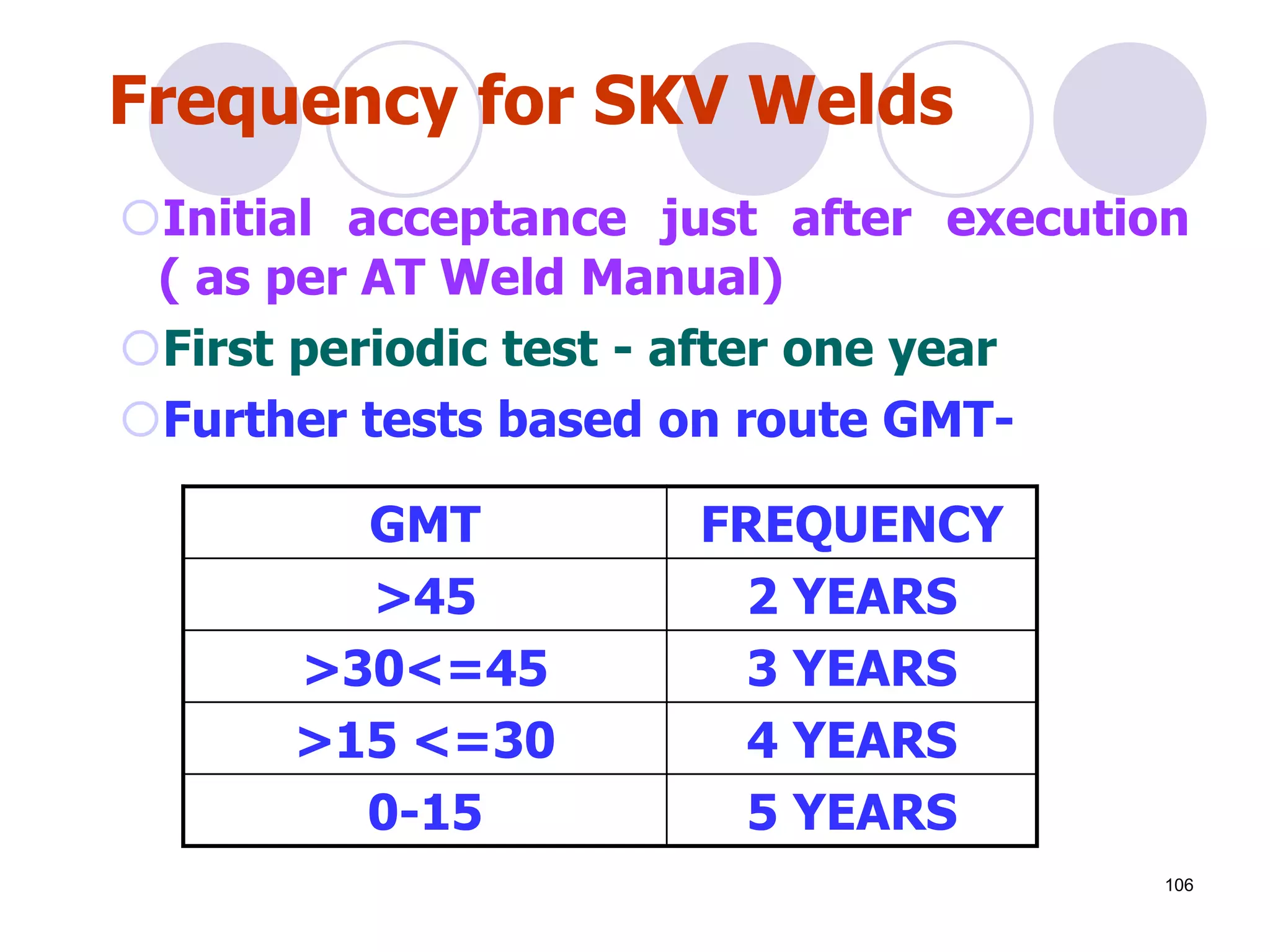
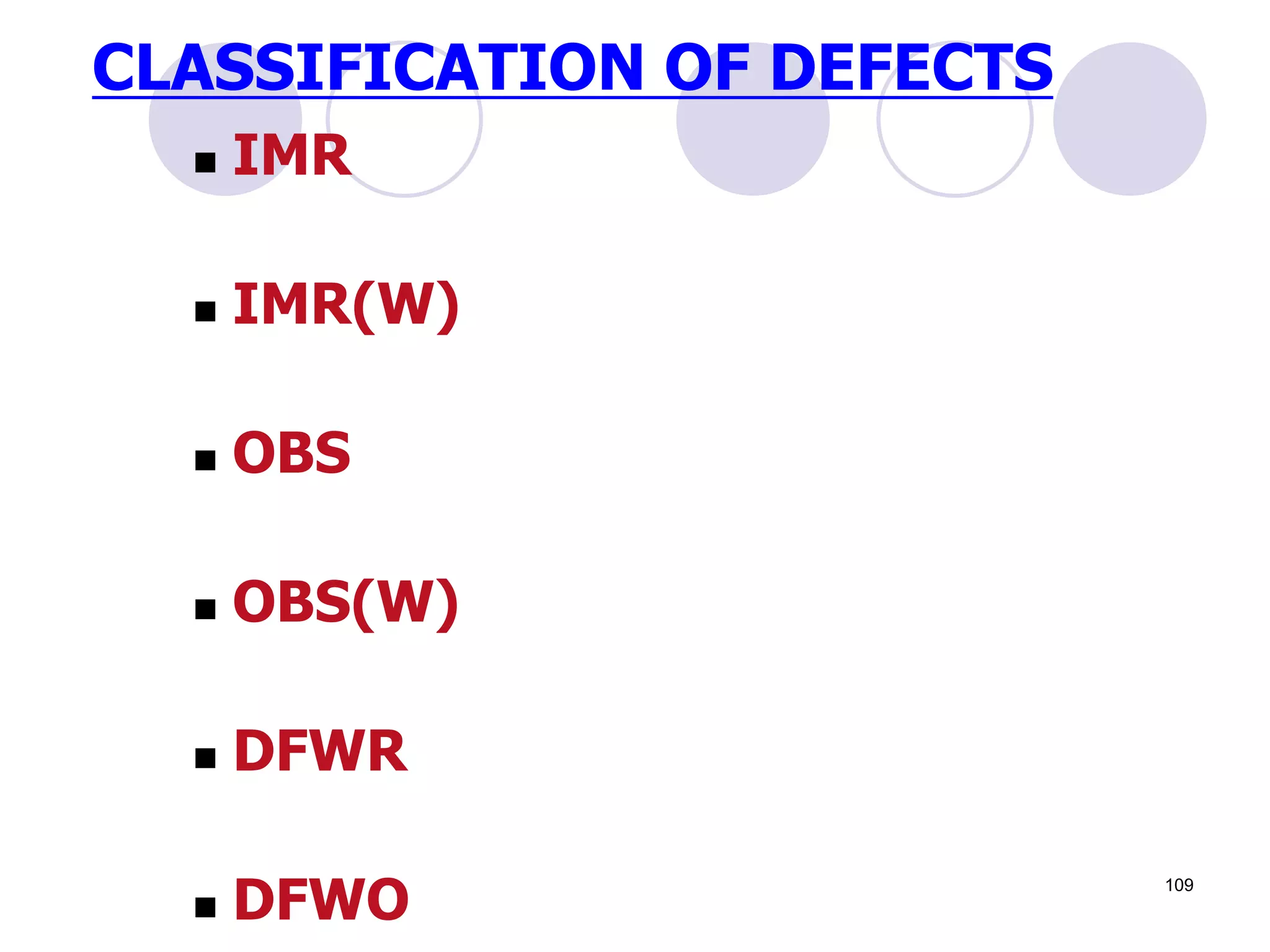
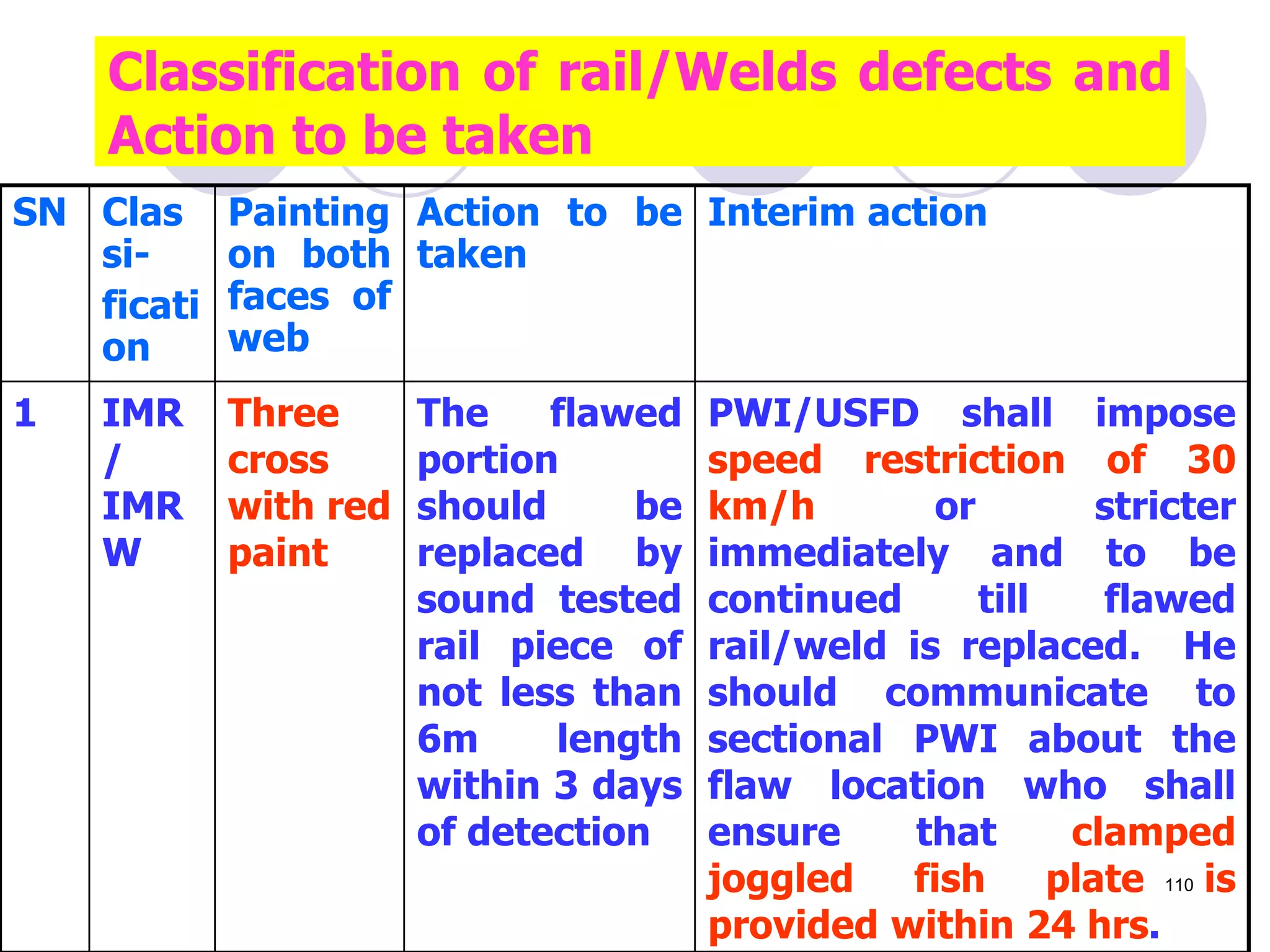
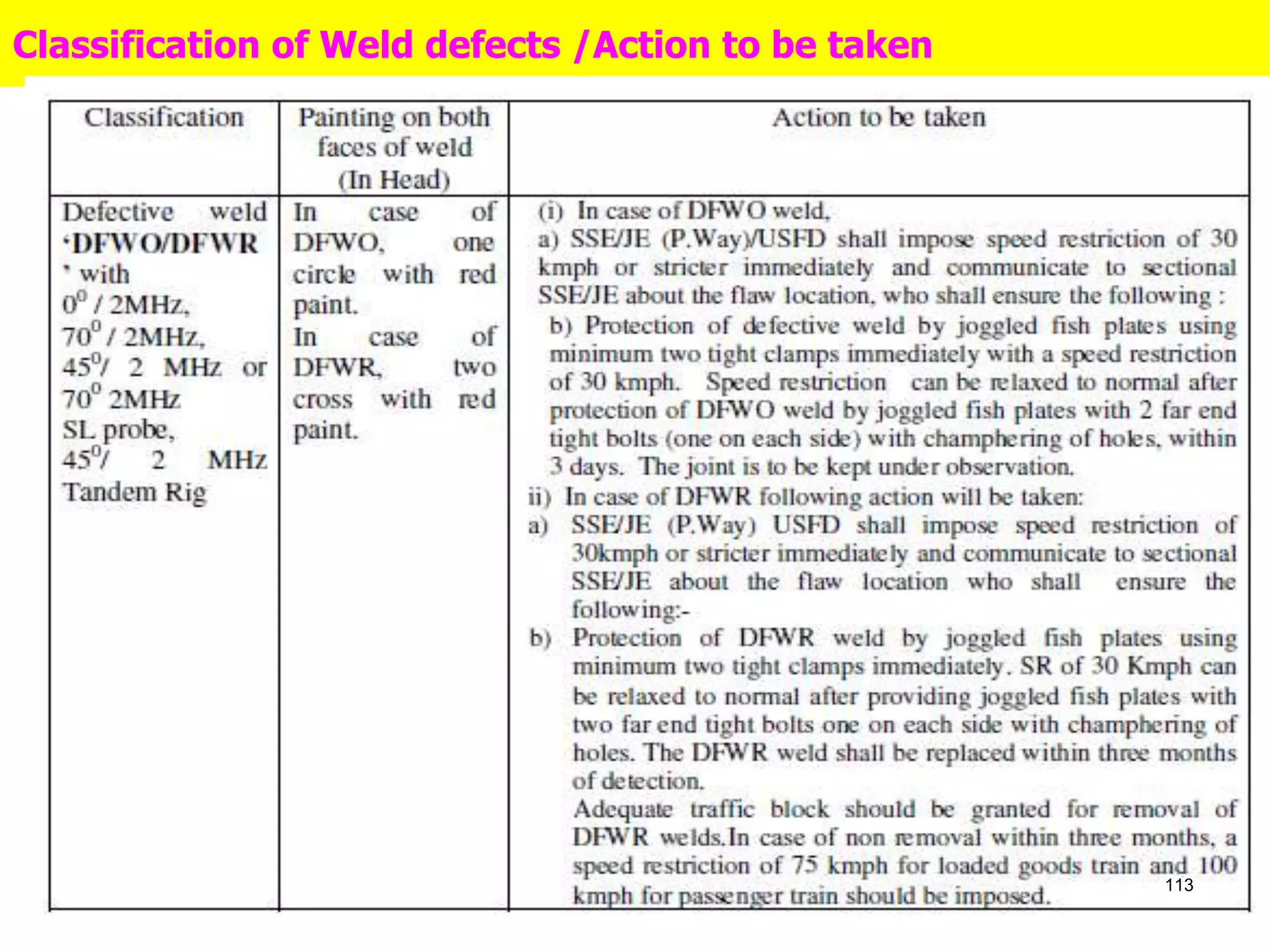
This document discusses flaws in rails and ultrasonic flaw detection testing. It covers three main points:
1. Flaws inevitably develop in rails due to inherent defects and fatigue from train traffic. Rail stresses are increasing, exceeding the mechanical properties of rail steel.
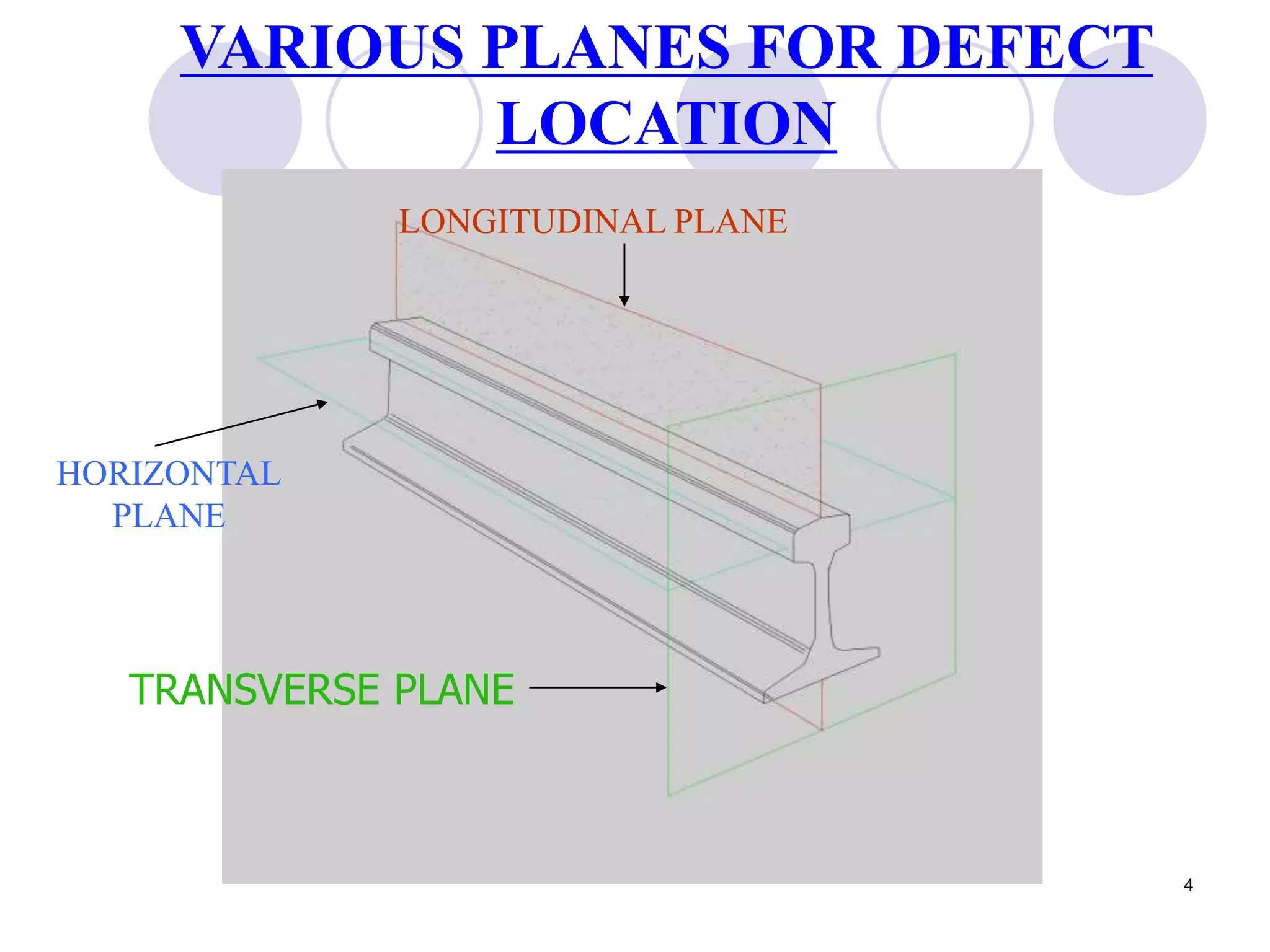
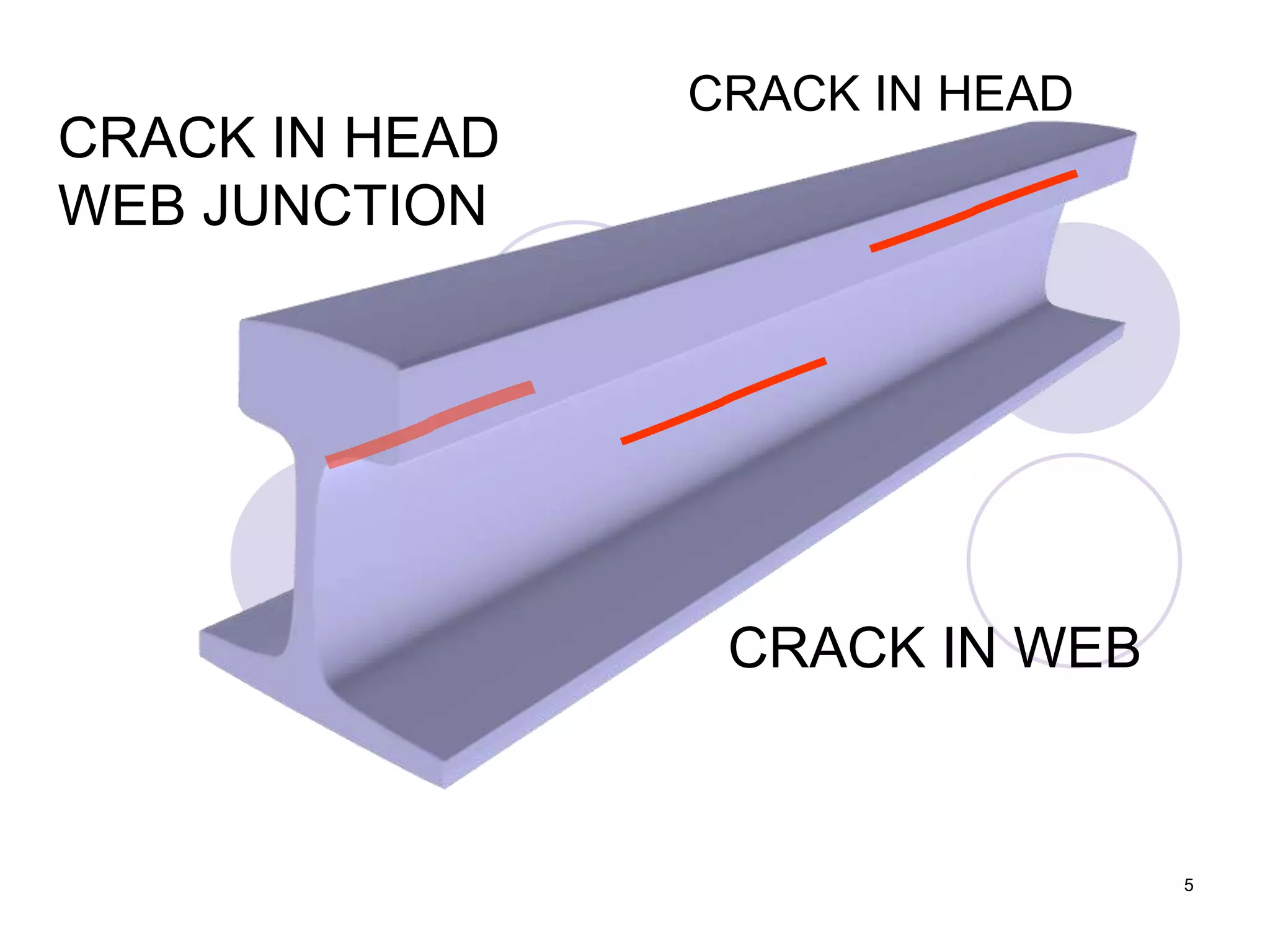
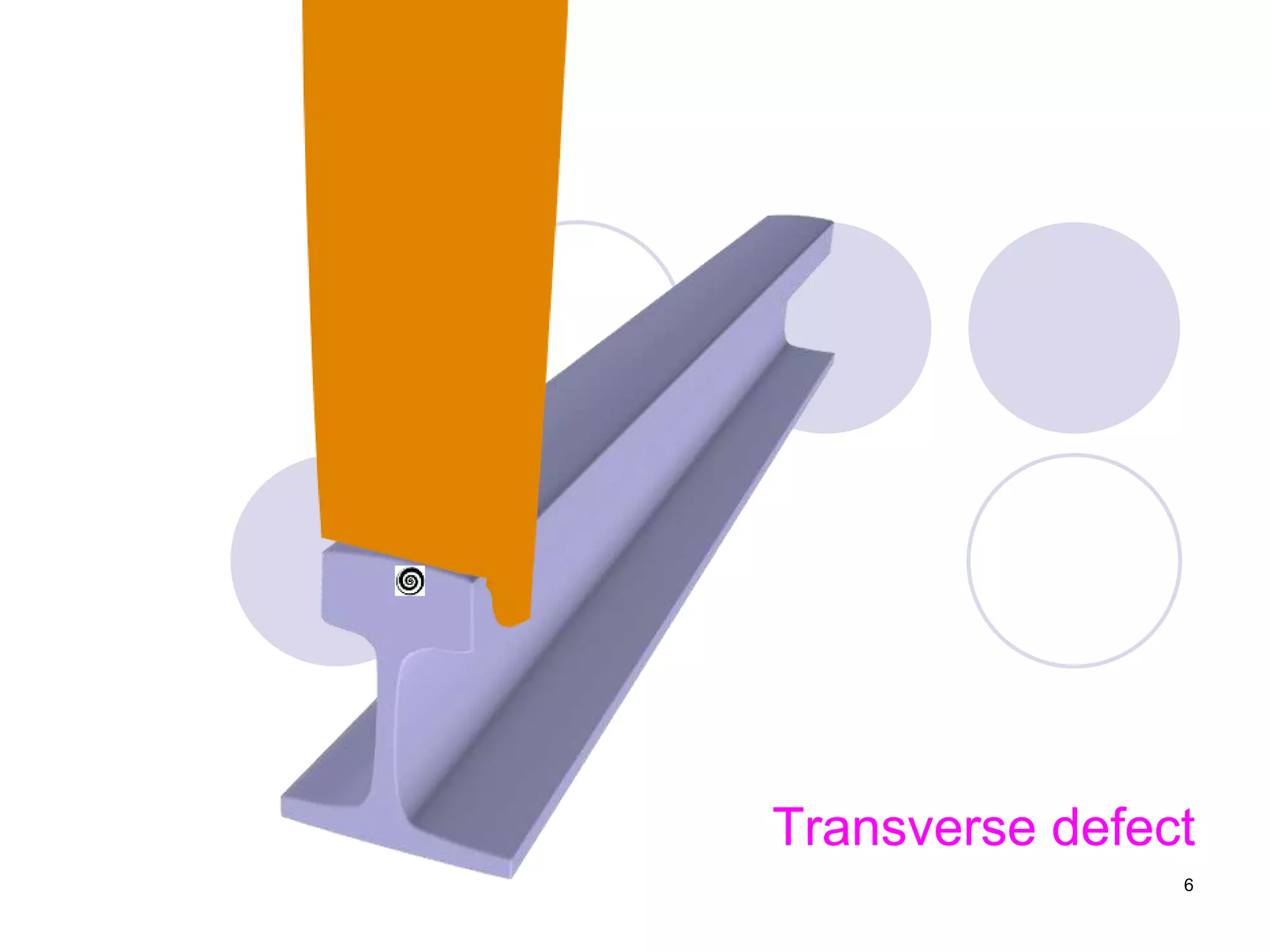
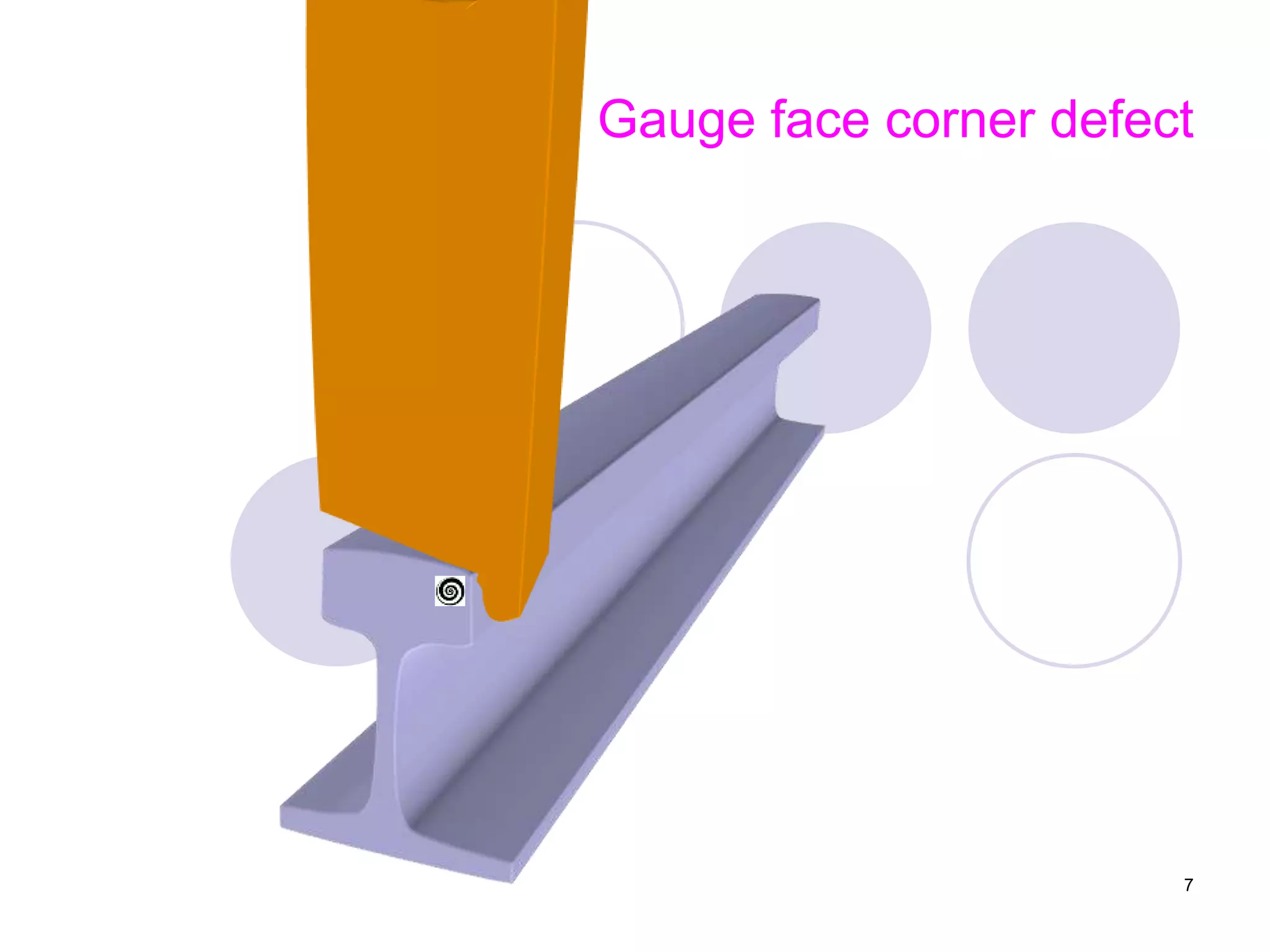
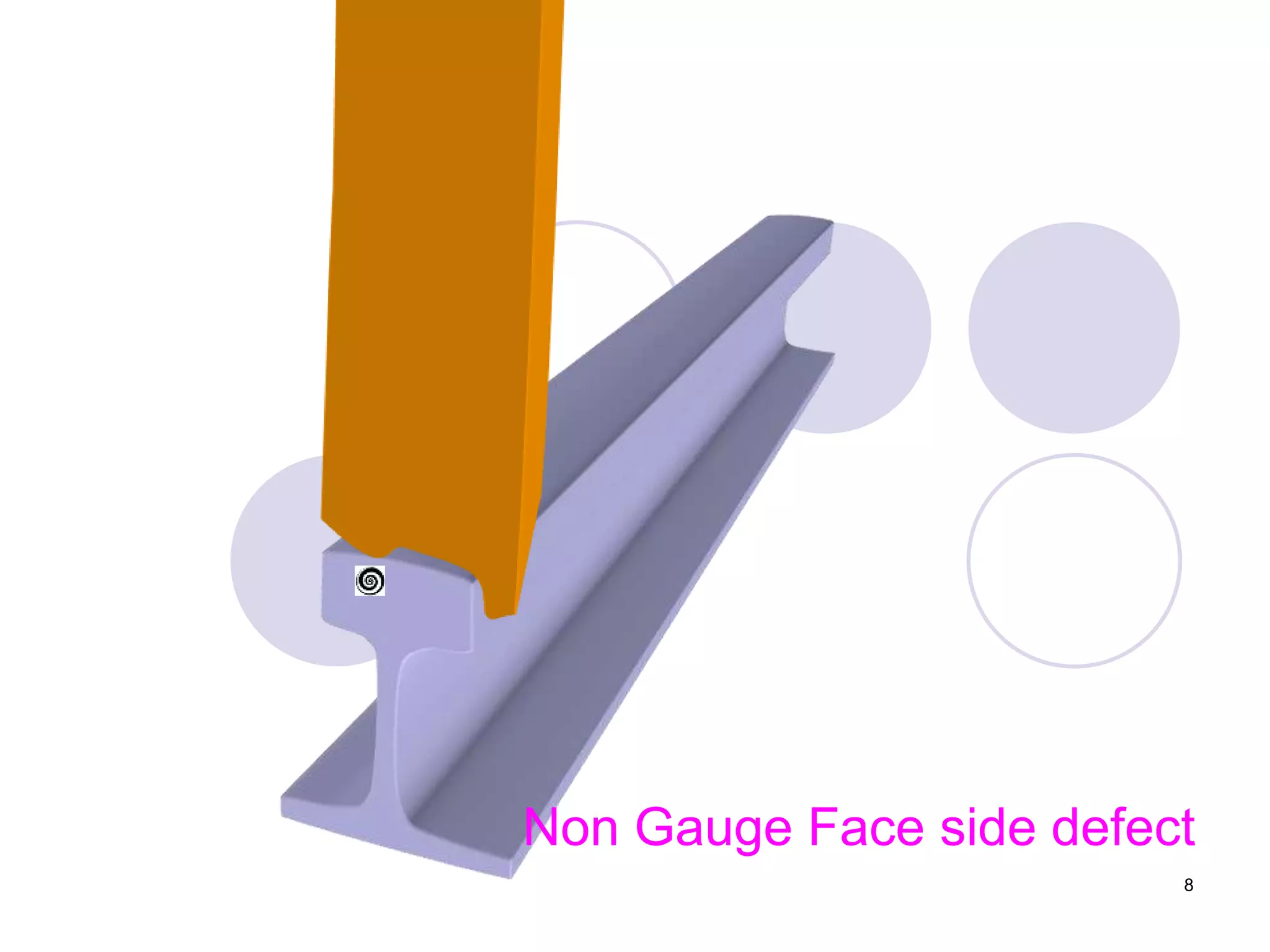
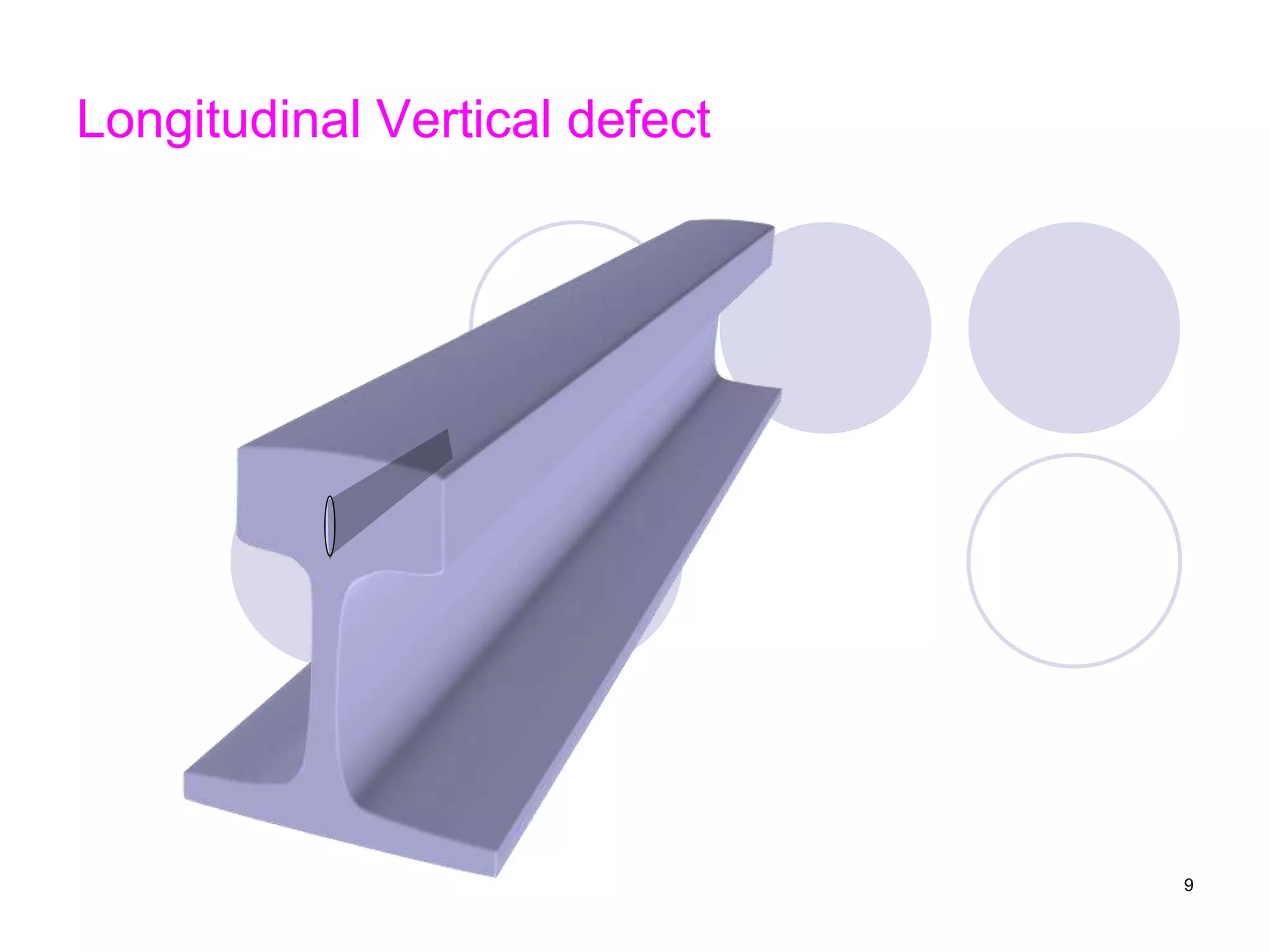
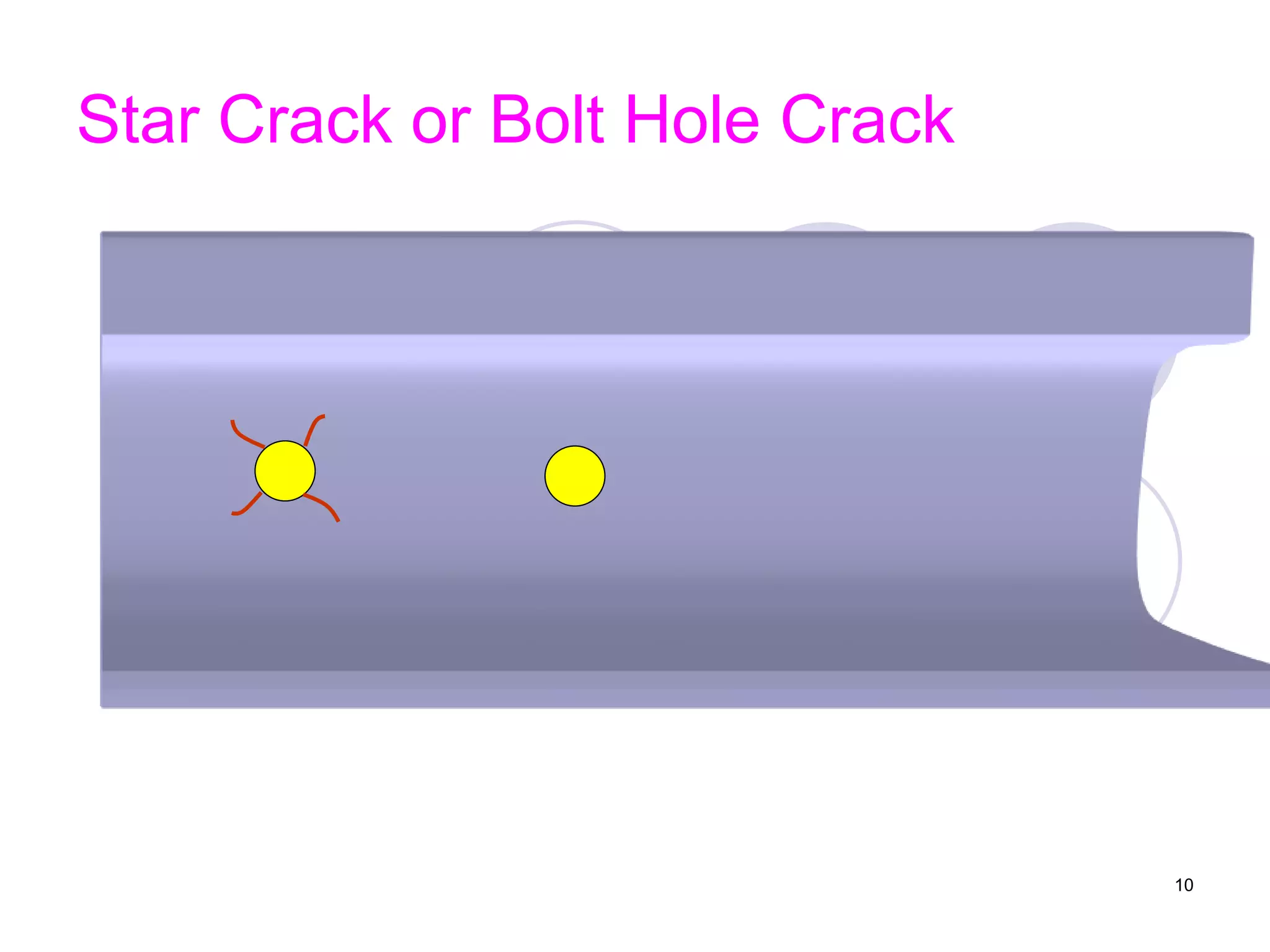
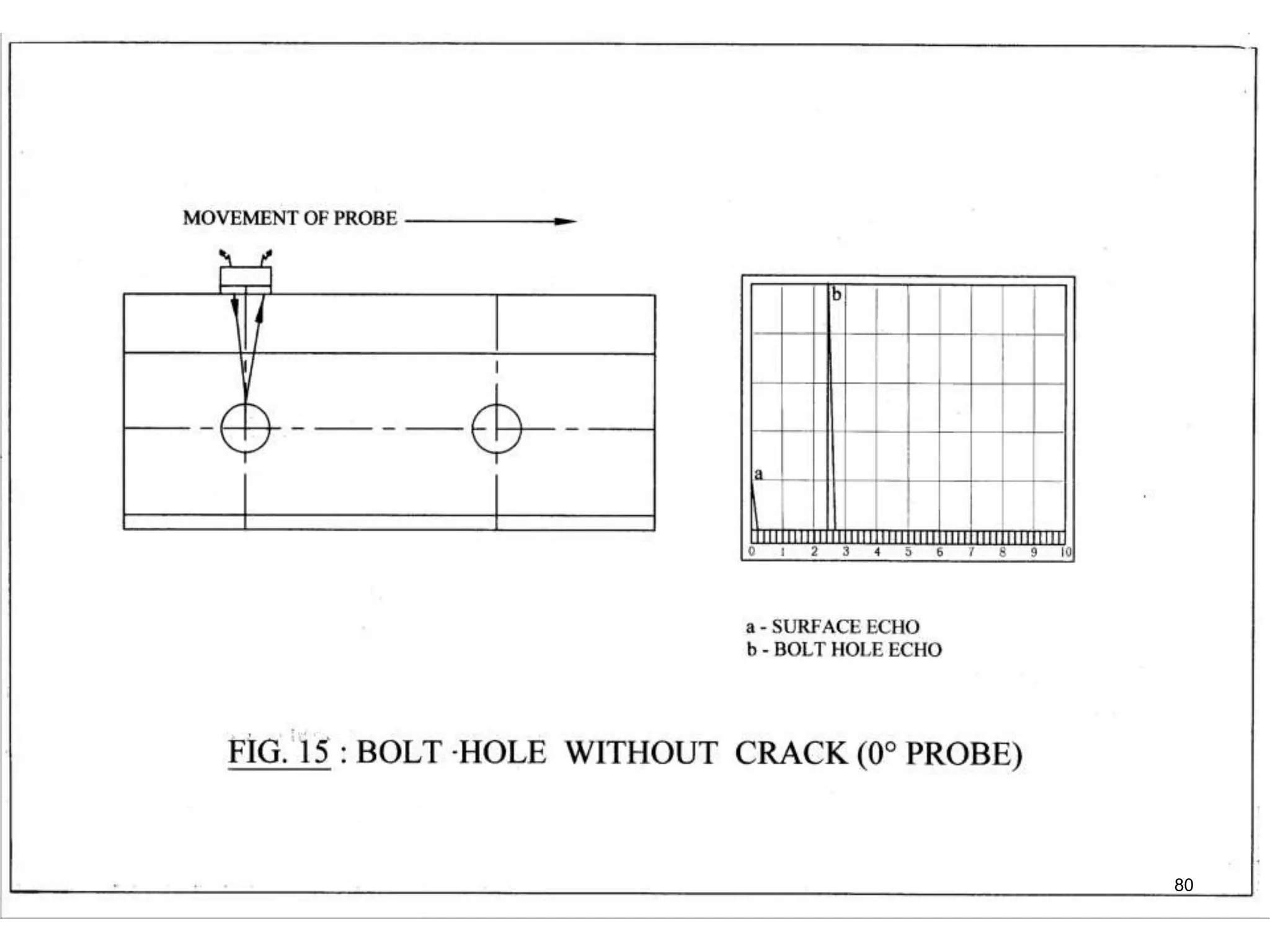
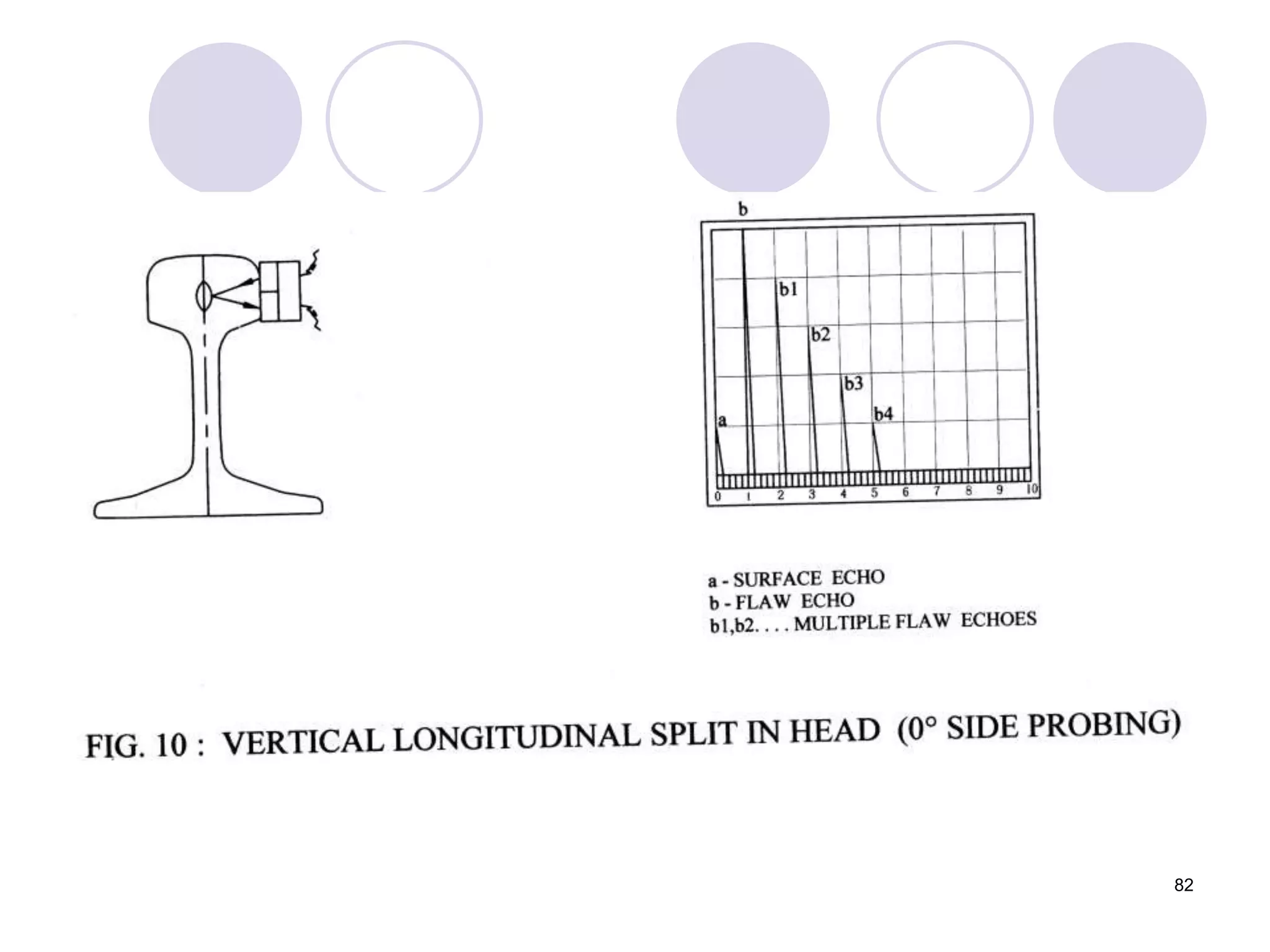
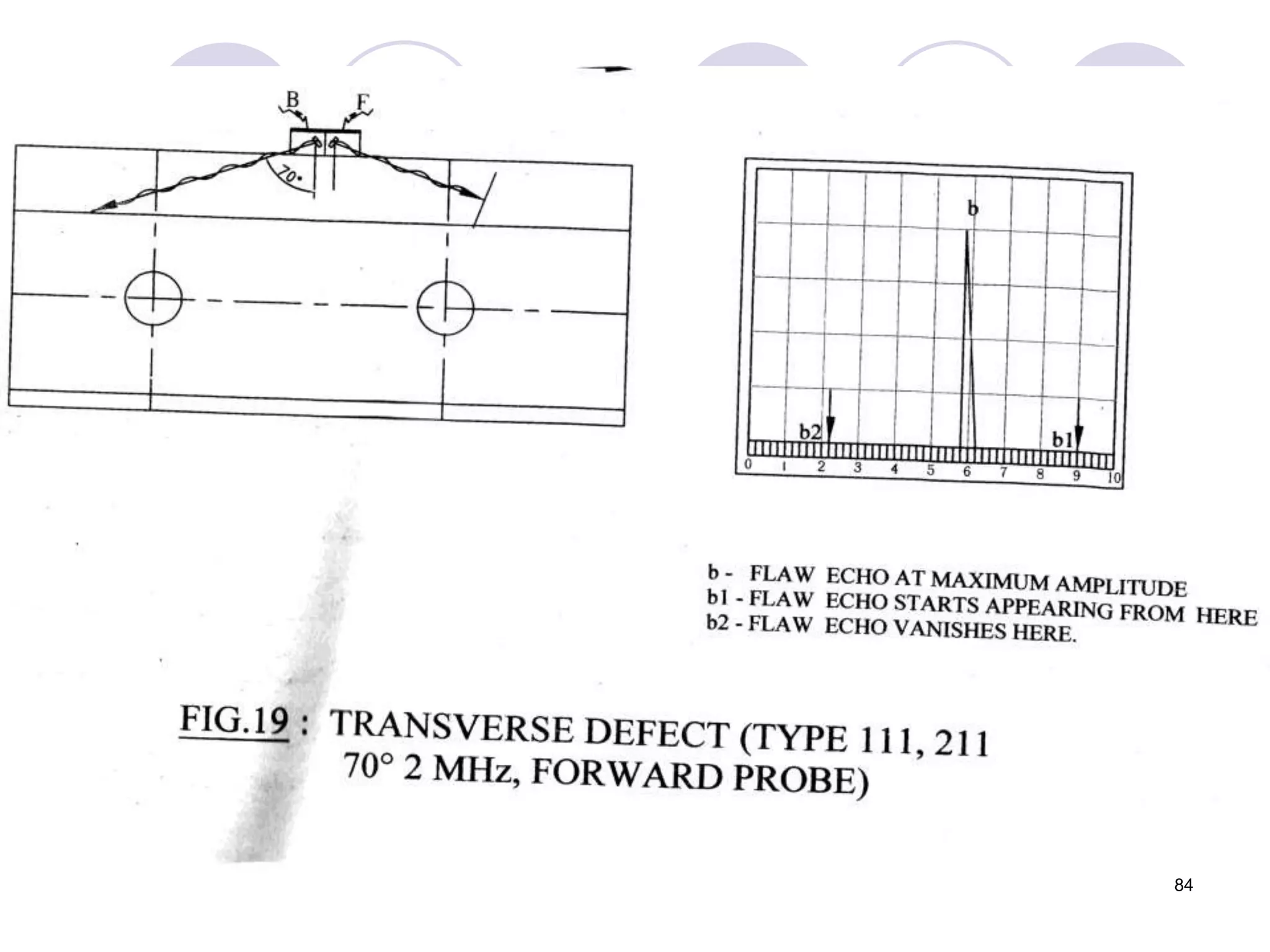
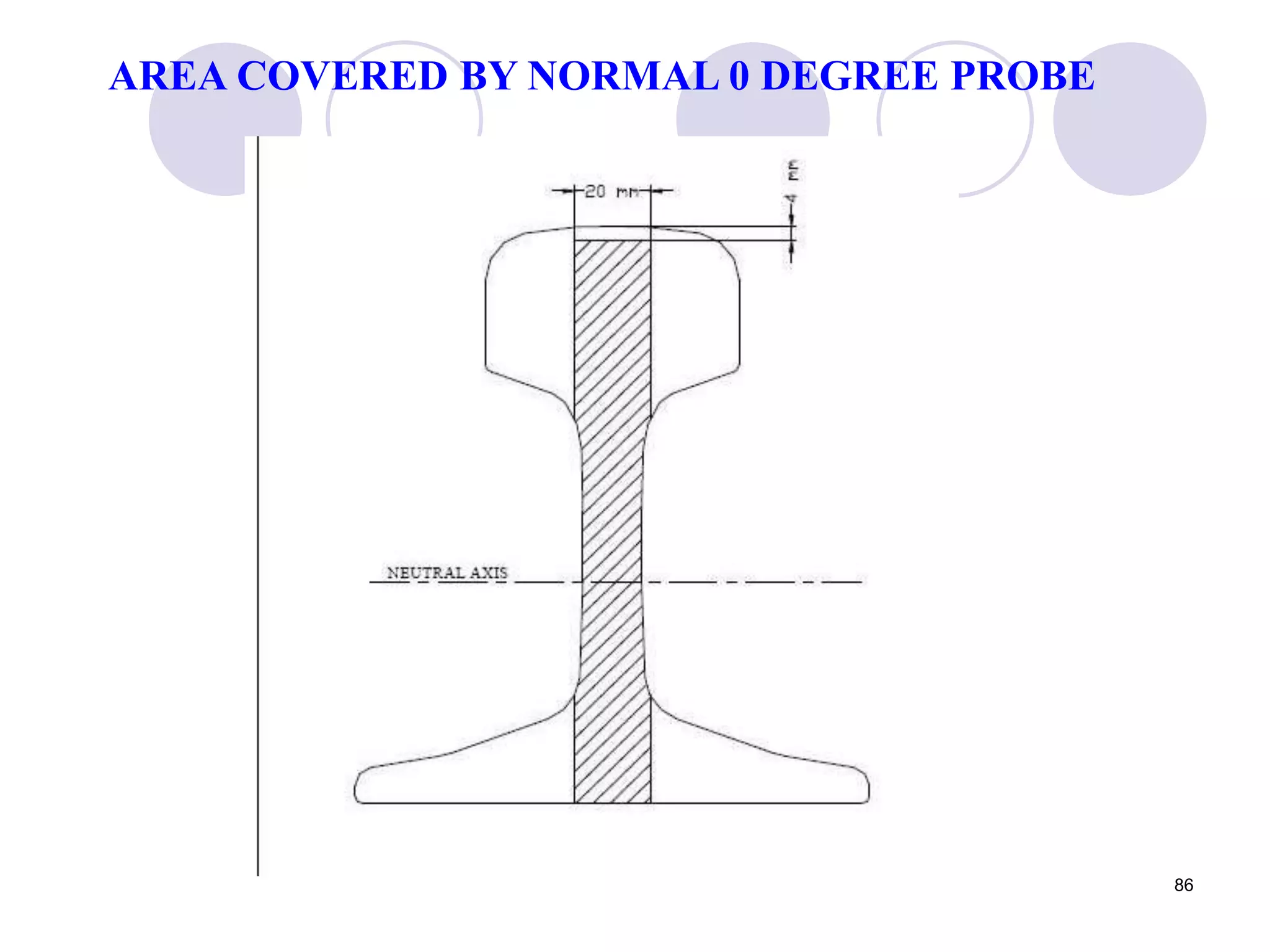
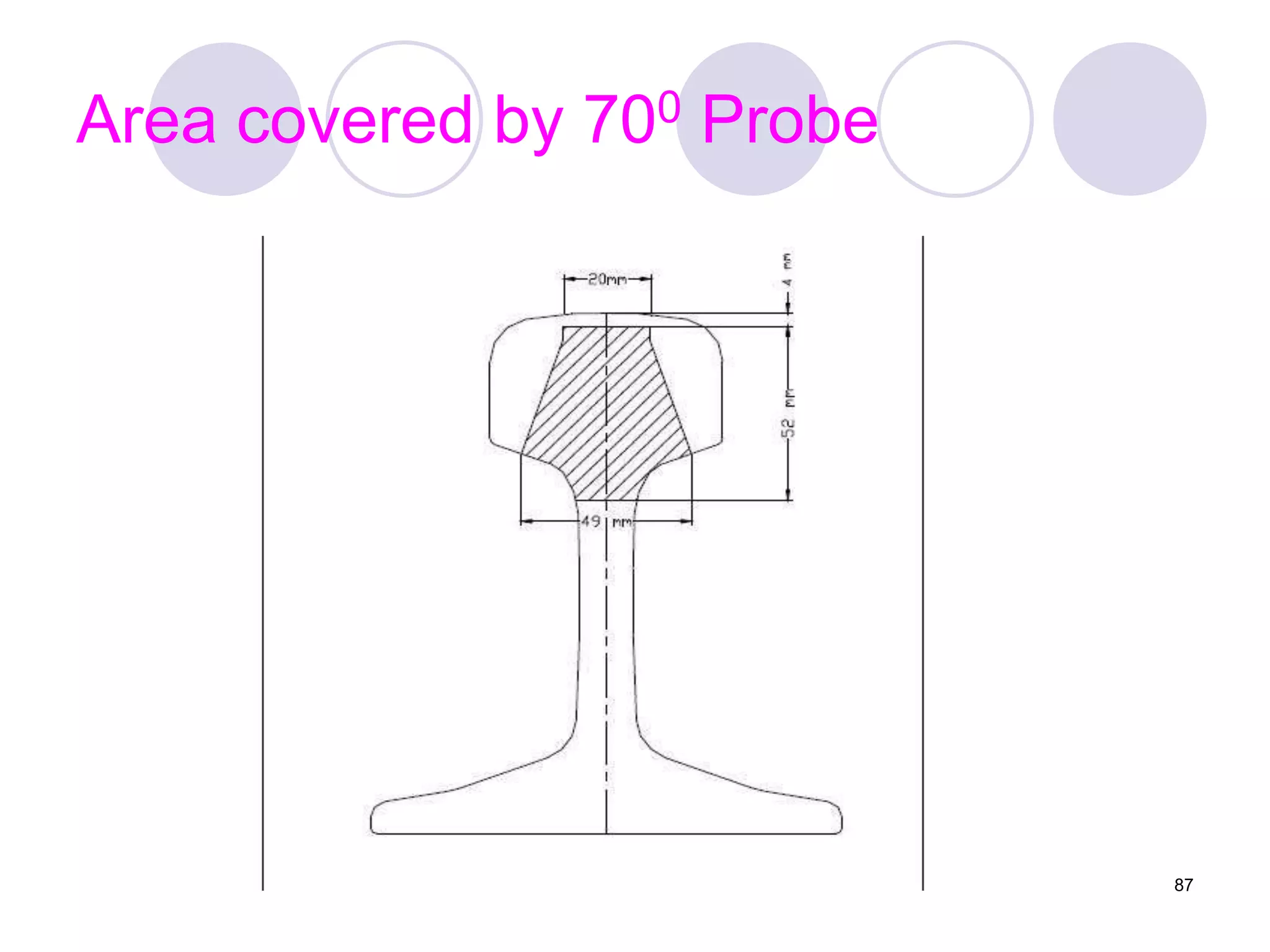
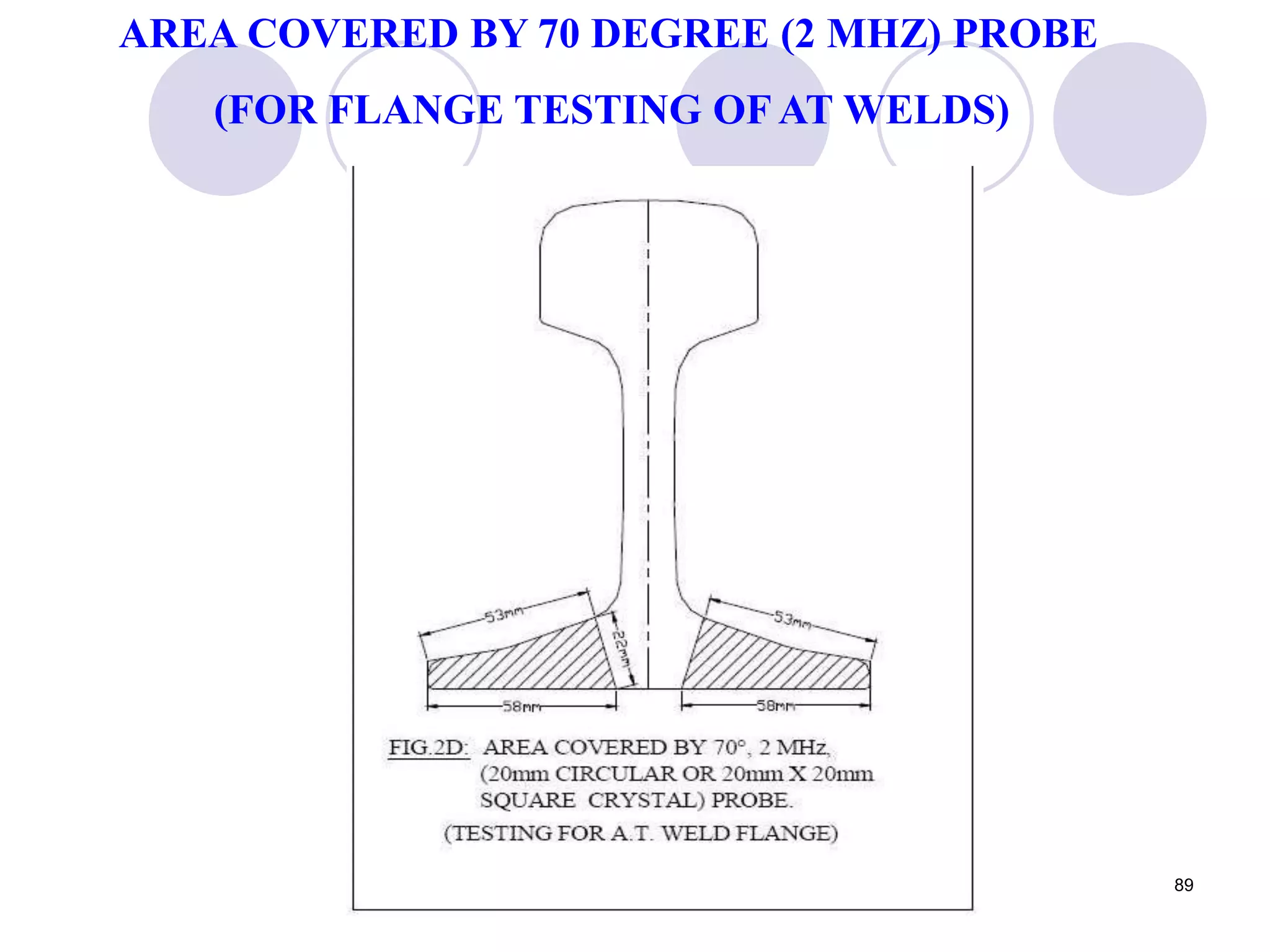
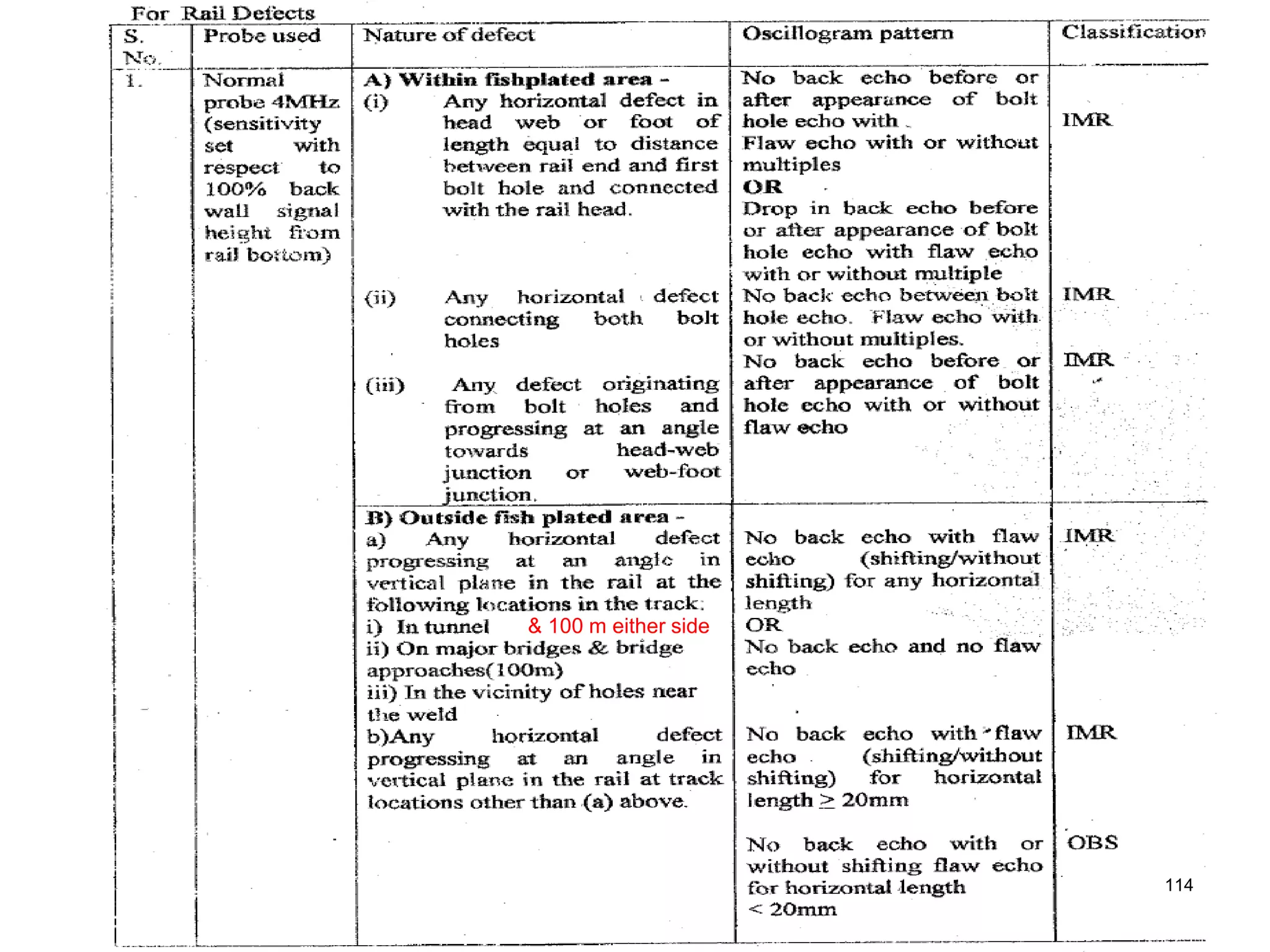
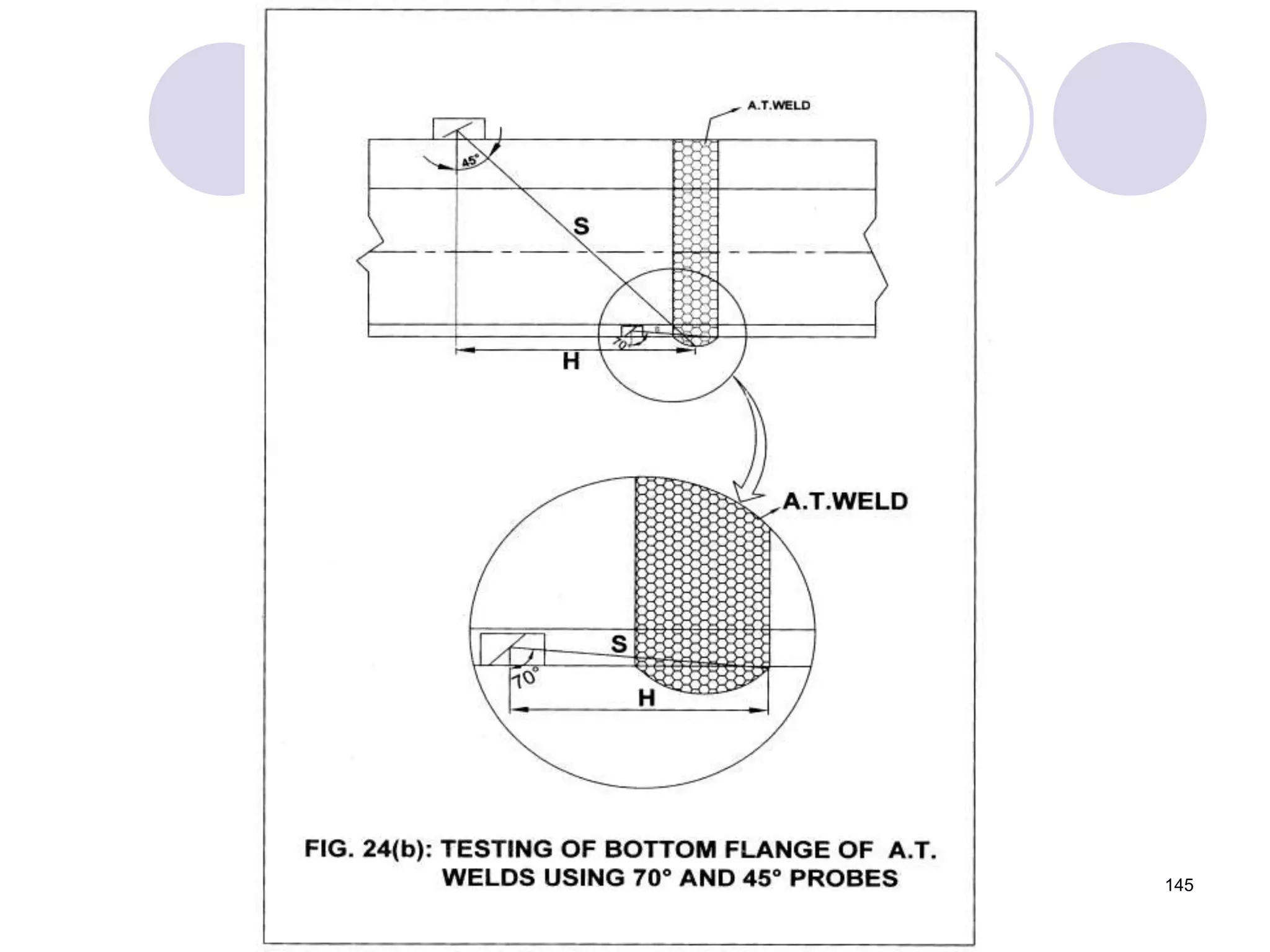
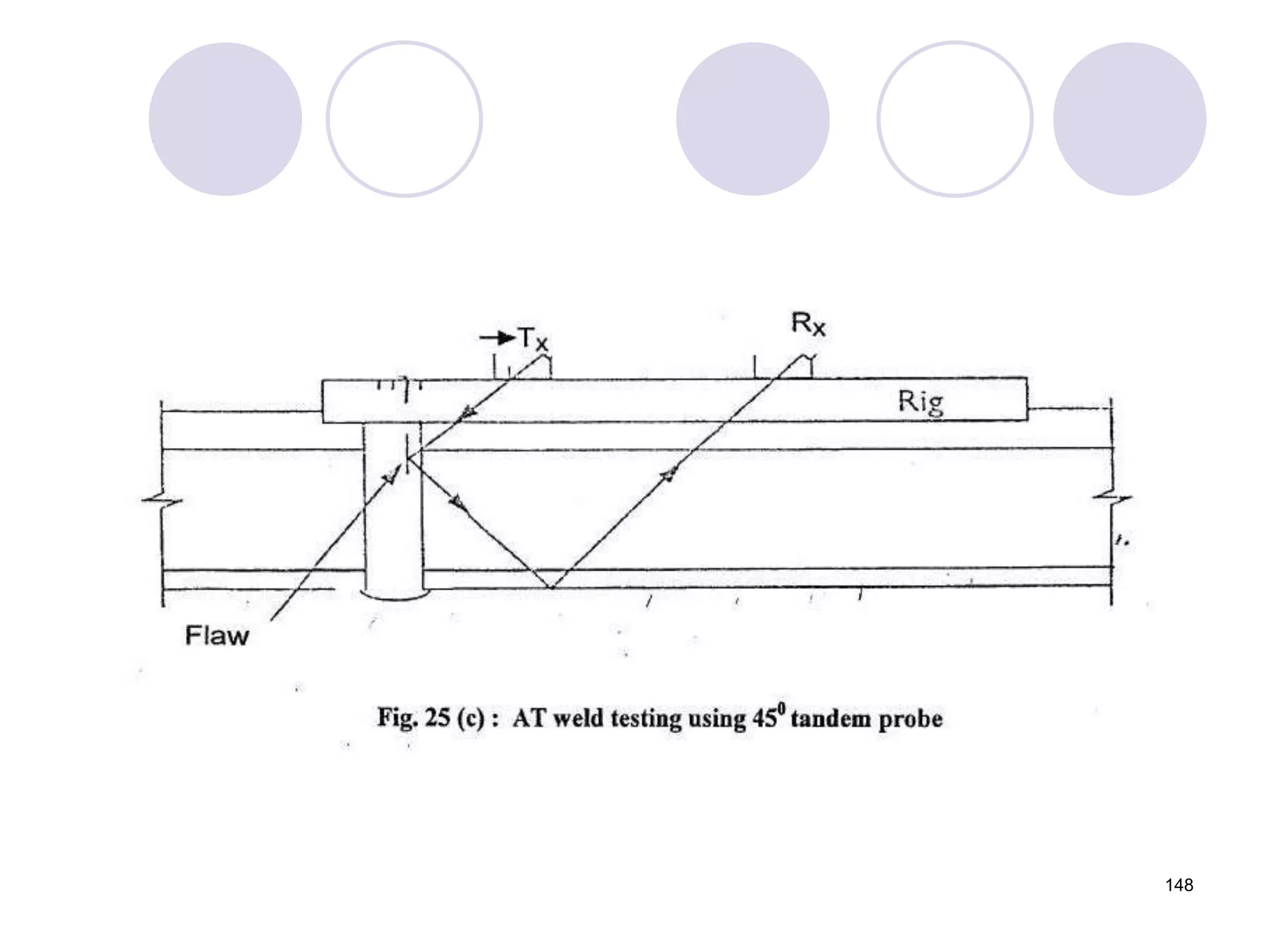
2. Various types of flaws can occur on the surface or internally in different planes of the rail. Examples of flaws shown include cracks in the head, web, and bolt holes.
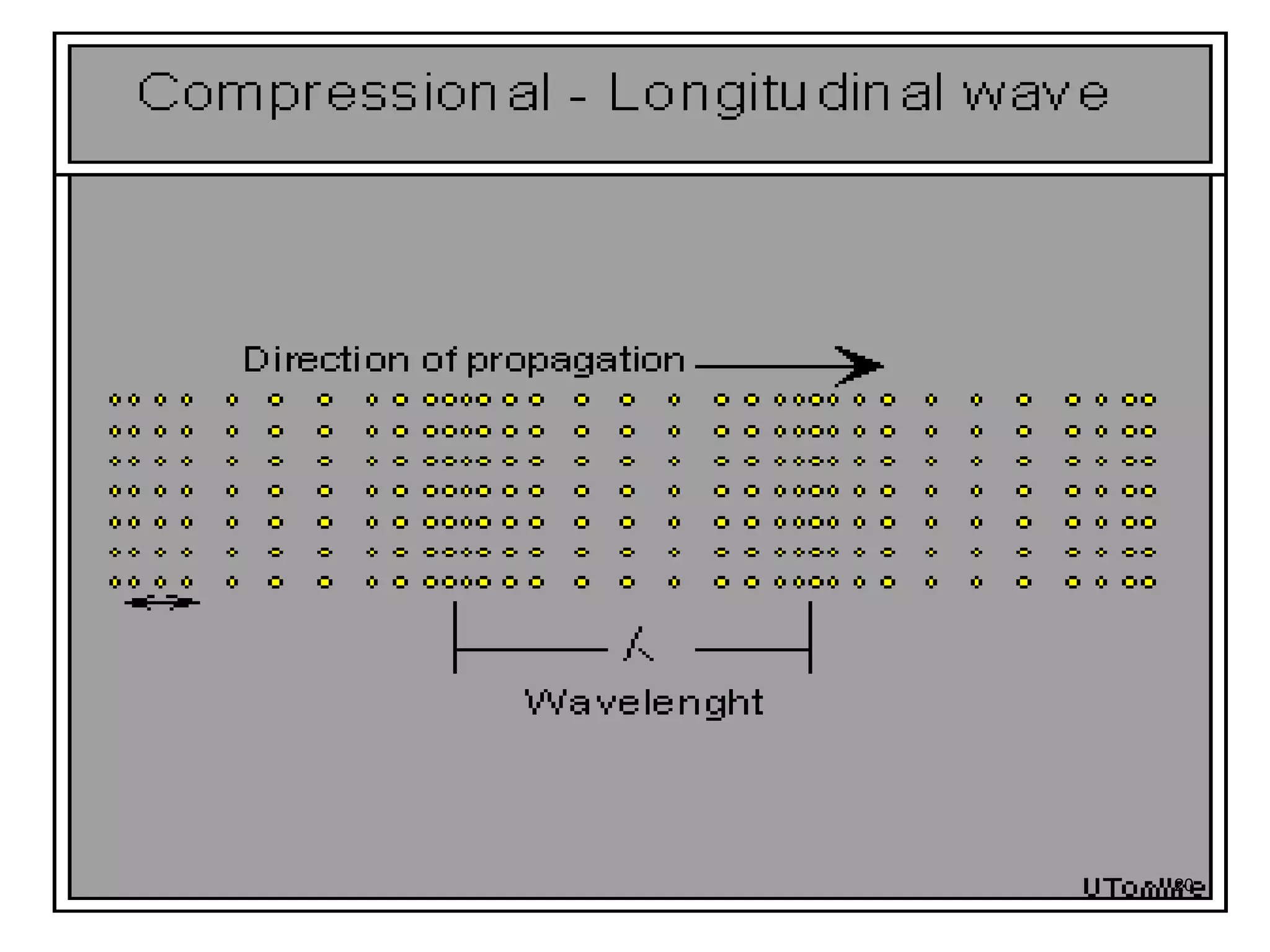
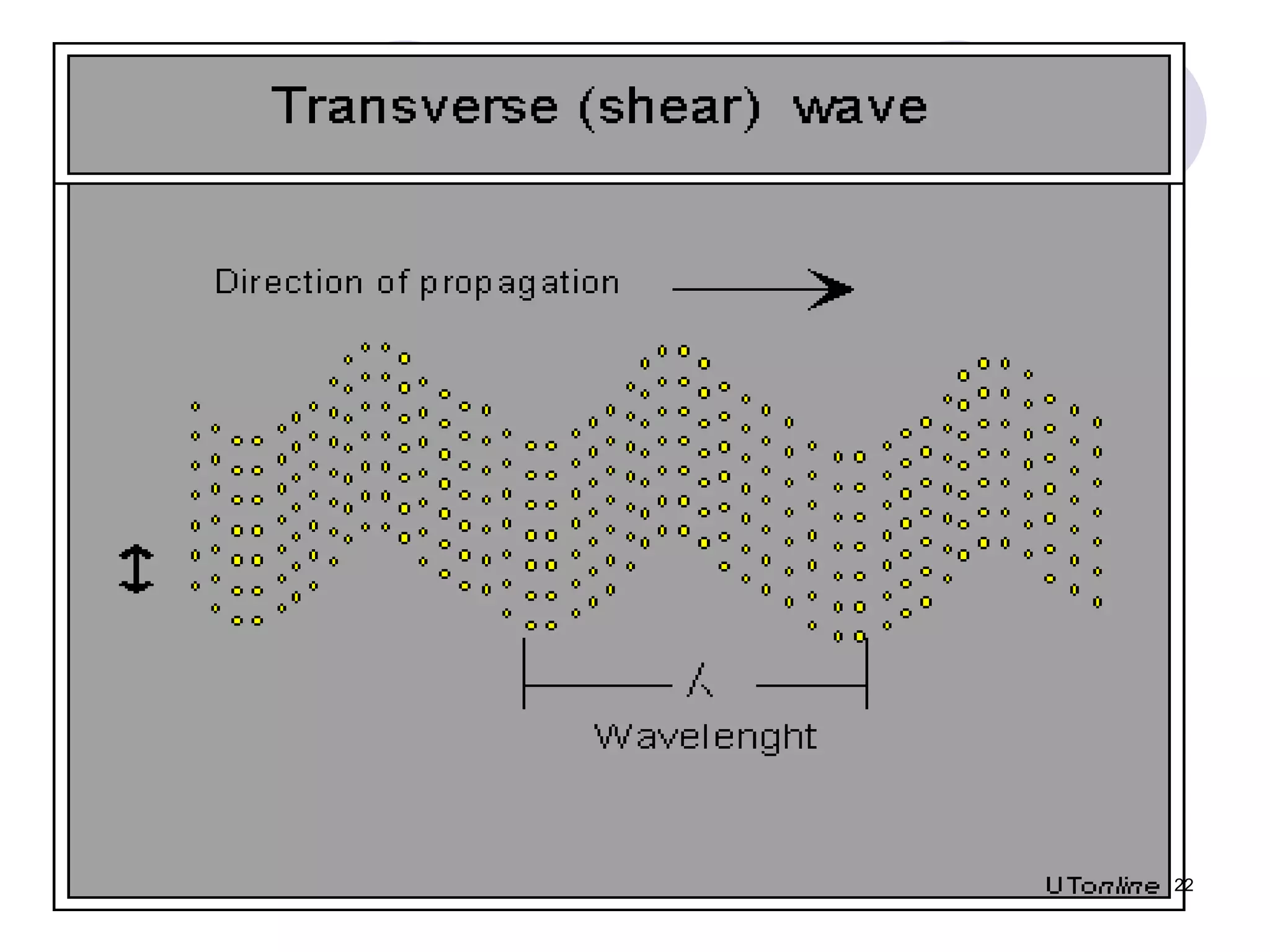
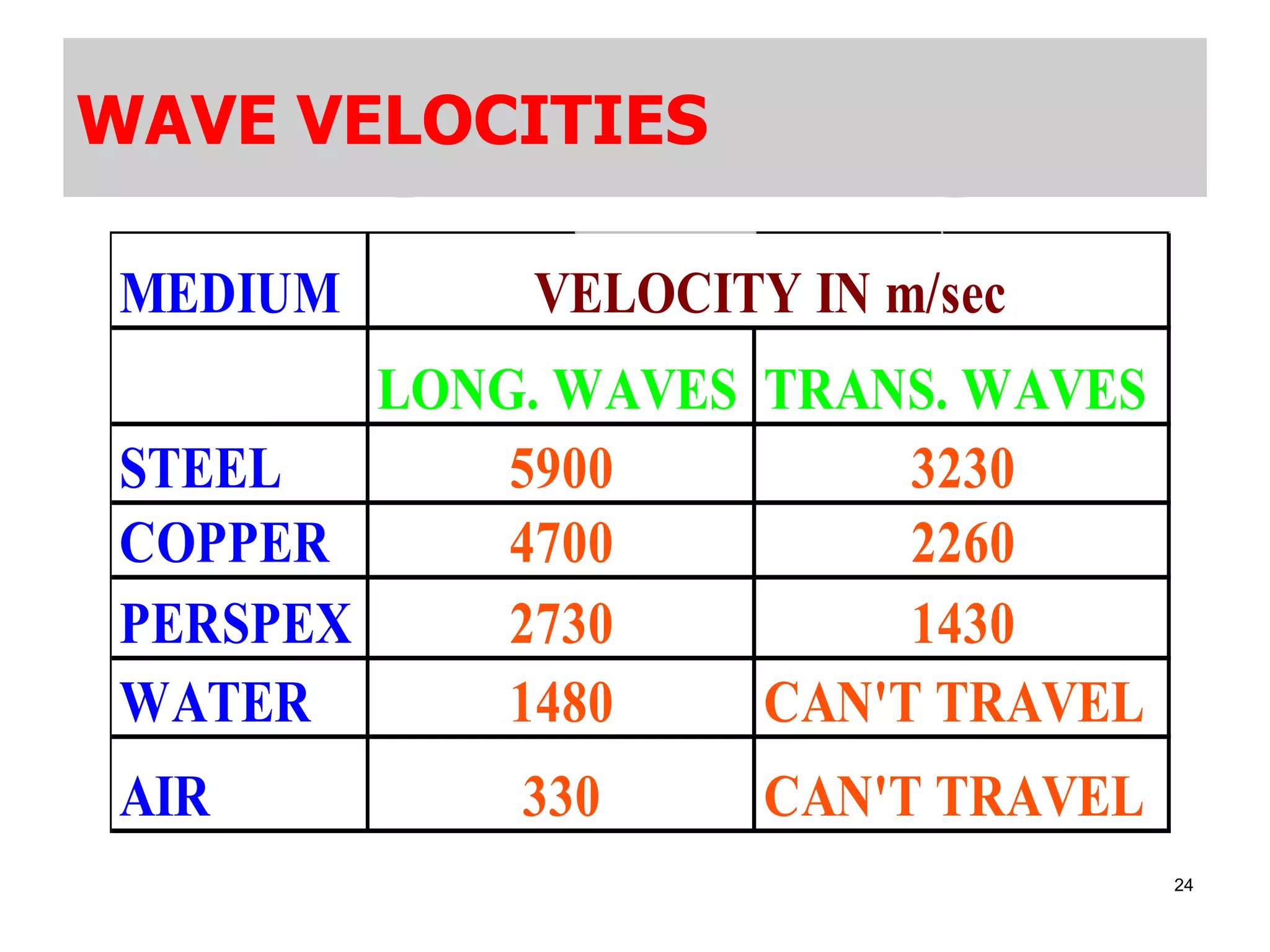
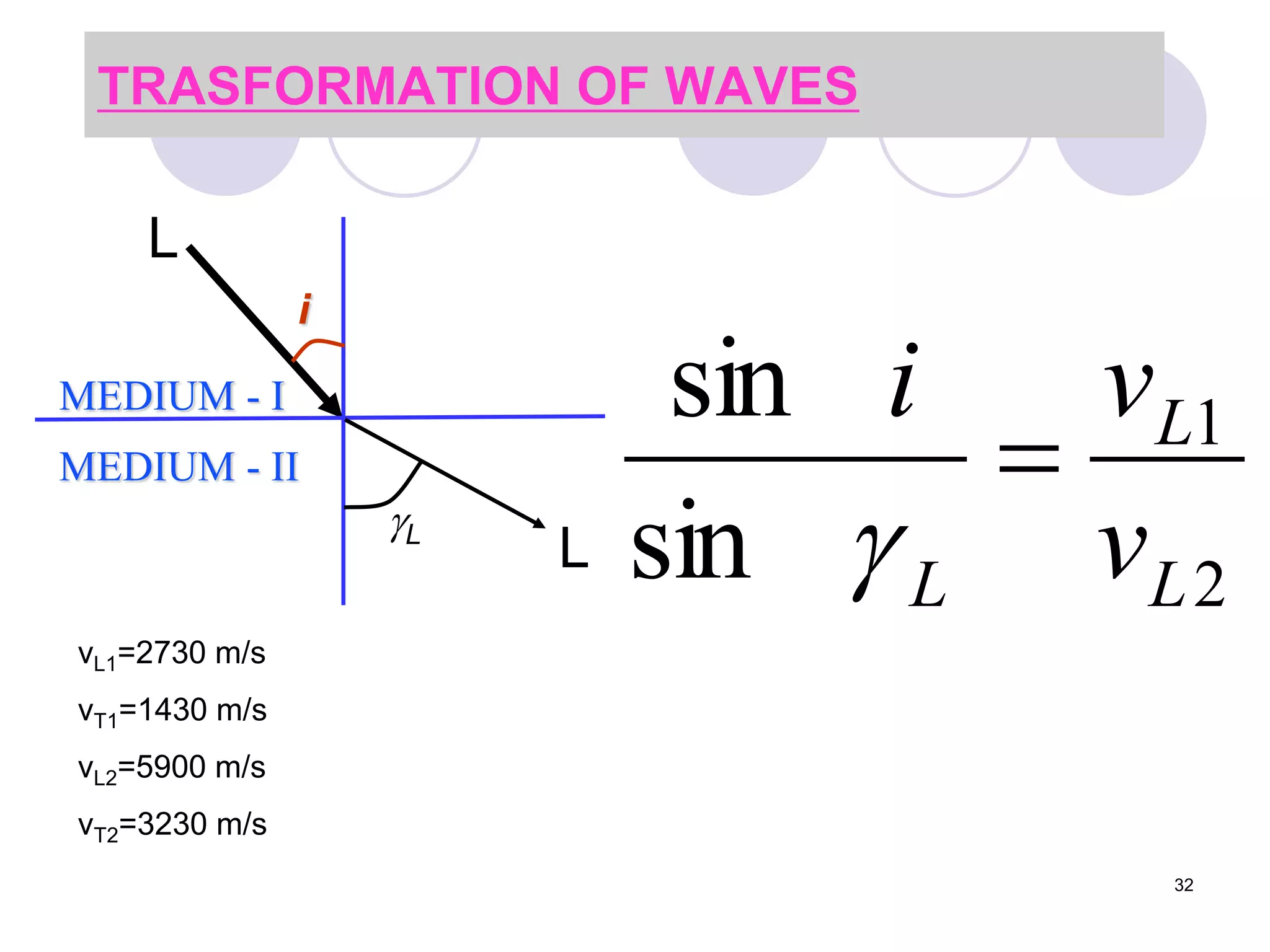
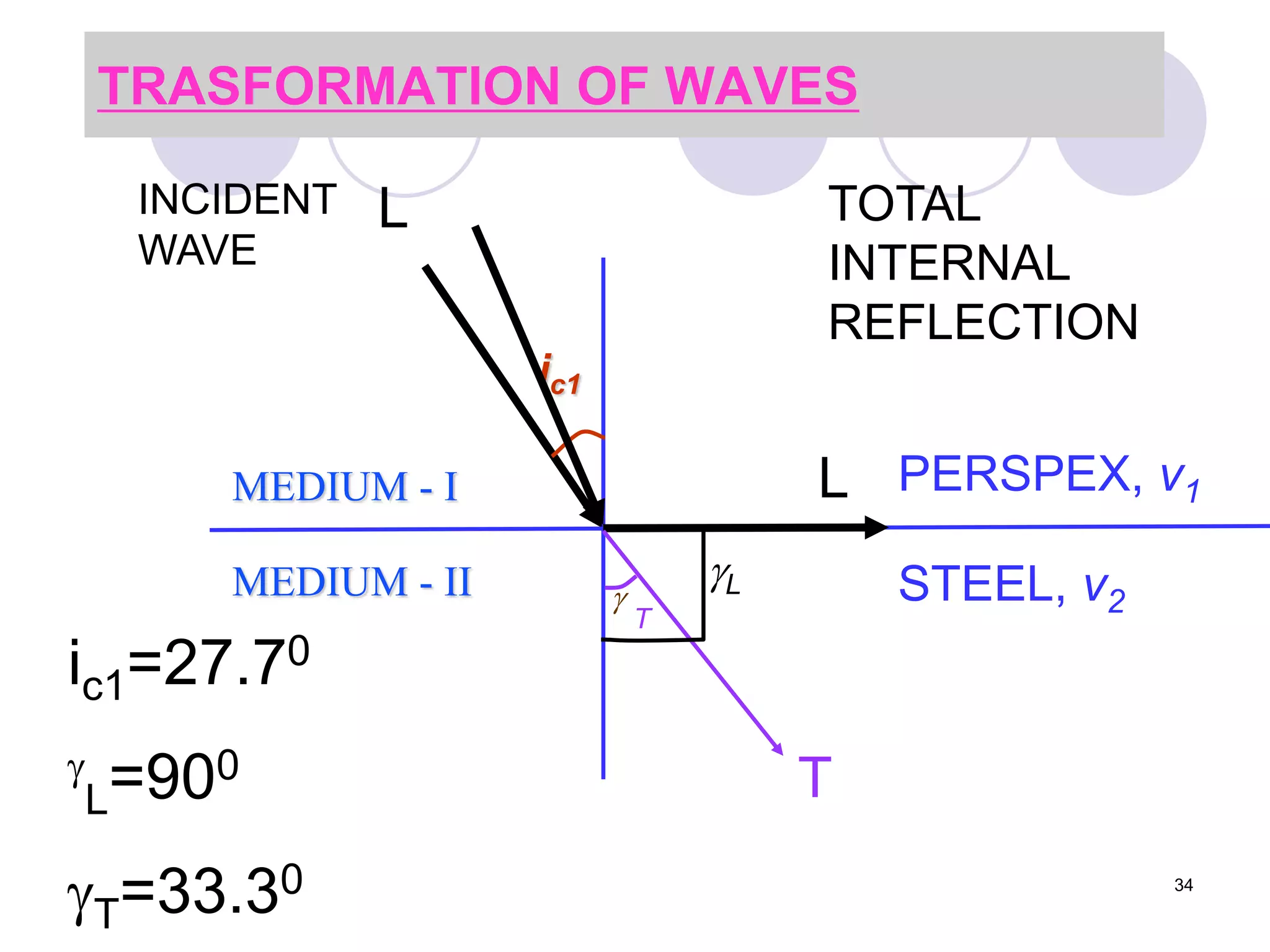
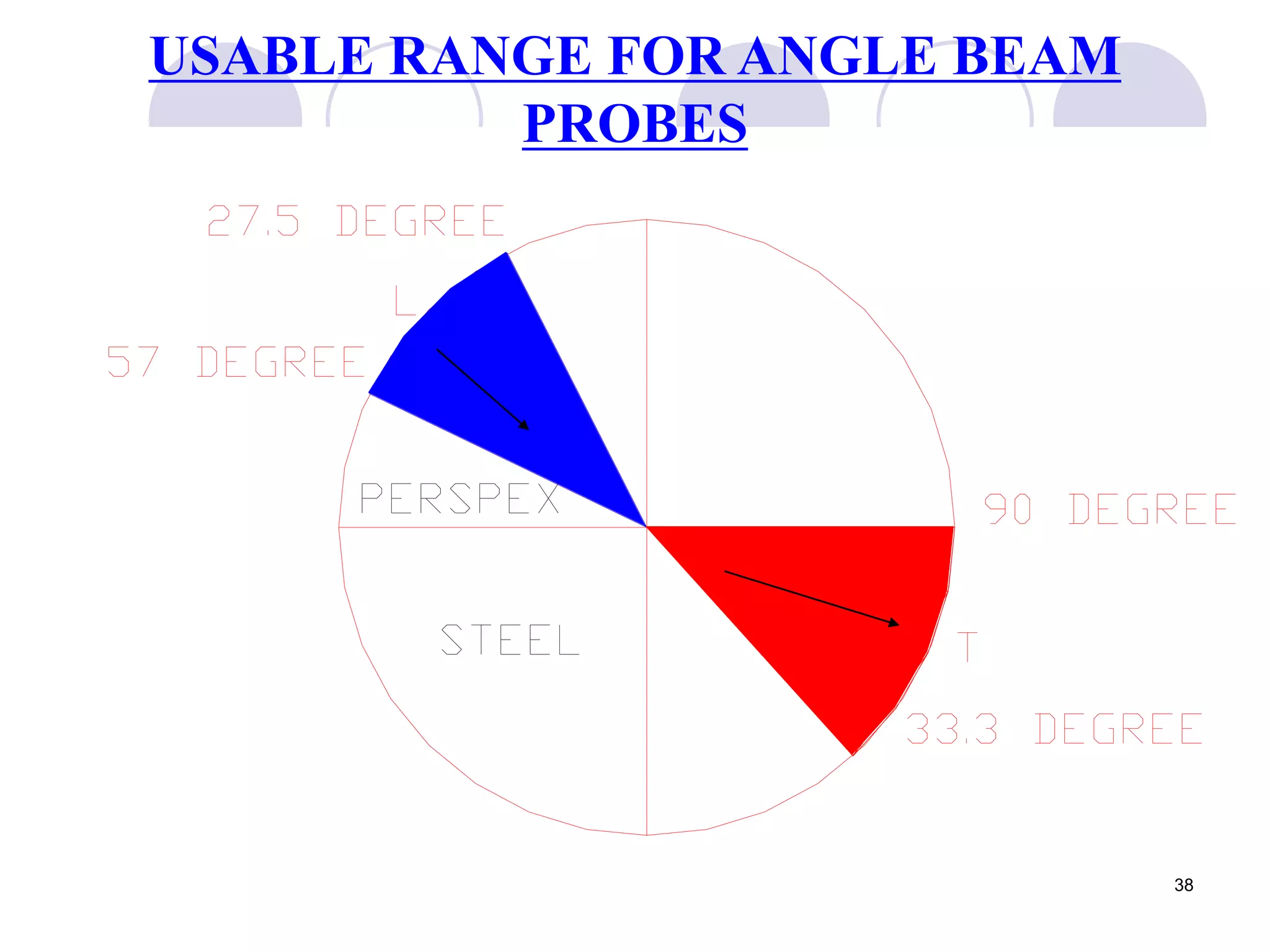
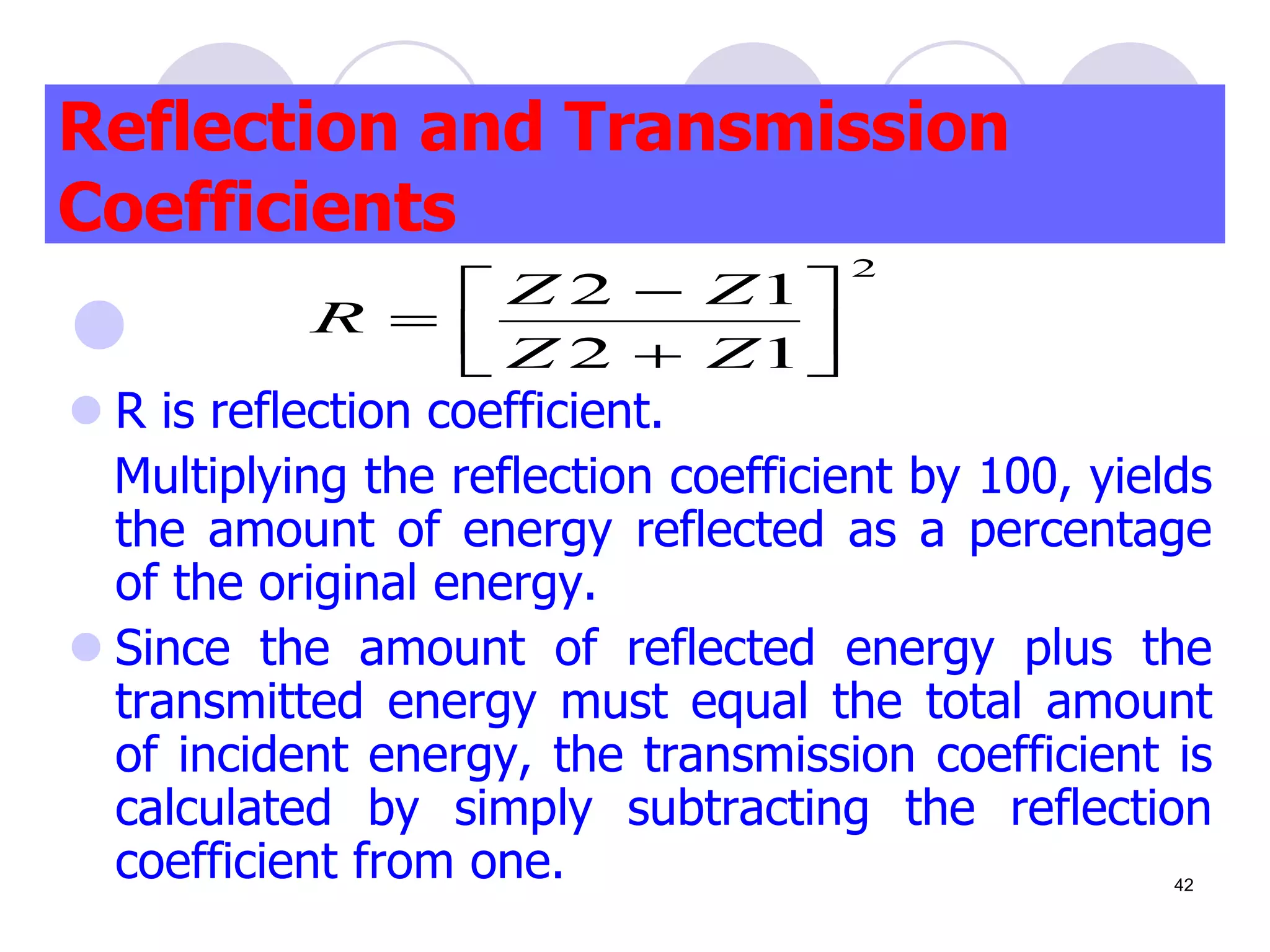
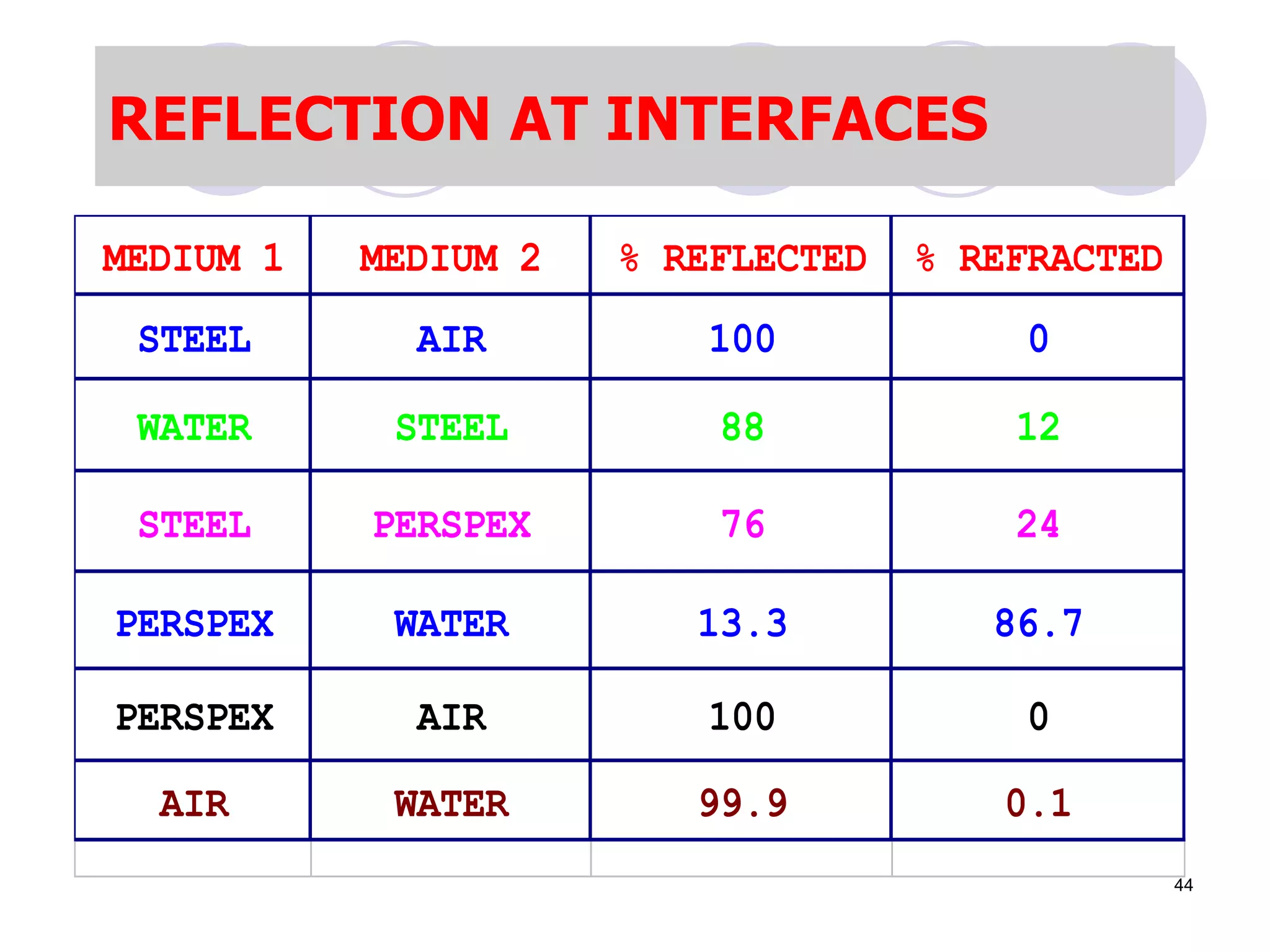
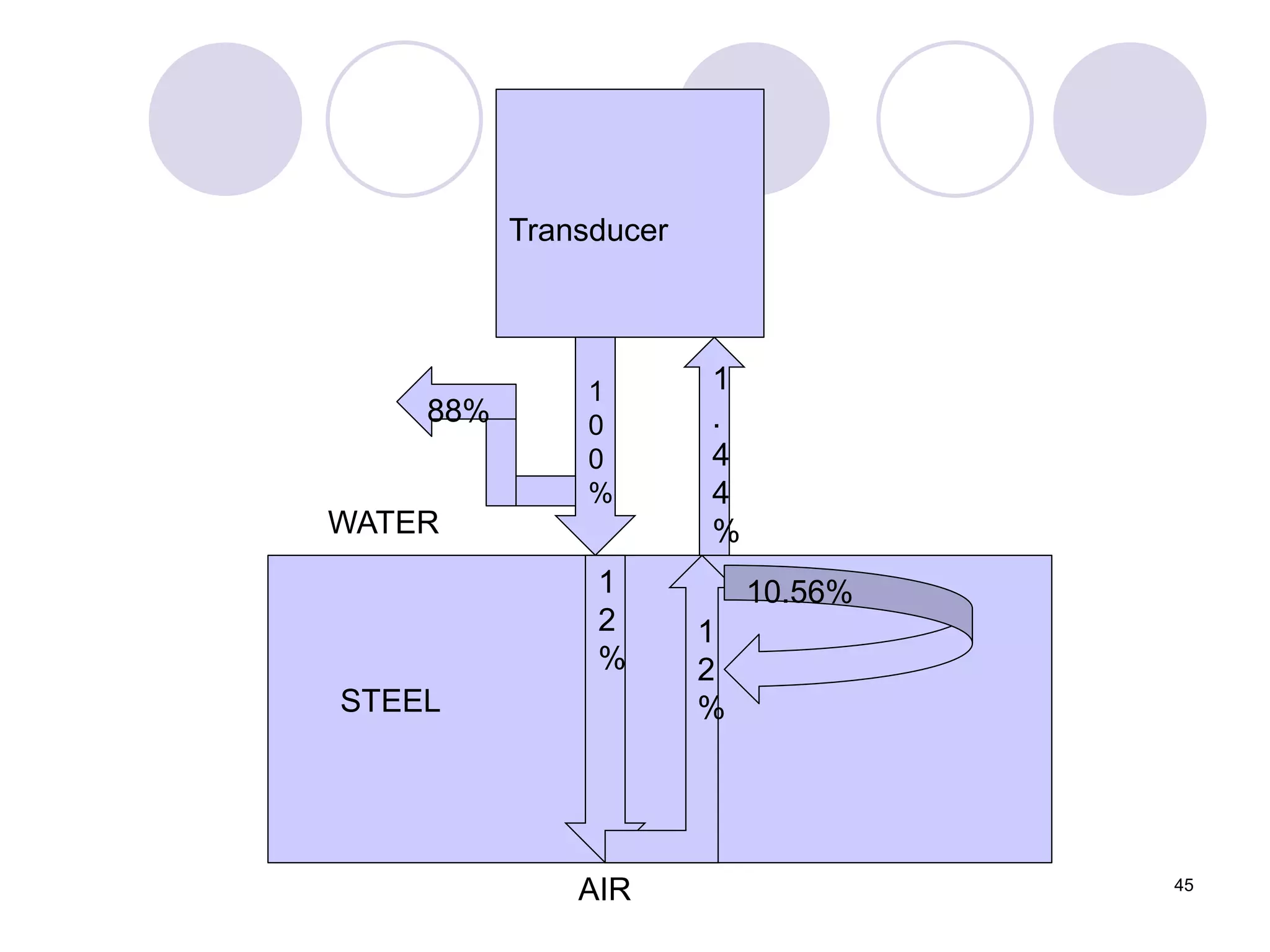
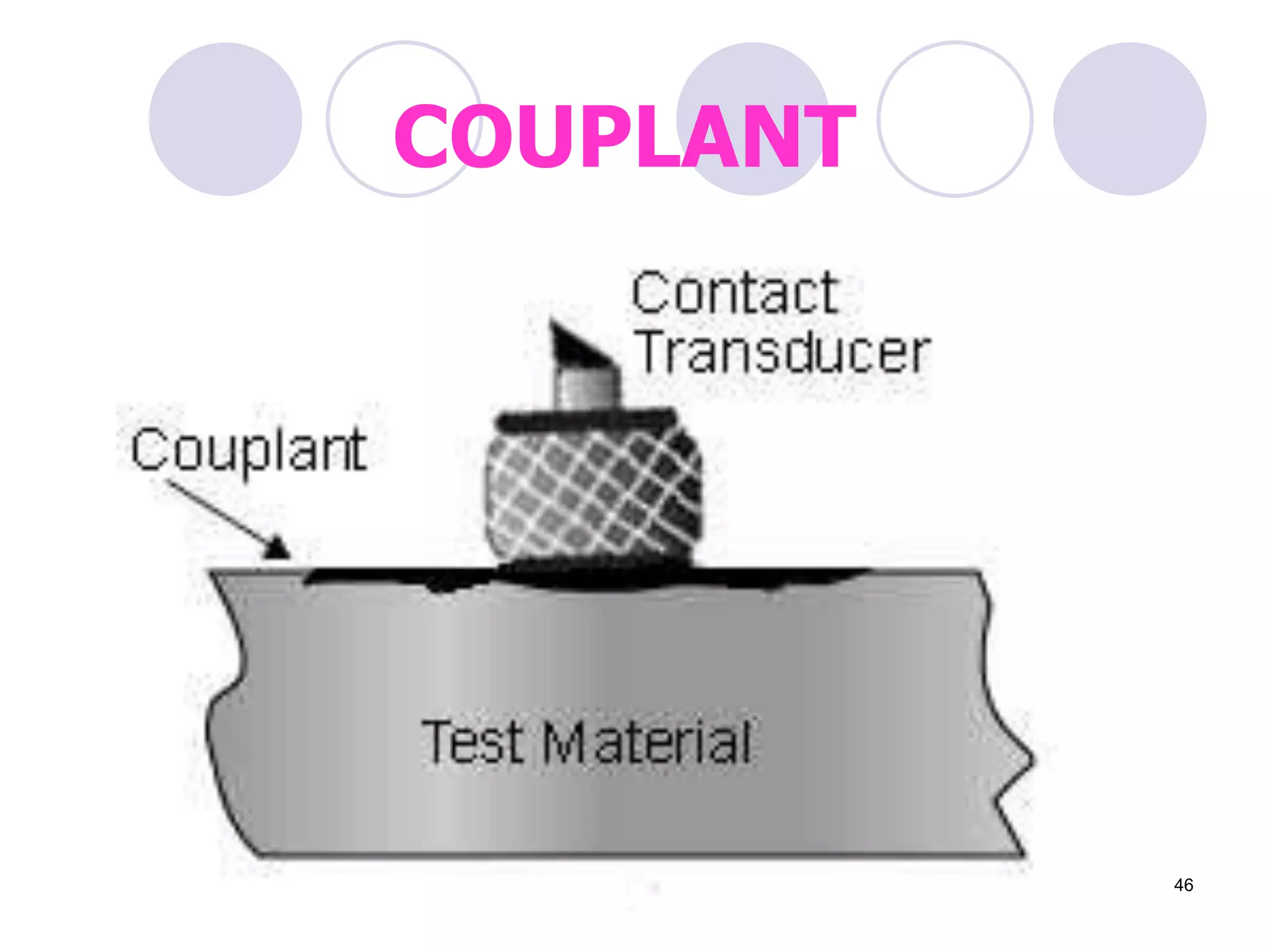
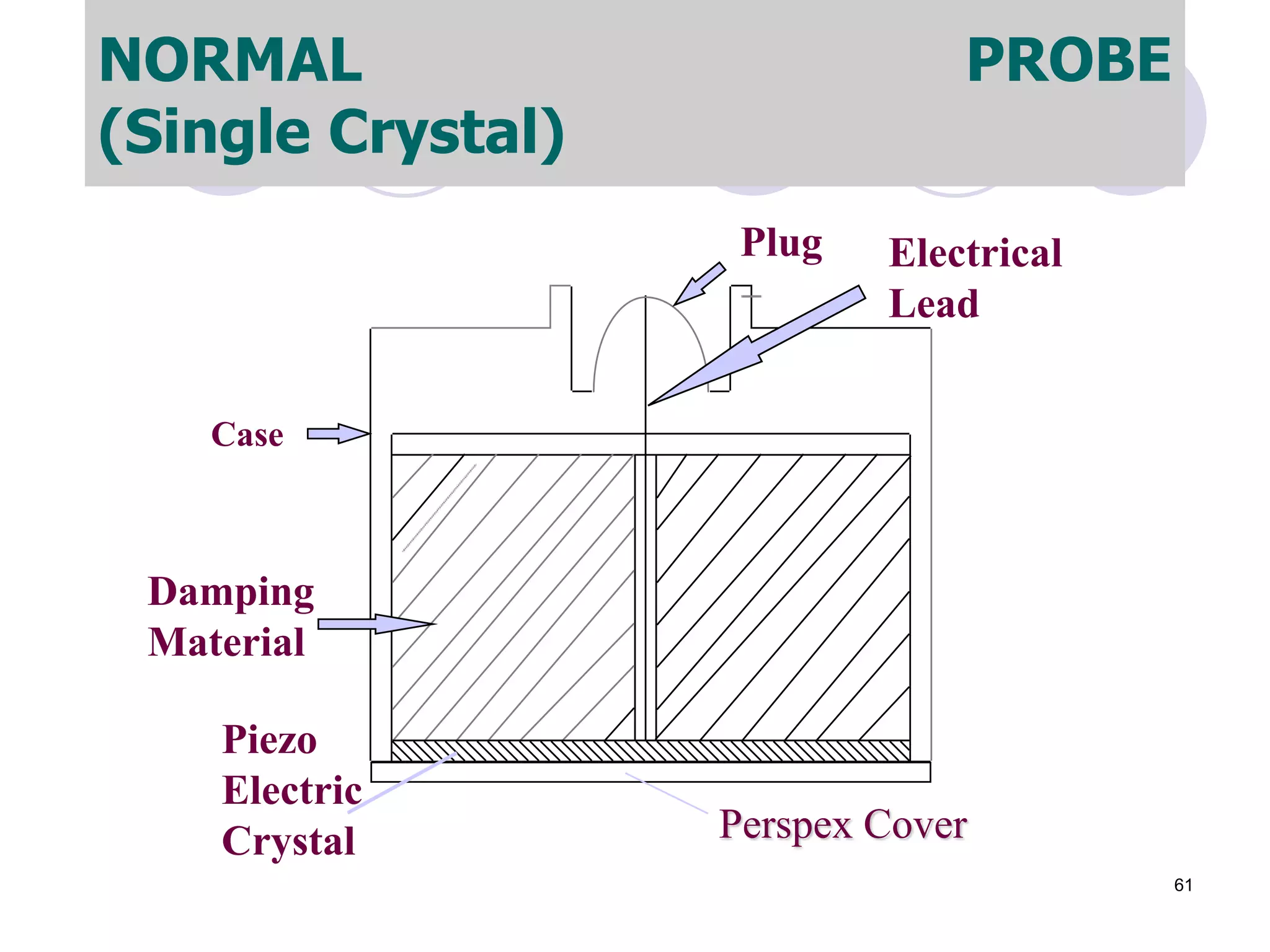
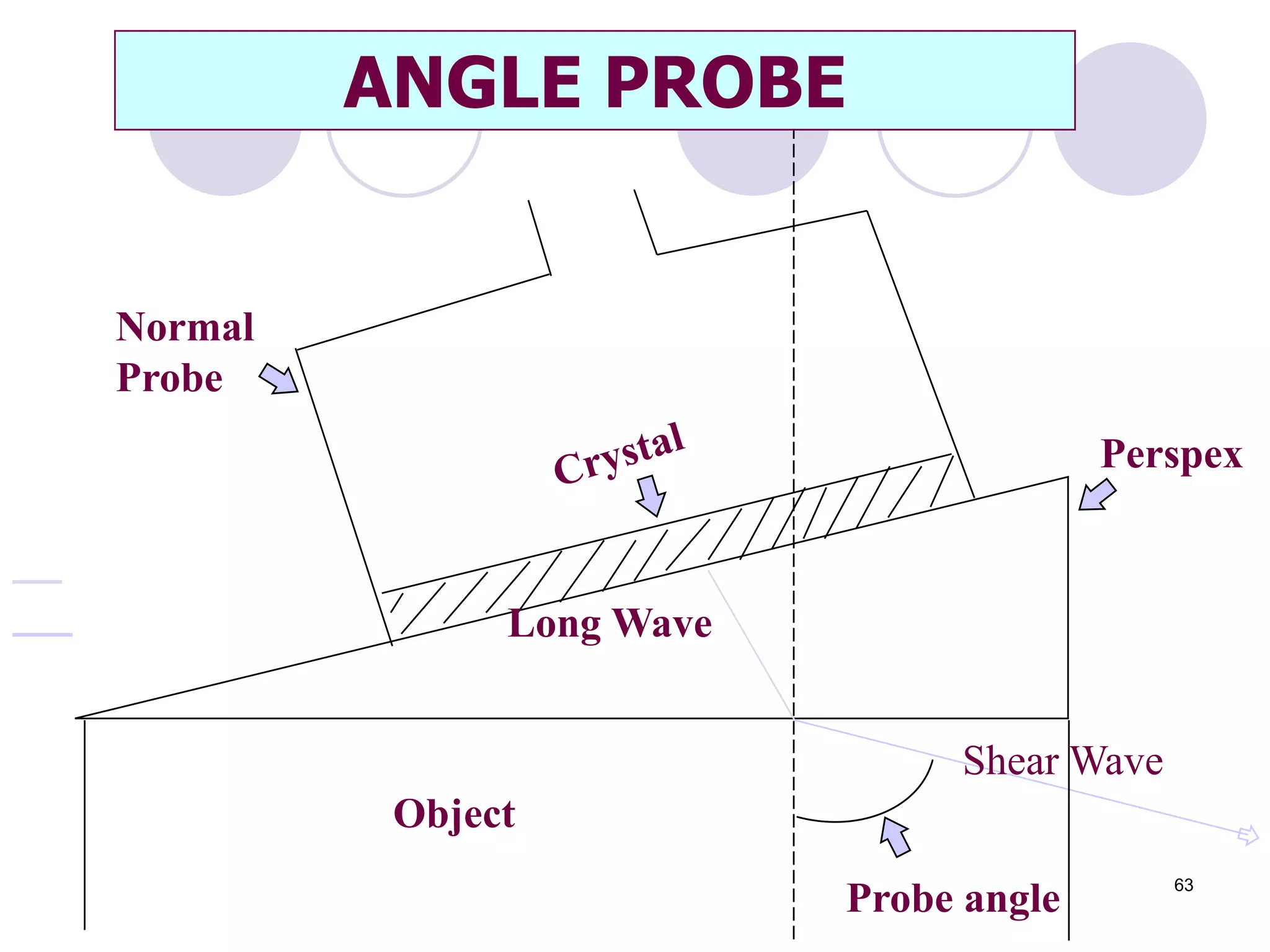
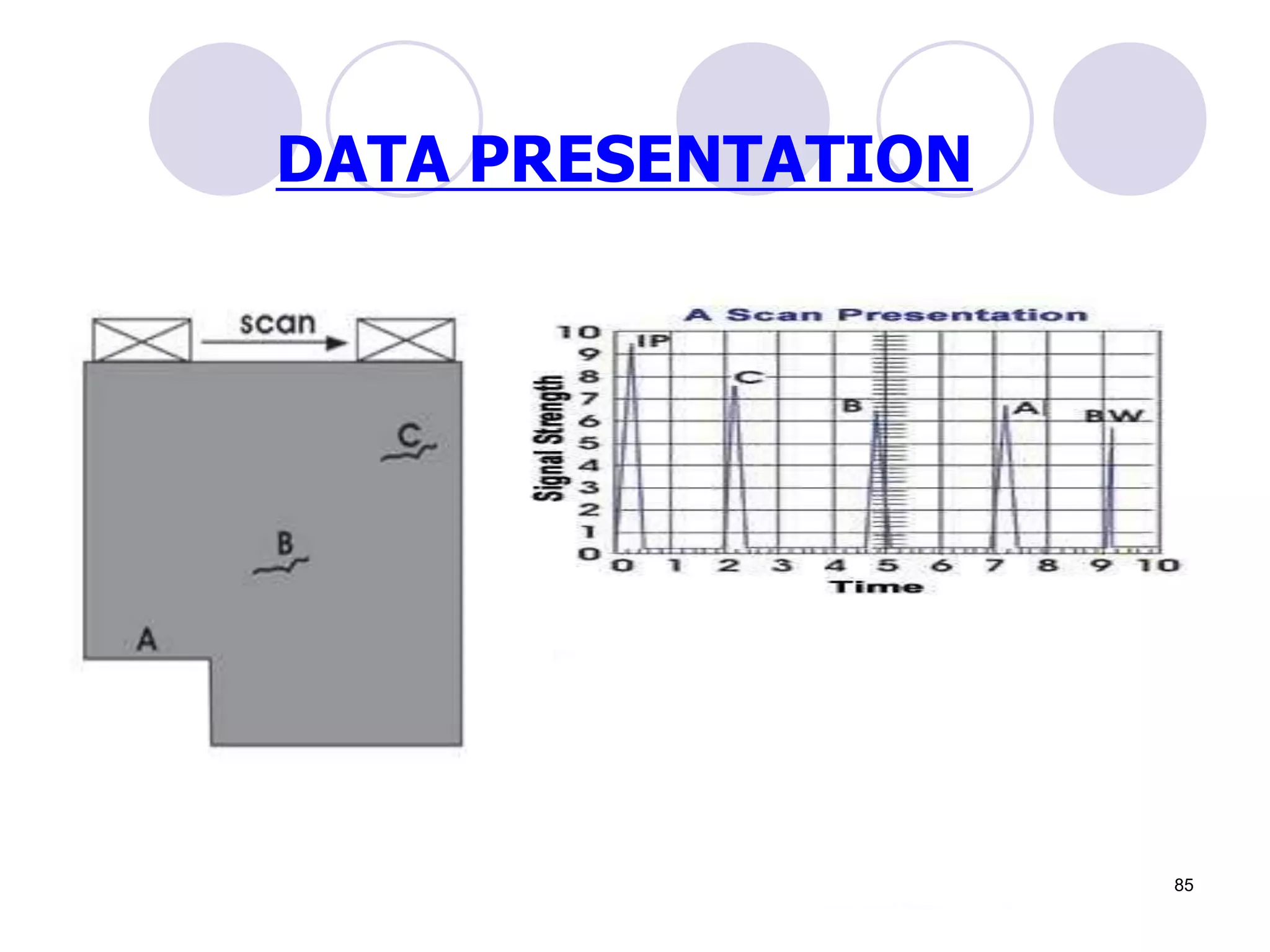
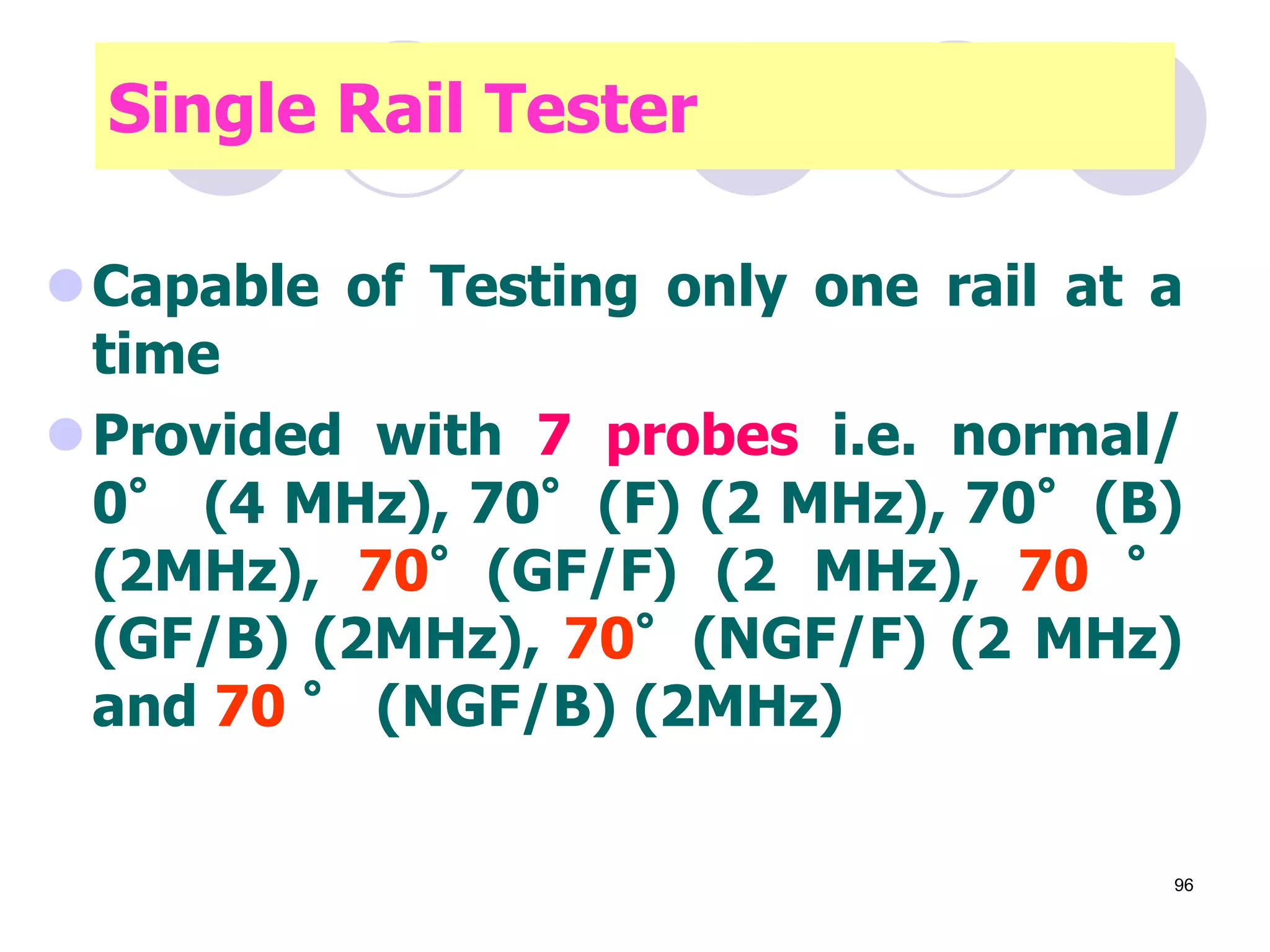
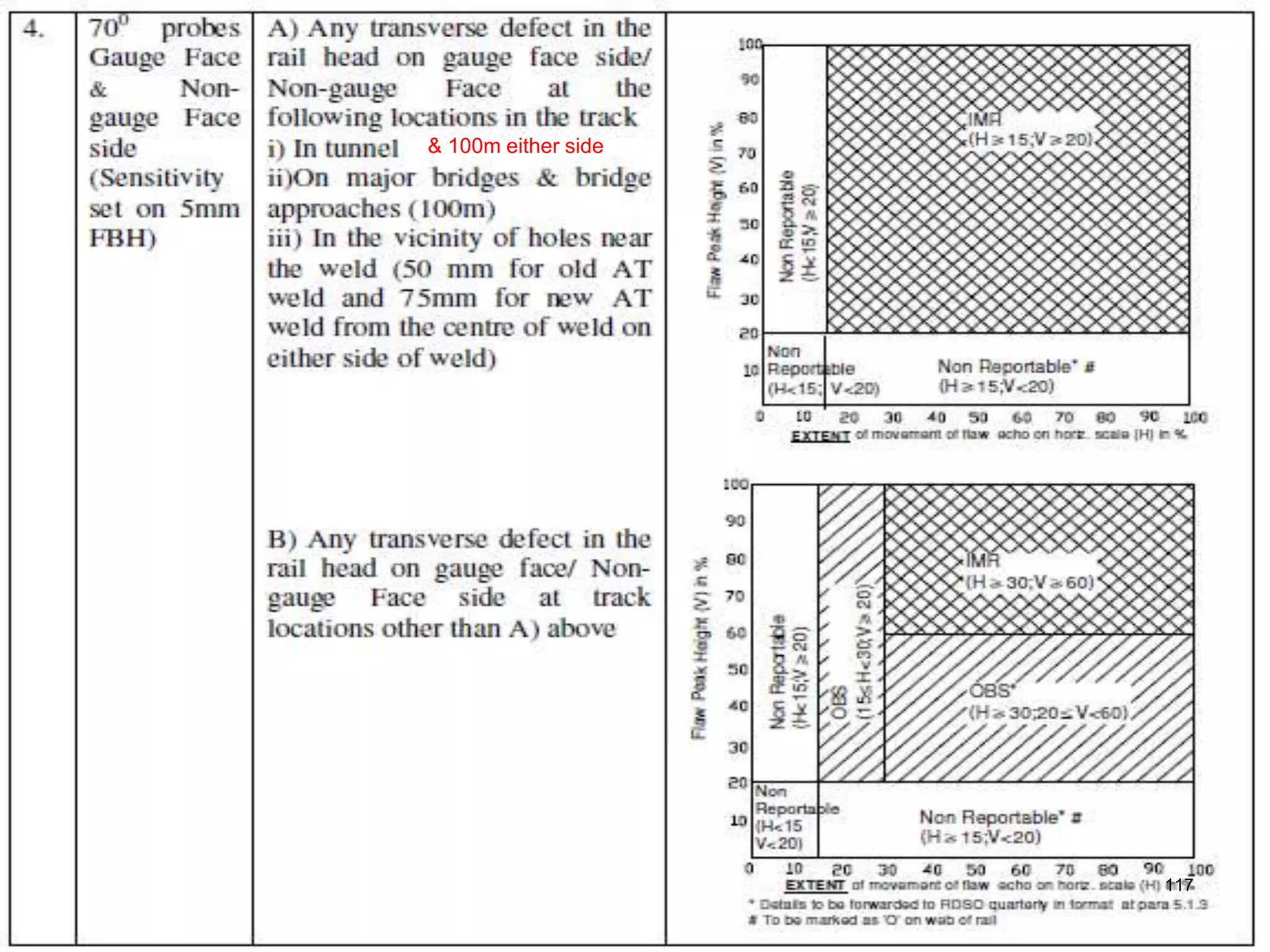
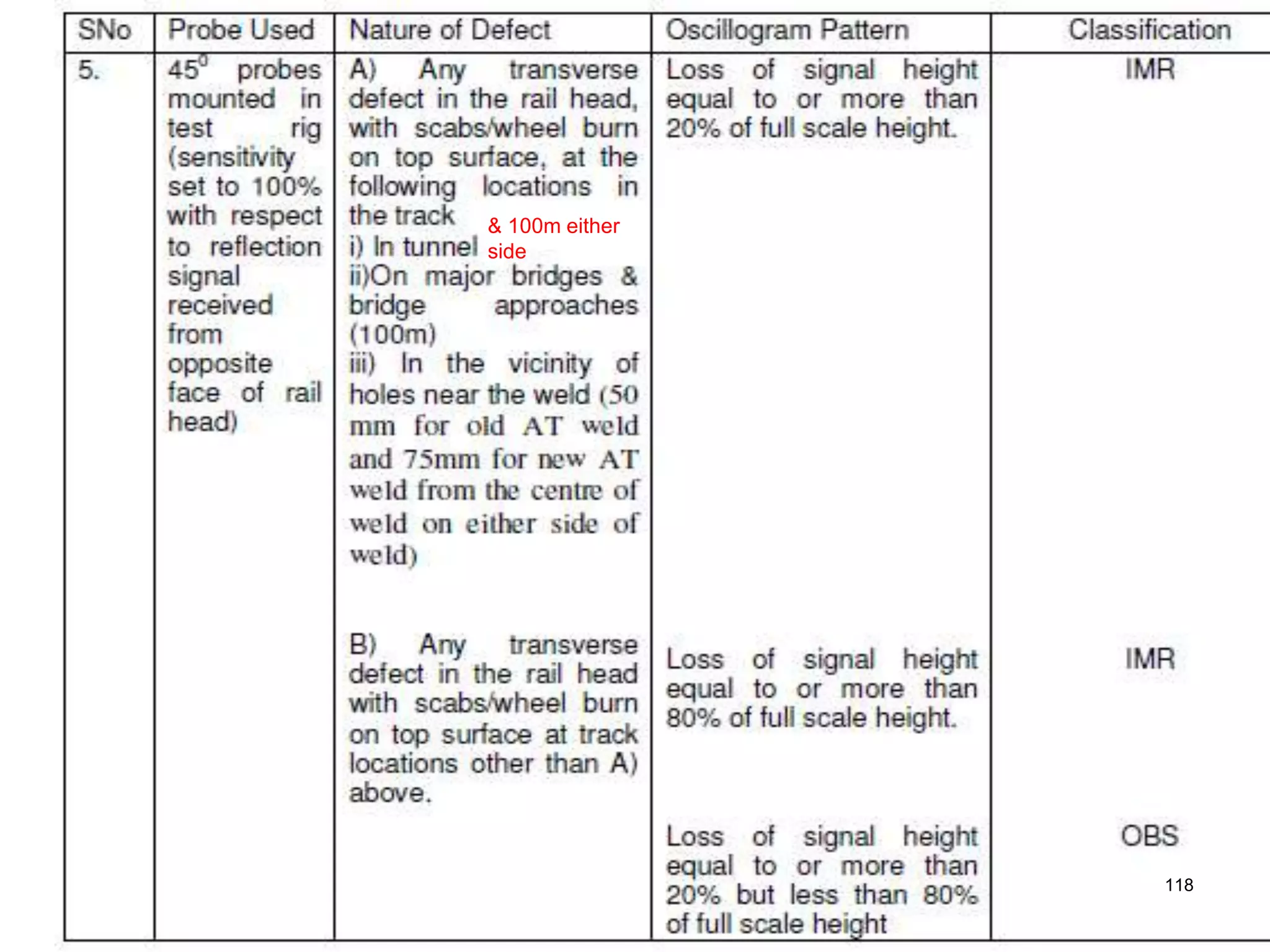
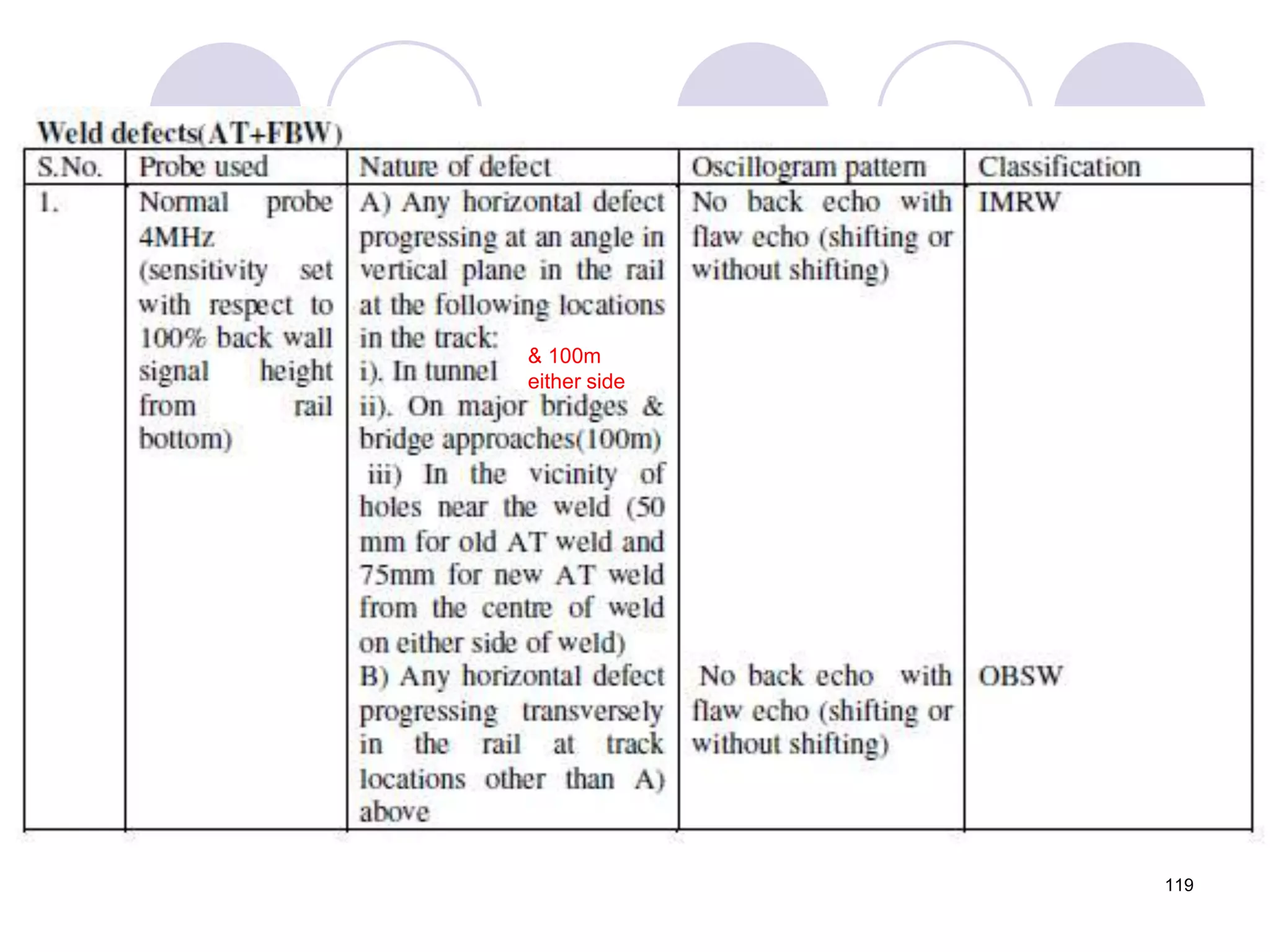
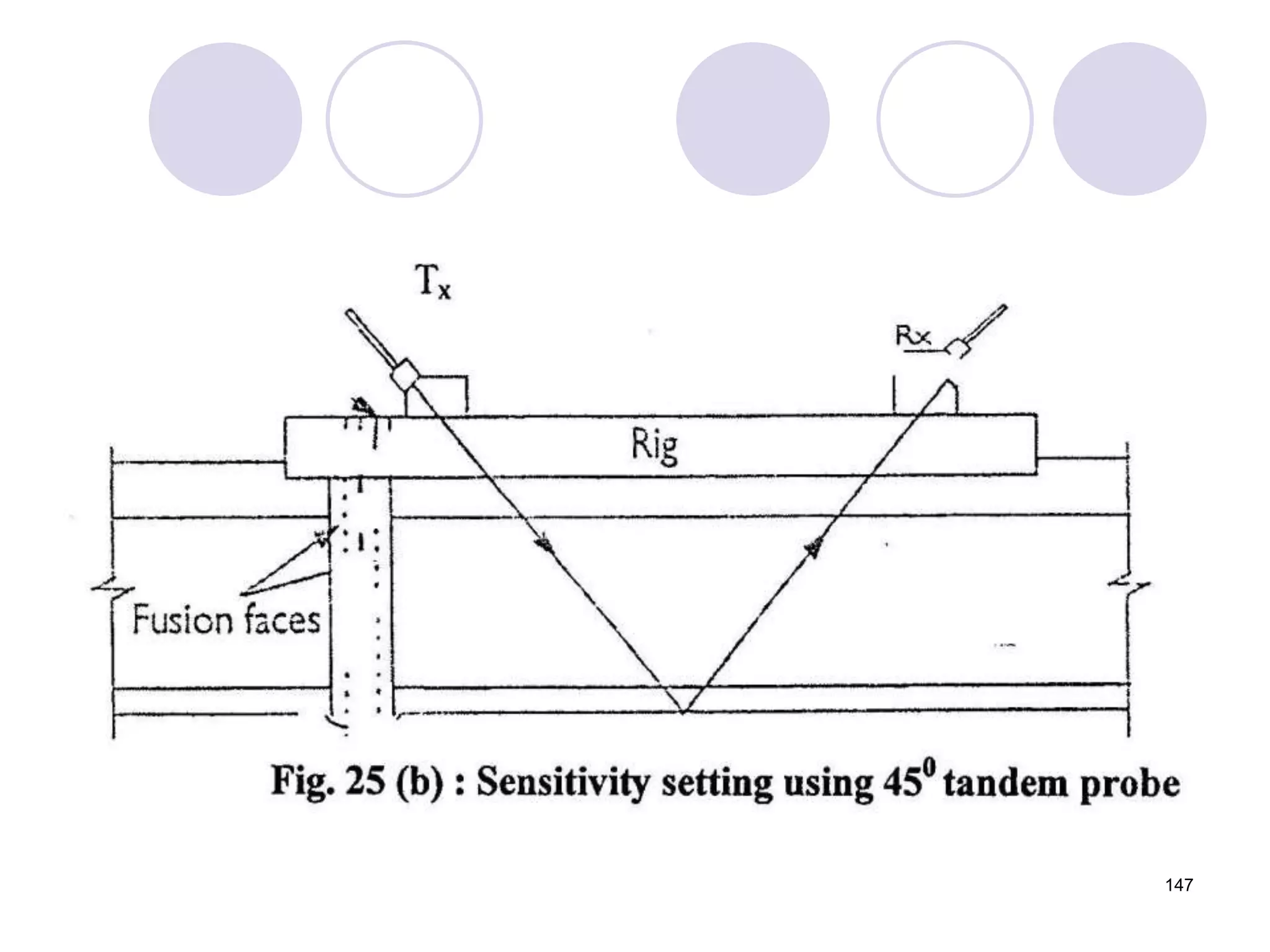
3. Ultrasonic testing uses probes with piezoelectric crystals to generate and receive sound waves. Reflections from flaws are detected to locate and size defects. Factors like wave types, frequencies, velocities and attenuation in different materials are explained for accurate flaw detection