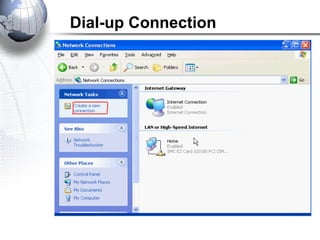
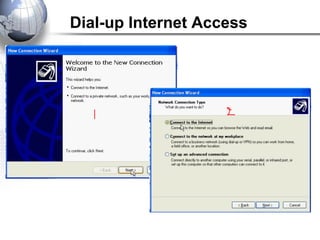
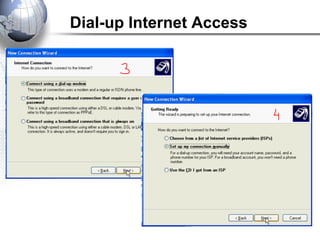
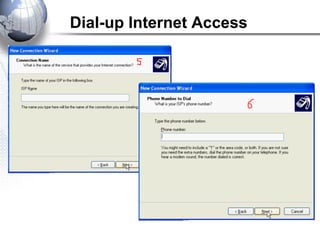
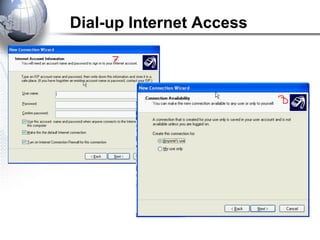
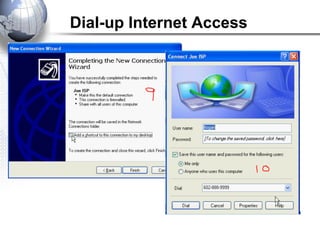
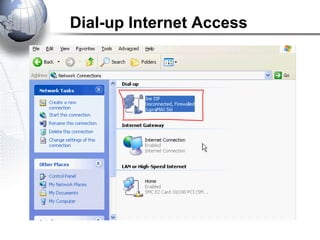
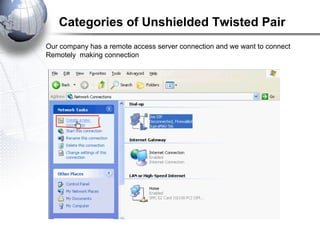
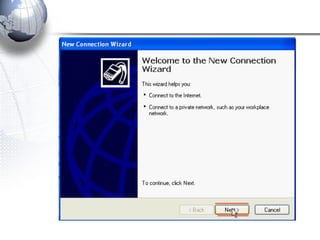
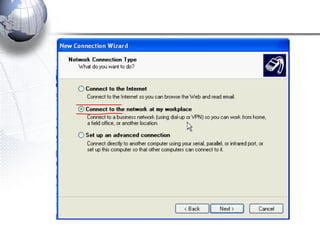
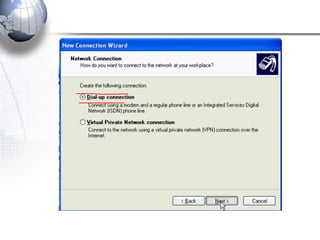
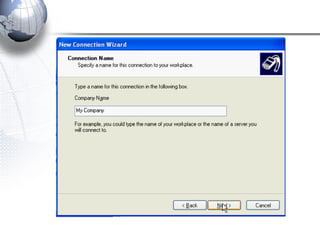
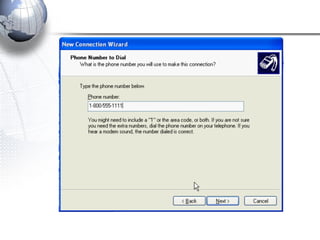
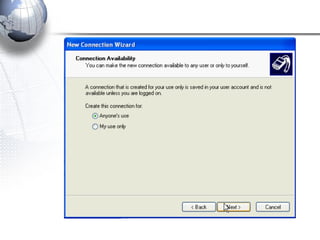
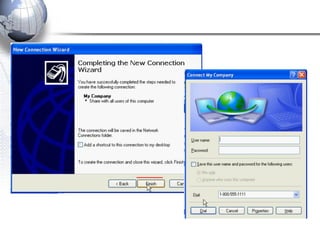
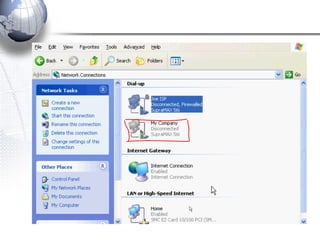
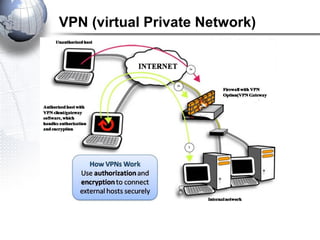
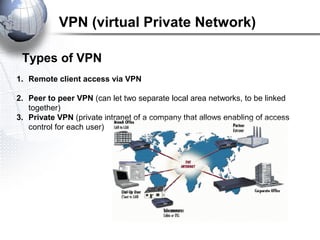
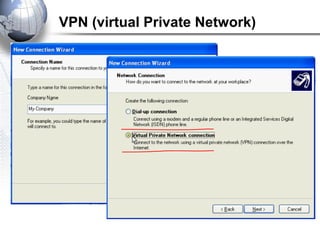
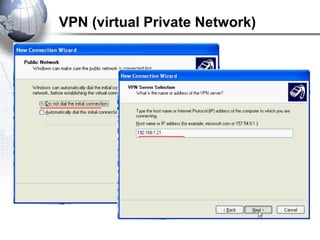
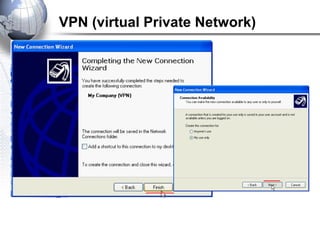
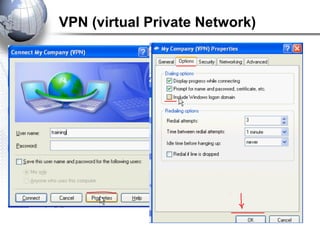
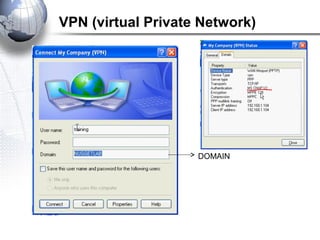
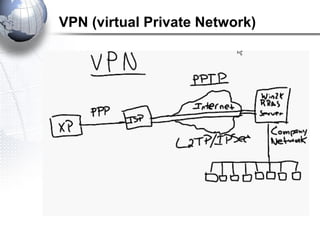
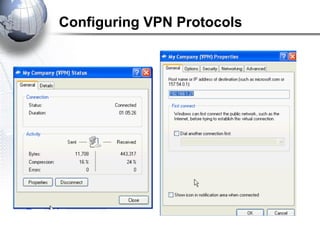
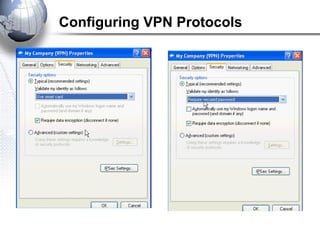
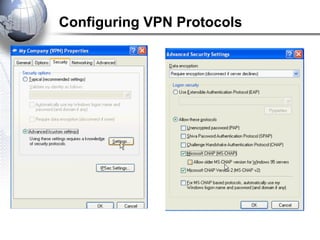
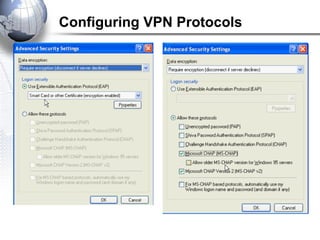
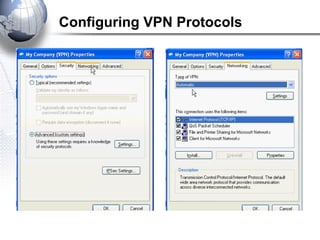
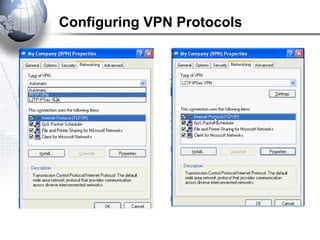
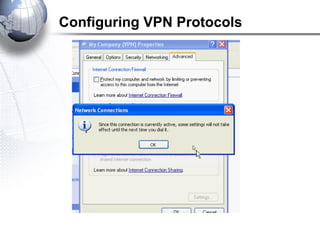
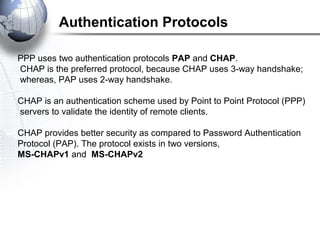
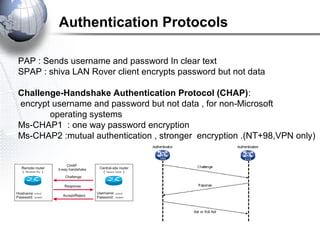
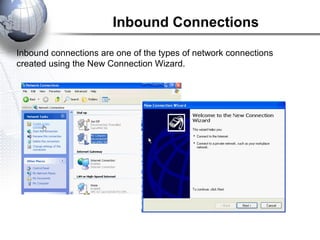
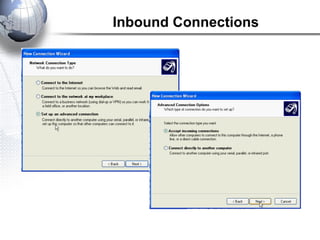
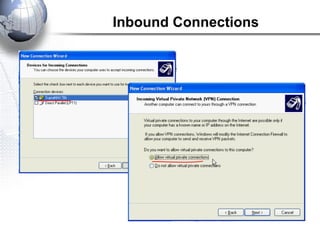
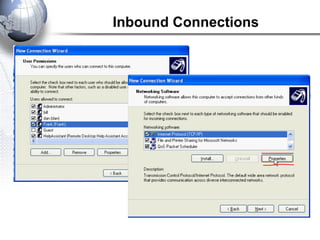
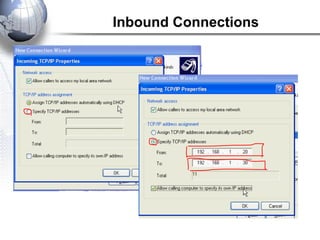
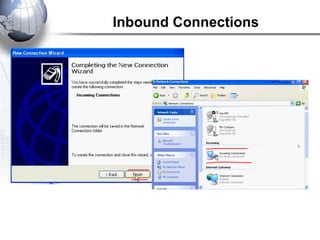
This document discusses remote access connections and virtual private networks (VPNs). It provides contact information for Ah. Fawad 'Saiq' and describes dial-up and broadband internet access. It also discusses remote client access via VPN, VPN protocols, authentication protocols like PAP and CHAP, and inbound connections.