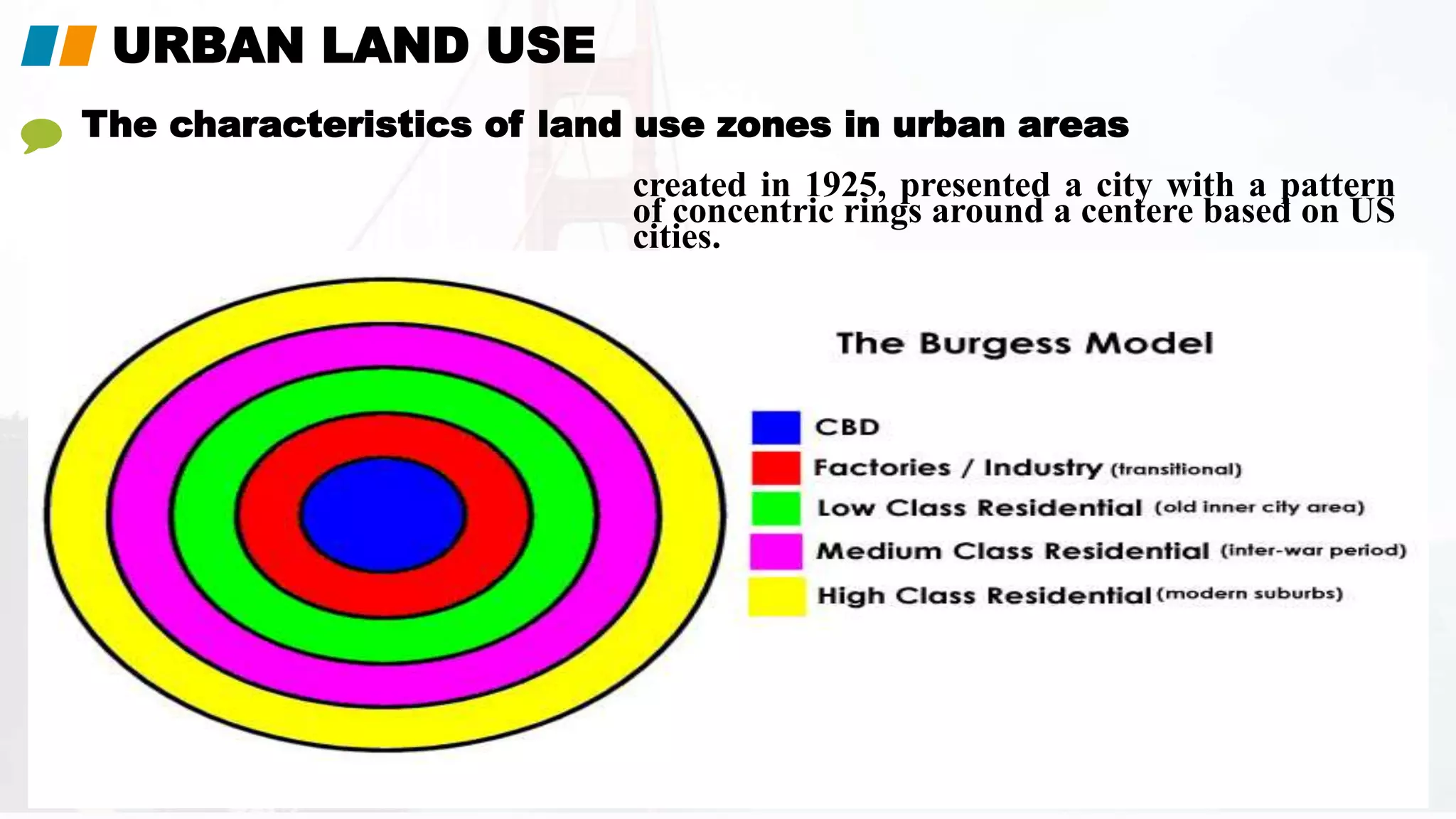
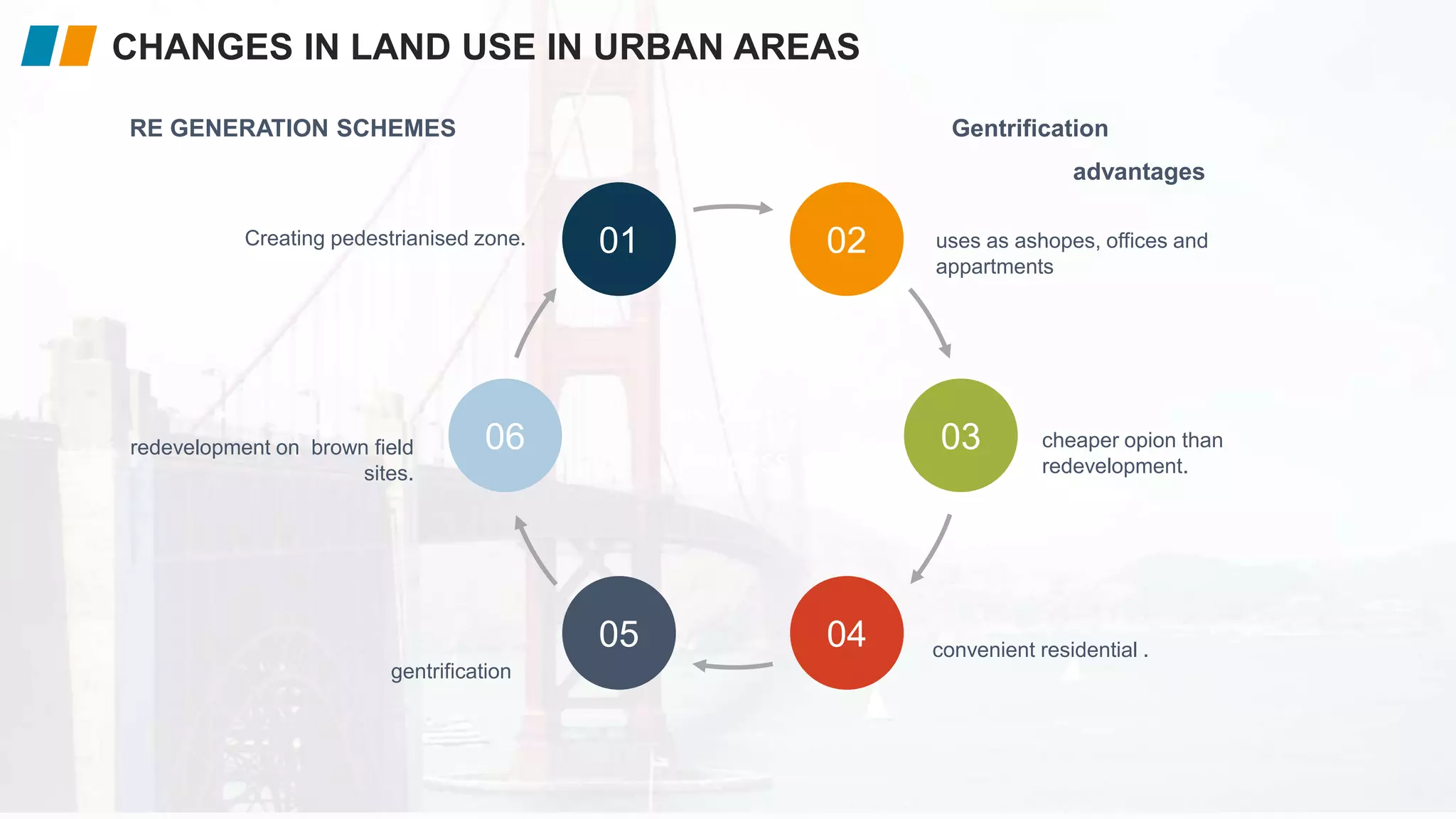
The document covers urban land use, characteristics of urban areas, and issues related to rapid urban growth, particularly focusing on case studies like Dubai and Rio de Janeiro. It discusses models like the Hoyt and Burgess models that describe land use patterns, along with challenges such as traffic congestion, pollution, and inadequate infrastructure. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for effective urban planning and strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of urbanization.