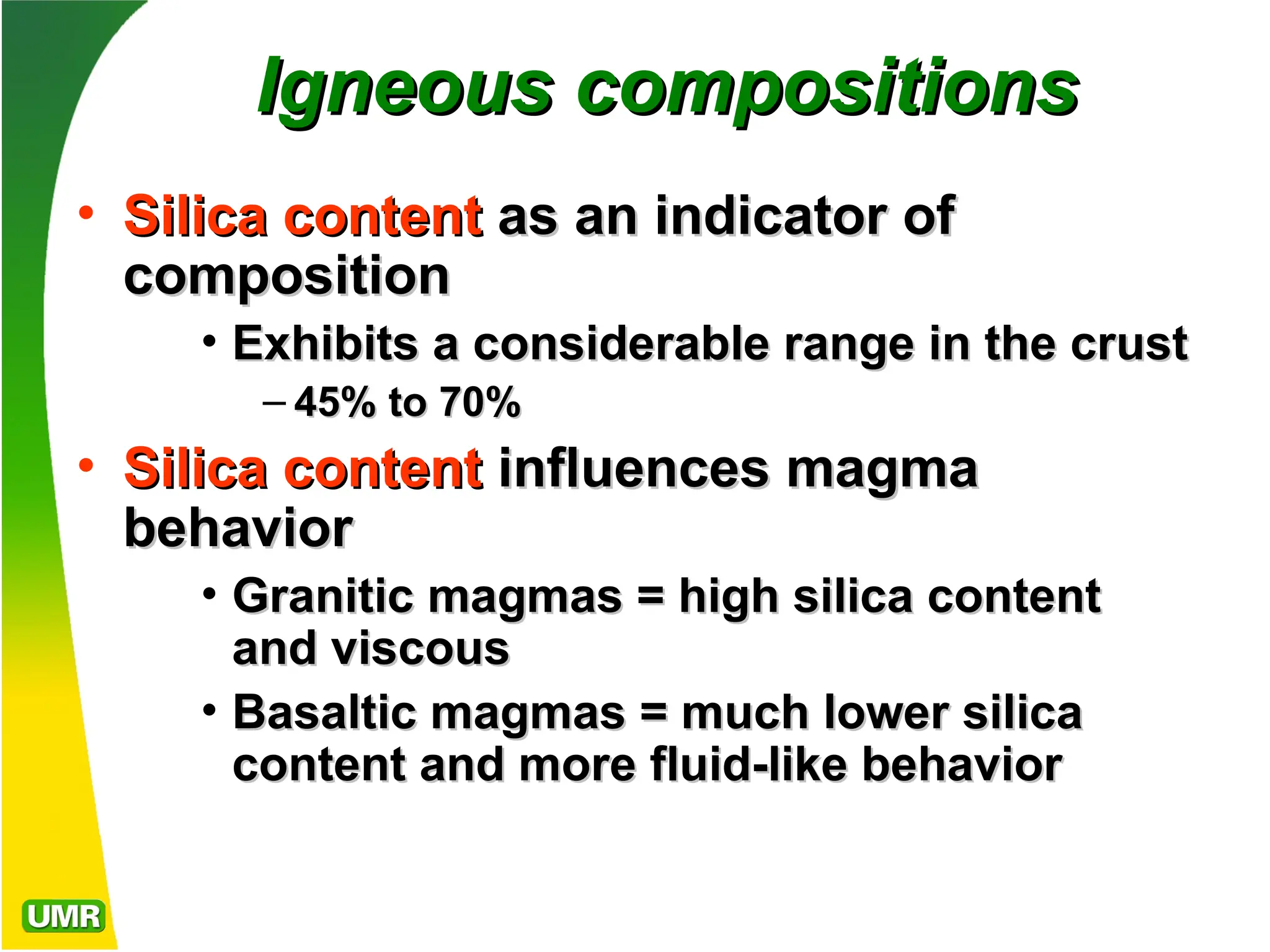
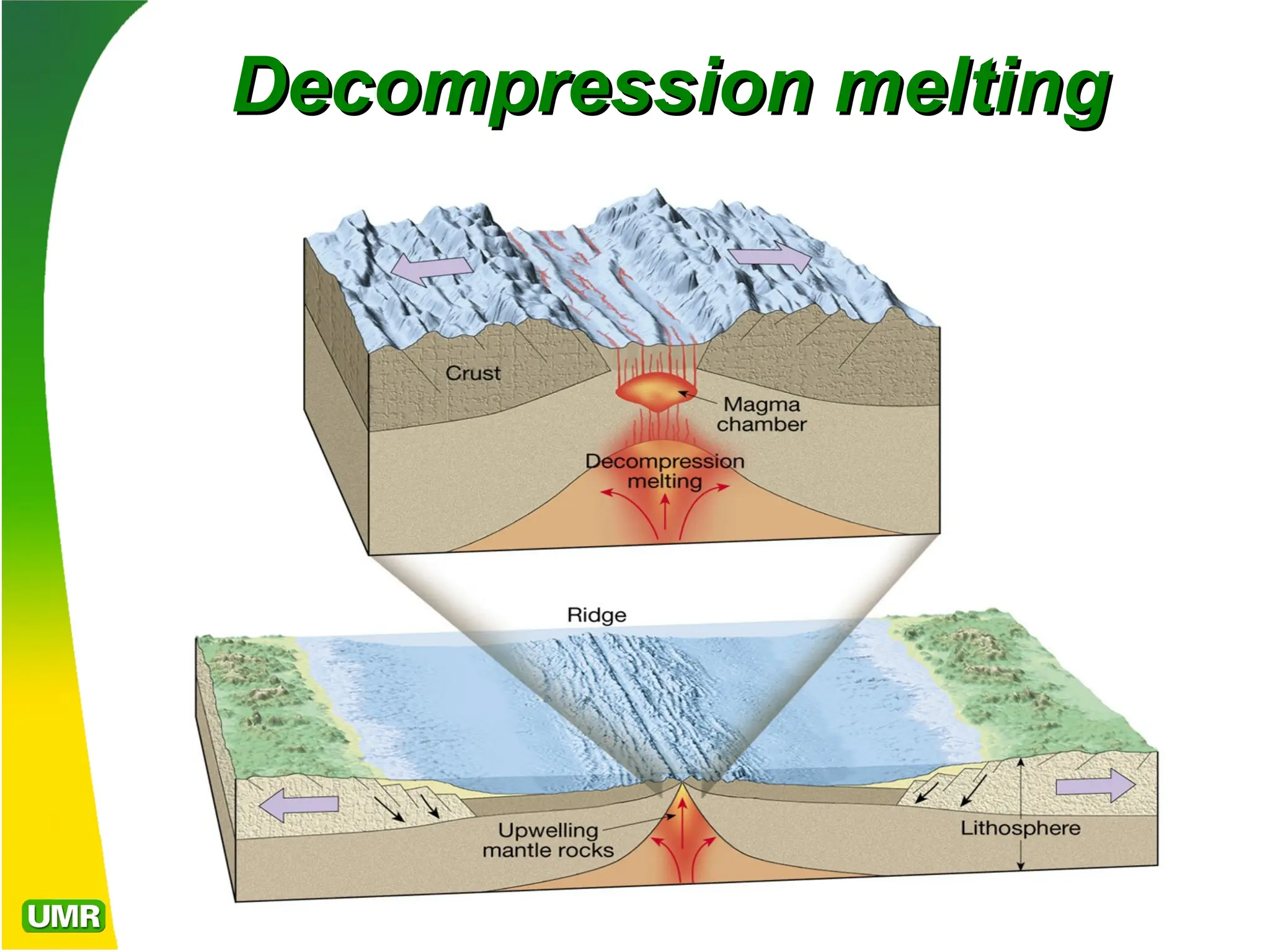
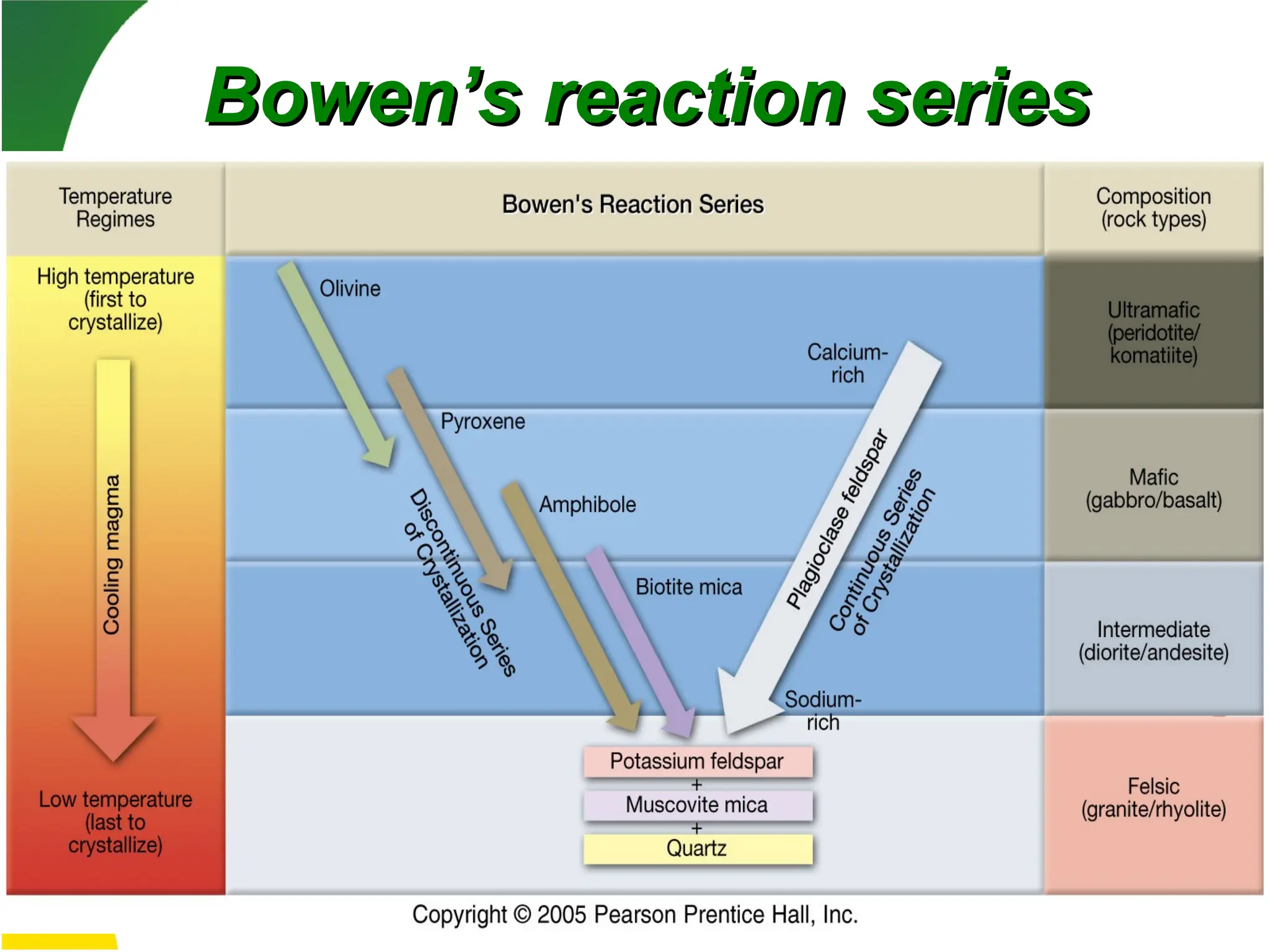
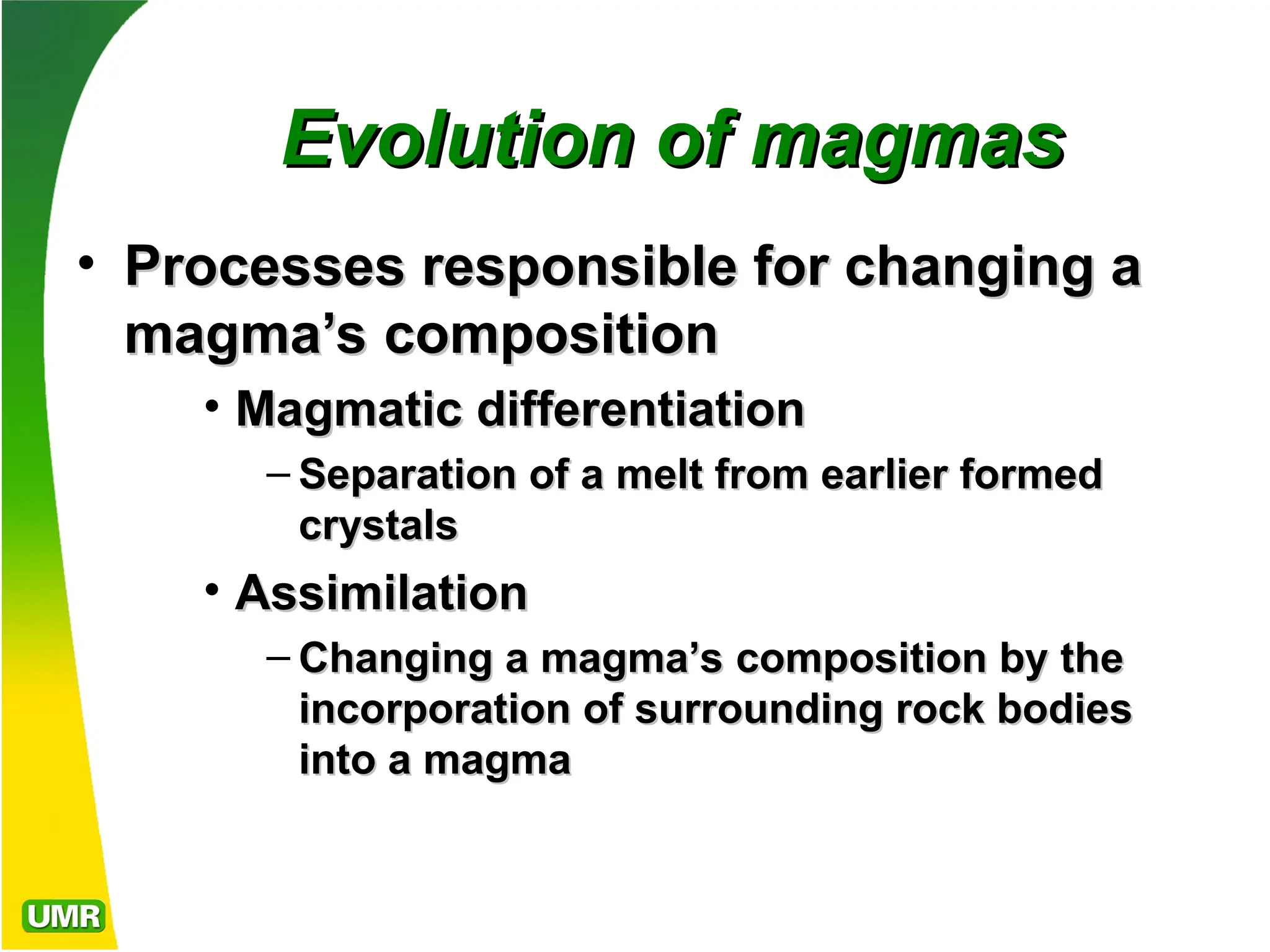
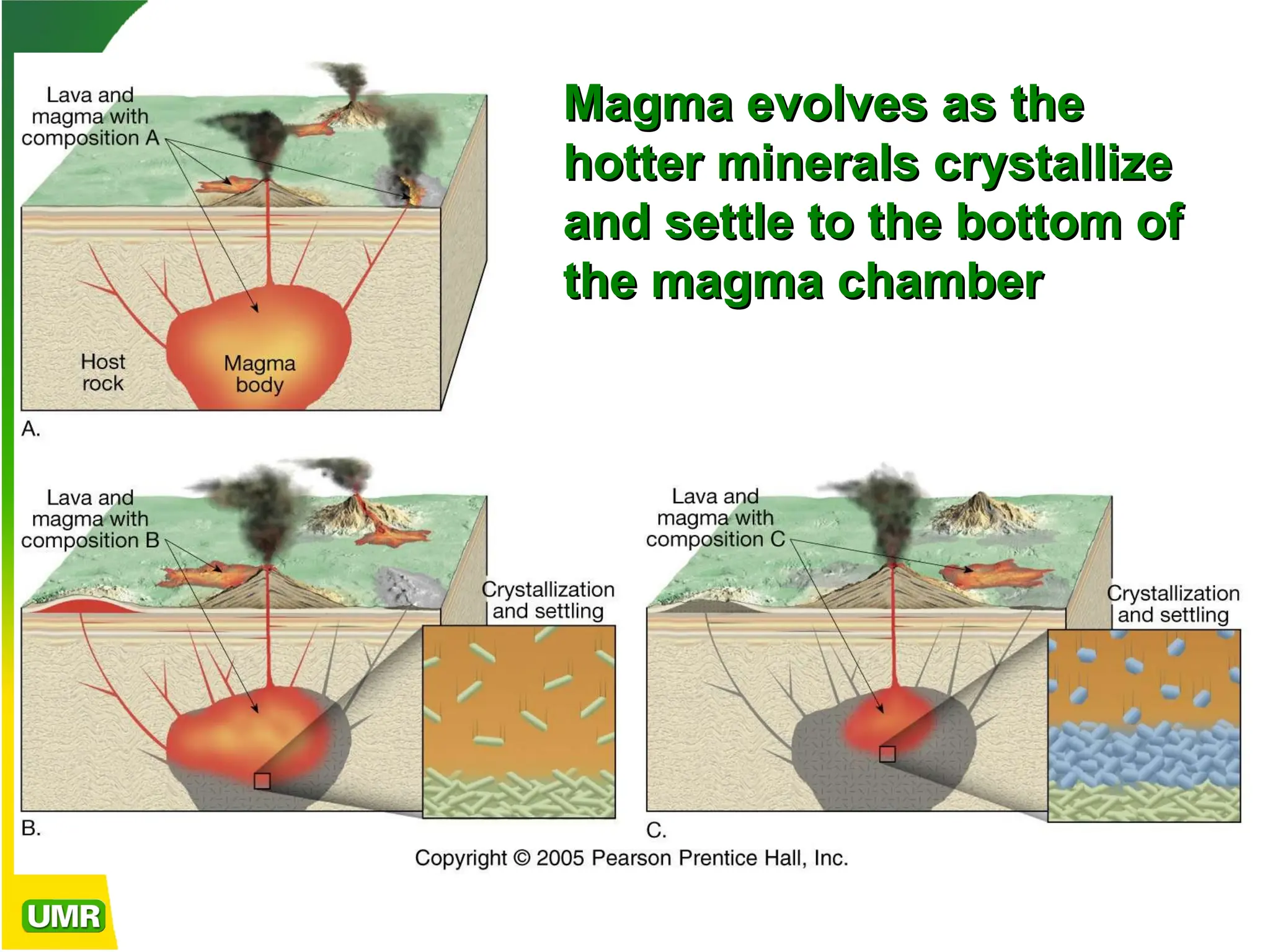
Igneous rocks form from molten rock called magma, which can either cool at the surface as lava (extrusive rocks) or at depth (intrusive rocks). Magma consists of liquid, solid silicate minerals, and volatiles; its cooling rate affects crystal size and texture, with different texture types indicating various cooling histories. The composition of igneous rocks ranges from granitic (felsic) to basaltic (mafic) and is influenced by processes such as partial melting, magmatic differentiation, and magma mixing.