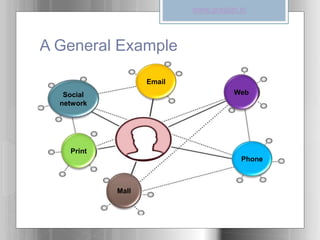
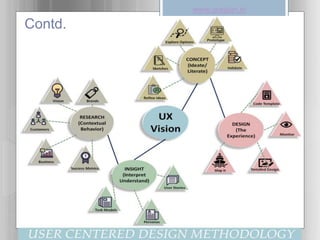
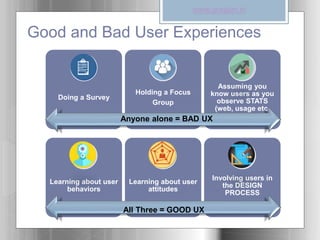
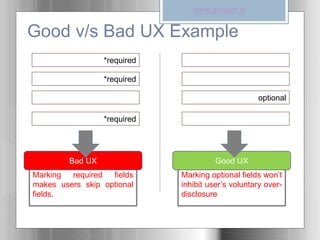
The document introduces user experience (UX) as the interaction a person has with a product, service, or organization, highlighting its multi-disciplinary contributions from fields like psychology and design. It outlines key factors affecting UX, such as usefulness, usability, and aesthetics, and discusses a user-centered design methodology that includes research and iterative design processes. Examples of good and bad user experiences are provided, emphasizing the importance of understanding user behaviors and involving them in the design process.