1. The patient, a 65-year-old female, presented with complaints of dysuresis, low abdominal pain, fever, and rarely bloody urine. She was diagnosed with cystitis.
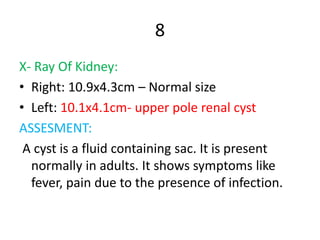
2. Objective findings included elevated pulse and temperature. Examination found systemic infection and a normal-sized right kidney but a left kidney with an upper pole renal cyst.
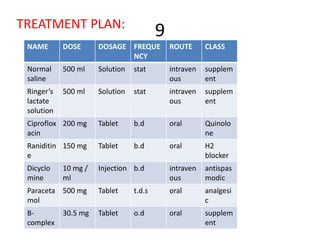
3. Treatment included antibiotics (ciprofloxacin), antacids (raniditine), analgesics (paracetamol), IV fluids (normal saline and Ringer's lactate), and antispasmodics (dicyclomine). The pharmacist noted some issues and interventions to address.