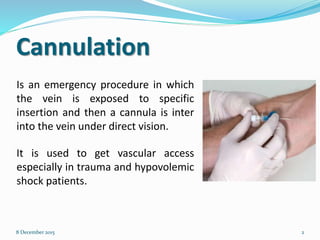
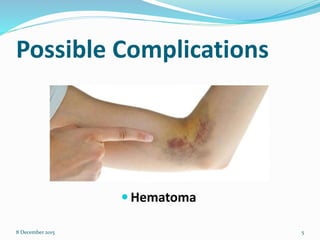
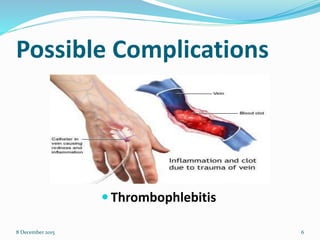
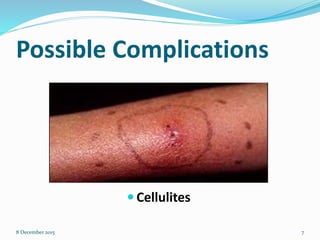
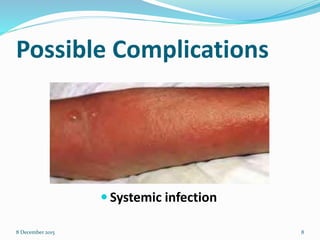
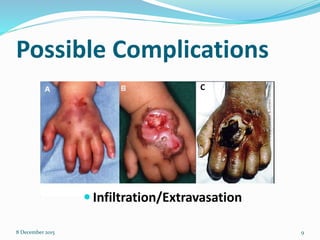
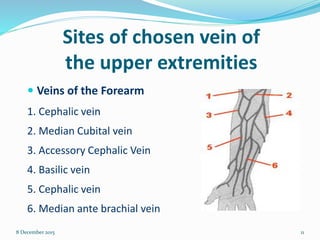
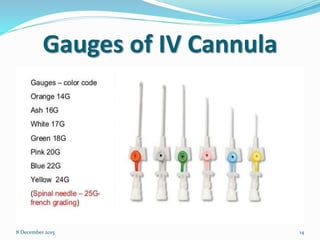
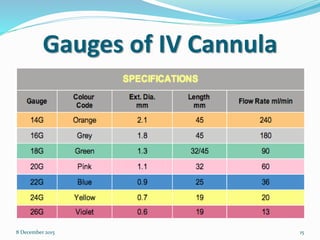
Cannulation is an emergency procedure to access veins by exposing the vein and inserting a cannula under direct vision. It is used for trauma and hypovolemic shock patients to gain vascular access. Intravenous (IV) therapy delivers medications, fluids, blood transfusions, and chemotherapy directly into veins. Advantages include immediate effect, controlled administration, and avoidance of pain compared to other routes. Possible complications are hematoma, thrombophlebitis, cellulitis, systemic infection, and infiltration/extravasation. The lecture discusses sites for IV cannulation in upper extremities like hand and forearm veins, signs of good veins, veins to avoid, and gauges of IV cannulas.