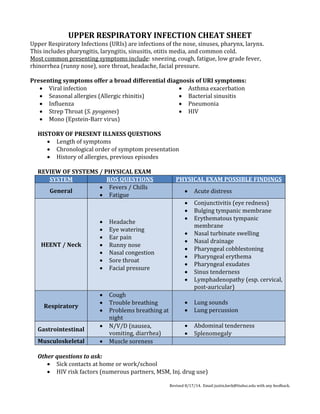
The document serves as a cheat sheet for upper respiratory infections (URIs), outlining common symptoms, differential diagnoses, and recommended histories and physical exams. It provides guidelines for laboratory testing, diagnosis, and treatments, emphasizing that most URIs are viral and treatment is generally symptomatic. Specific pathogen treatments are also detailed, along with Centor criteria for assessing strep throat risk.