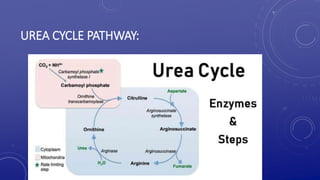
The urea cycle is a series of chemical reactions that converts toxic ammonia into urea in the liver. There are 5 main steps: 1) carbamoyl phosphate formation, 2) citrulline formation, 3) arginosuccinate formation, 4) arginine or arginosuccinate cleavage, and 5) urea formation. The cycle uses two ATP in the first step and another ATP is converted to AMP in the third step, for a total of 4 high energy phosphate bonds. This allows toxic ammonia to be converted to the relatively nontoxic urea for excretion.

![REACTION:
• The entire process converts two amino groups, one from NH+
4 and one from aspartate, and a carbon atom from HCO−
3, to the relatively nontoxic excretion product urea.[3] This occurs
at the cost of four "high-energy" phosphate bonds (3 ATP
hydrolyzed to 2 ADP and one AMP). The conversion from ammonia
to urea happens in five main steps. The first is needed for
ammonia to enter the cycle and the following four are all a part of
the cycle itself. To enter the cycle, ammonia is converted
to carbamoyl phosphate. The urea cycle consists of four
enzymatic reactions: one mitochondrial and
three cytosolic.[1][4] This uses 6 enzymes.[3][4][5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ureacycle-230627140740-db677ec6/85/urea-cycle-pptx-2-320.jpg)