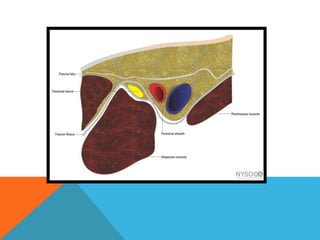
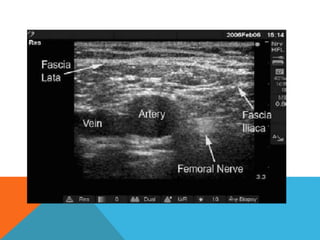
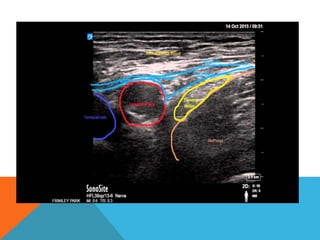
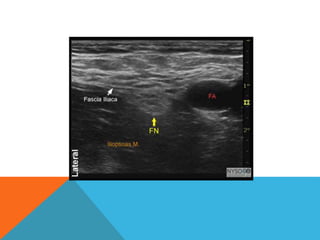
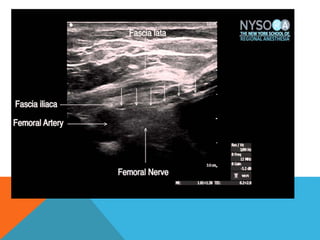
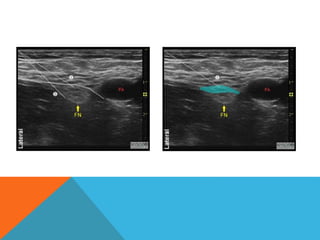
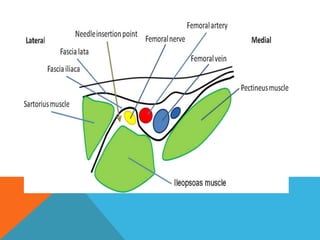
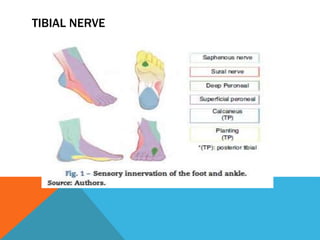
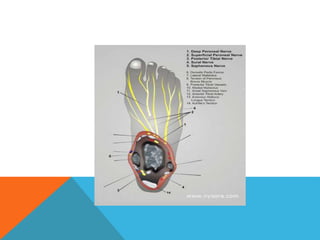
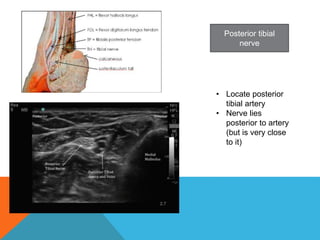
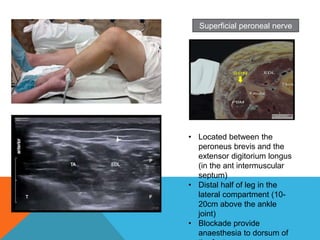
This document provides information on performing a femoral nerve block, including indications, contraindications, complications, equipment, positioning, ultrasound imaging, technical performance, and tips. The key steps are to use an 8-14MHz linear transducer to identify the hyperchoic oval or triangular femoral nerve lateral to the femoral artery under the fascia iliaca. The needle is then placed 1cm lateral to the nerve between the iliopsoas muscle and its fascia, and local anesthetic is injected to spread around the nerve. Proper deposition is confirmed by the nerve lifting off the iliopsoas muscle or spread of local anesthetic in the space lateral to the artery. The document also briefly outlines blocking the tib