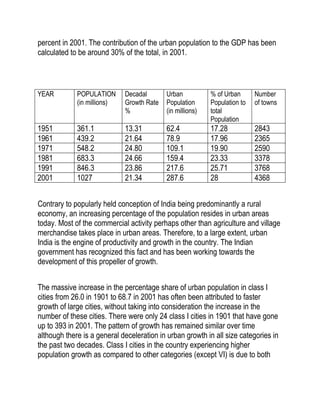
Urban infrastructure in India has grown dramatically since the 1950s. The percentage of the population living in urban areas has increased from 17.28% in 1951 to 28% in 2001. Urban areas now contribute around 30% of India's GDP. However, urban infrastructure still faces issues like lack of funds, high import duties on construction materials, and inadequate basic services in smaller towns. Going forward, public-private partnerships will be important to develop urban infrastructure, as the public sector alone cannot meet the large funding needs. The government needs to incentivize private and foreign investment to boost infrastructure development.