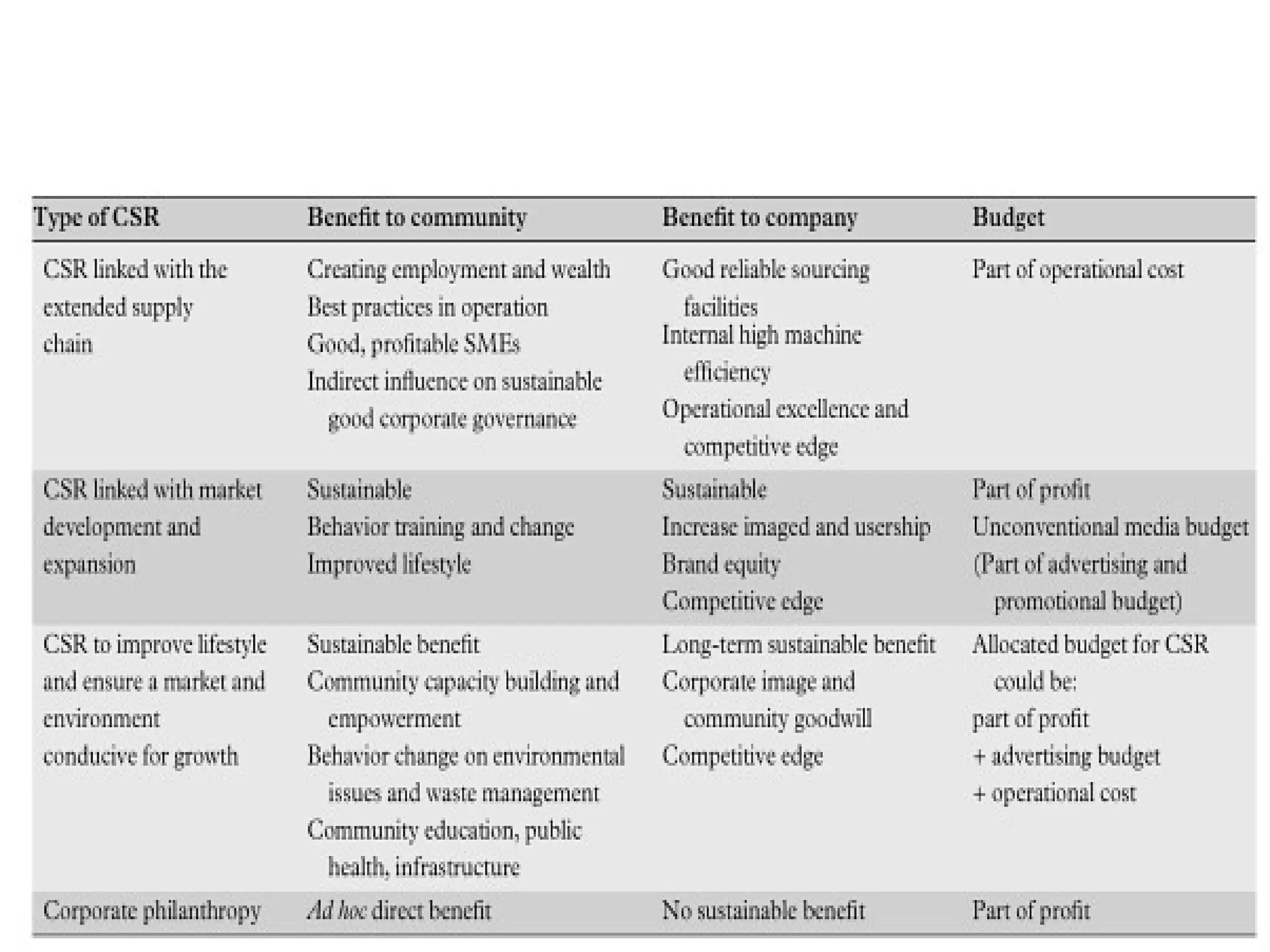
CSR refers to the economic, ethical, legal, and discretionary responsibilities of organizations to society. Firms have moral obligations along with earning profits and following laws. CSR policies aim to integrate public interest into decisions and balance stakeholders, planet, and profits. CSR involves various voluntary efforts to address societal and environmental issues in a responsible manner that benefits both society and the company. The history of CSR began in the 18th century but the concept gained prominence in the 1960s-1970s as societal expectations of businesses increased regarding civil rights, consumerism, and environmentalism.