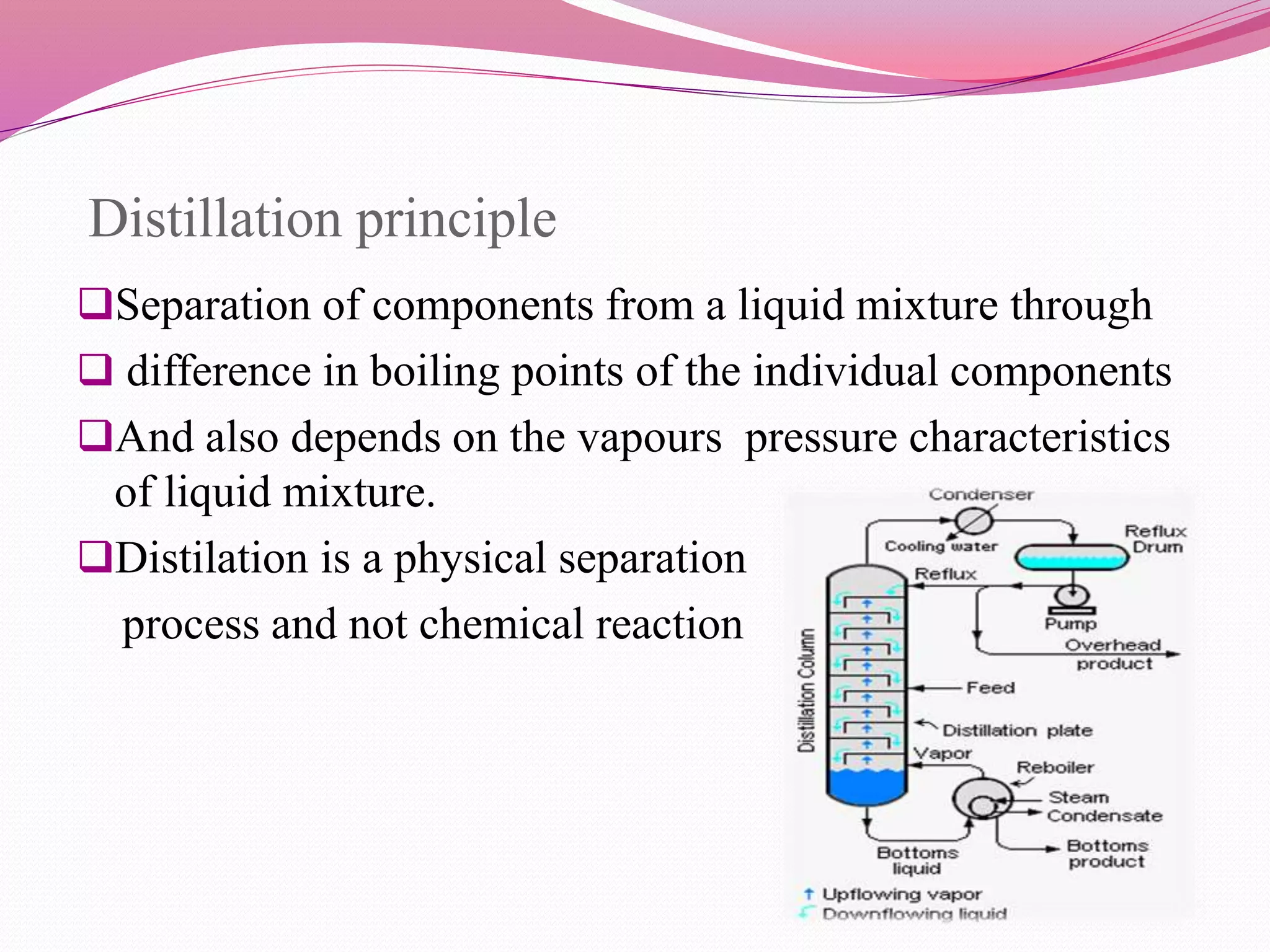
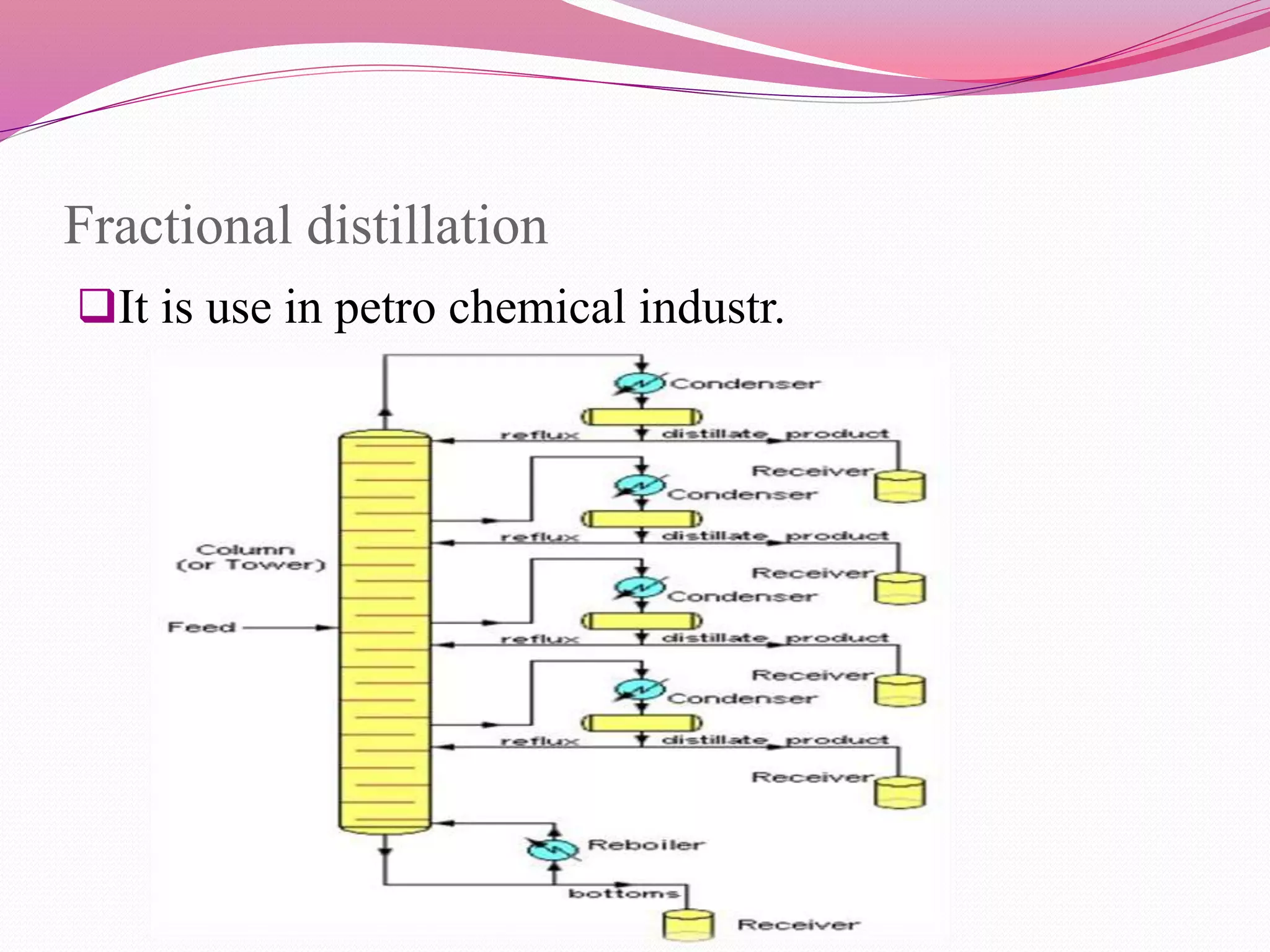
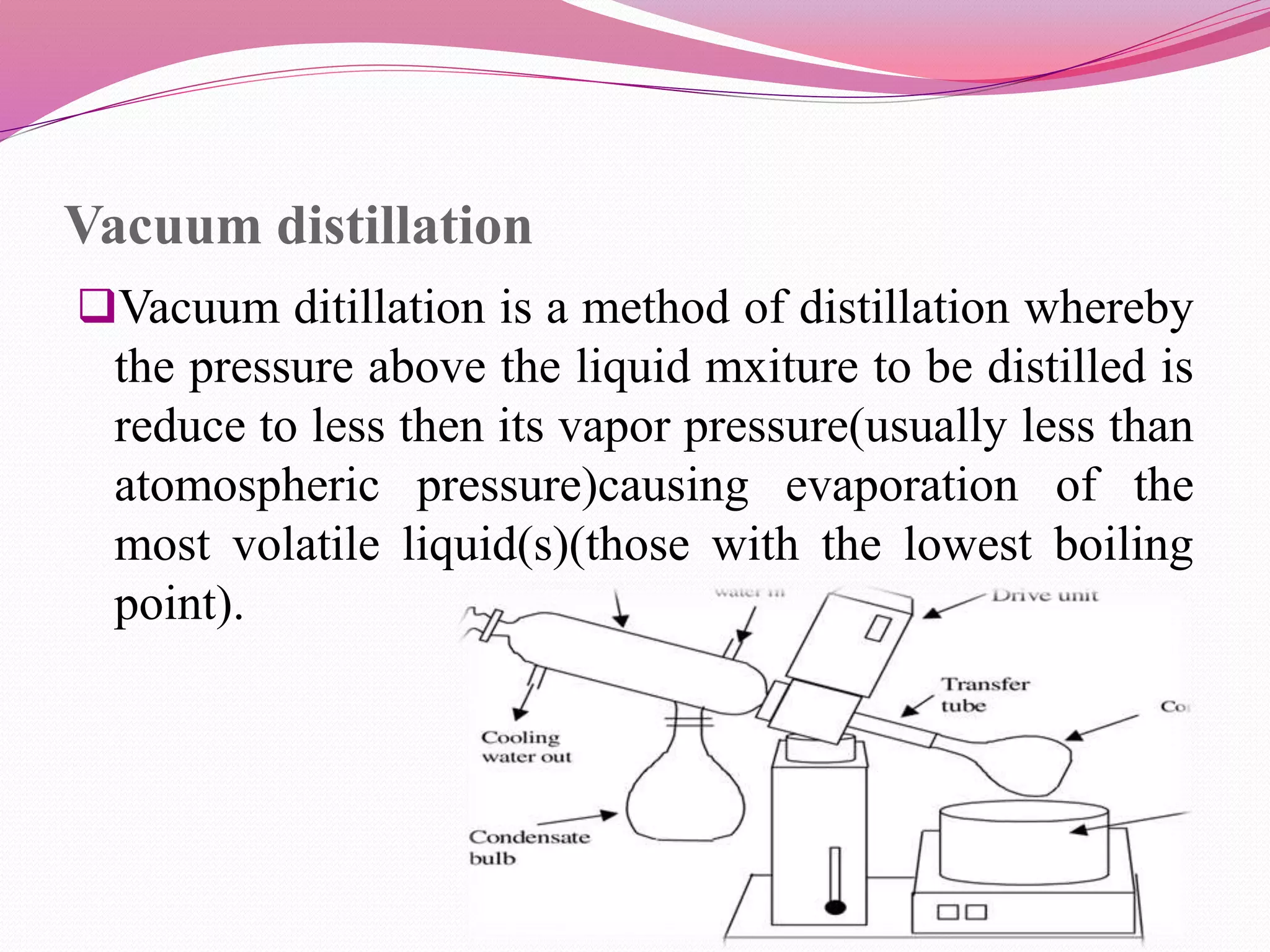
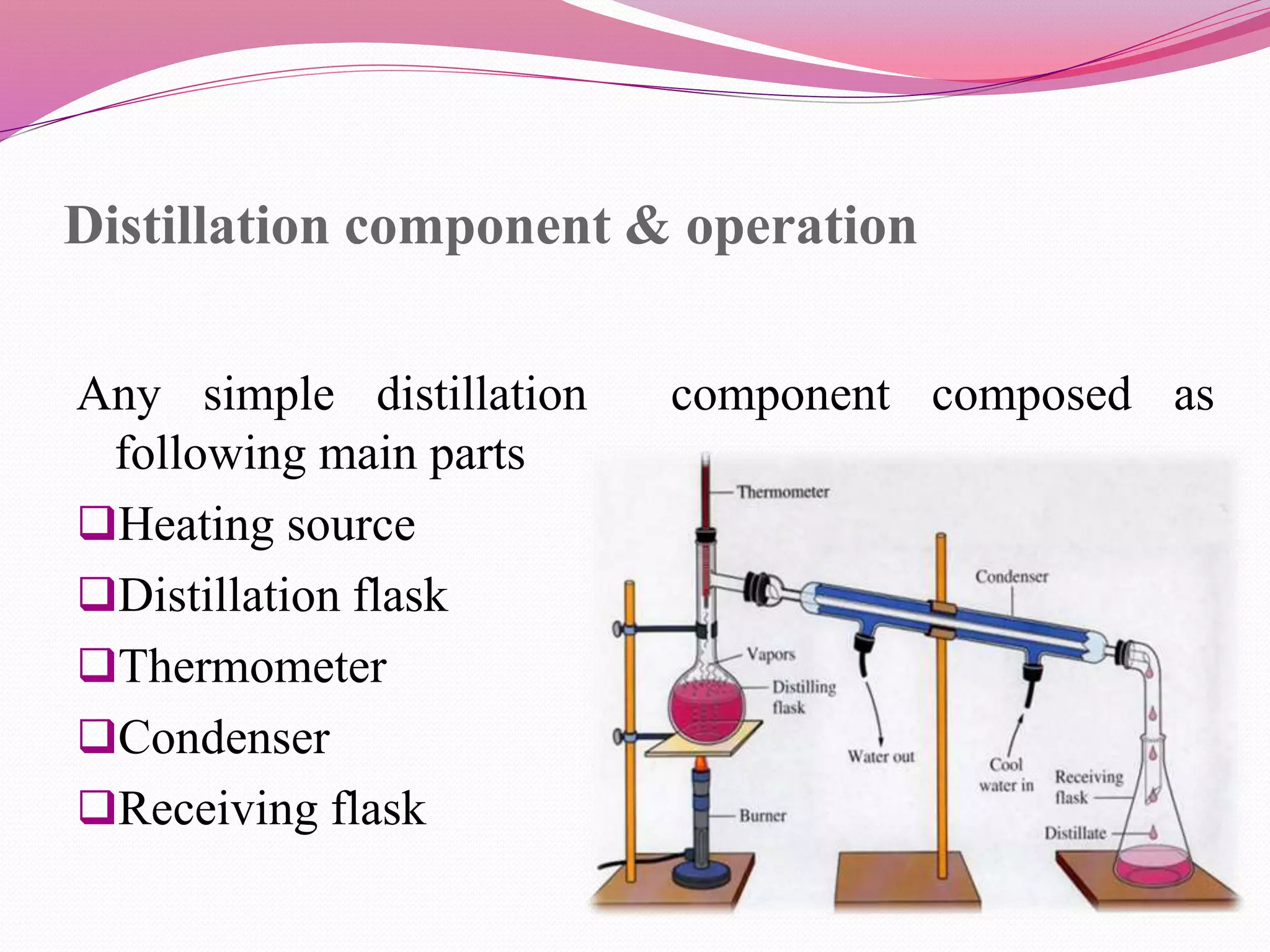
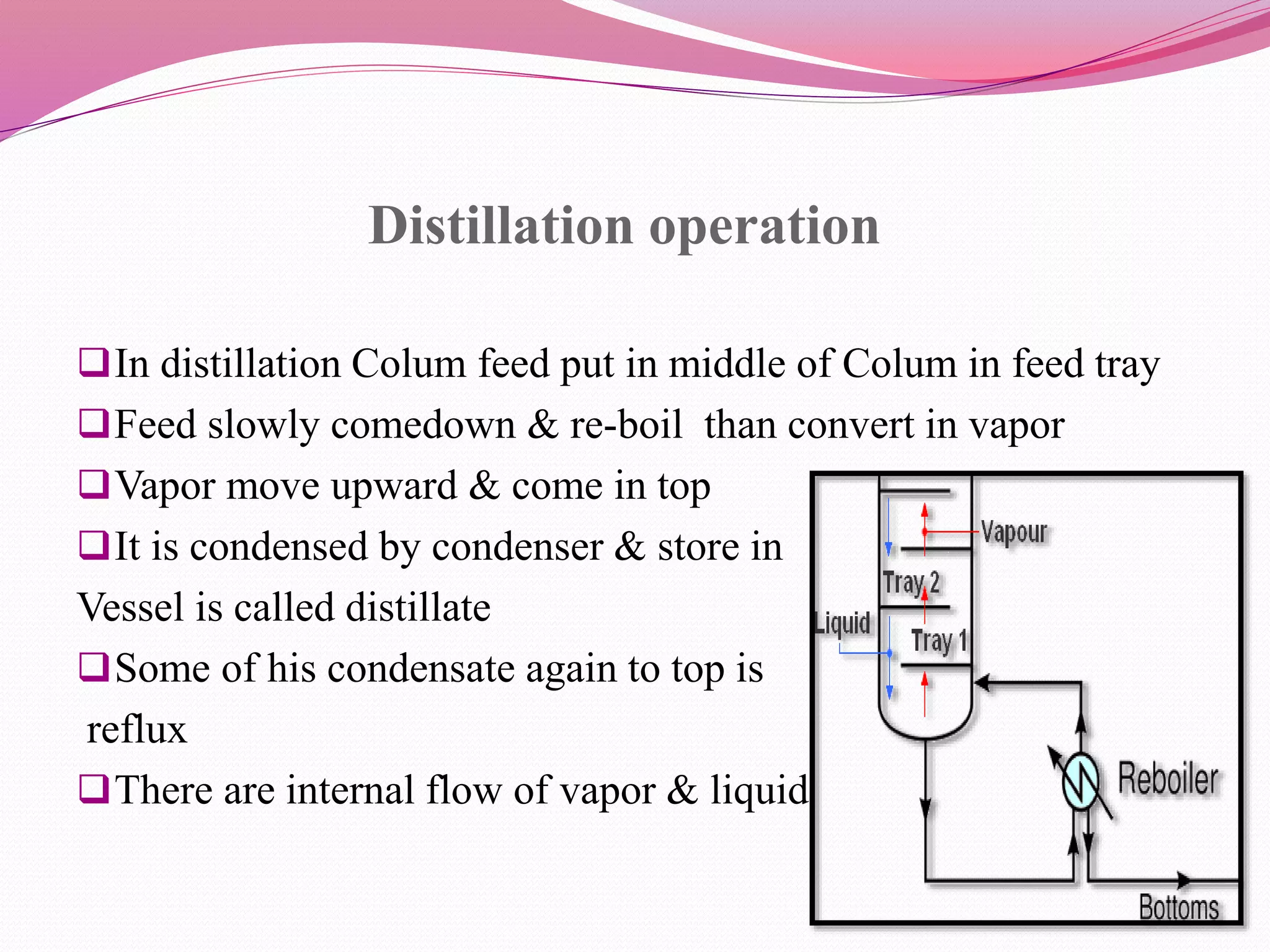
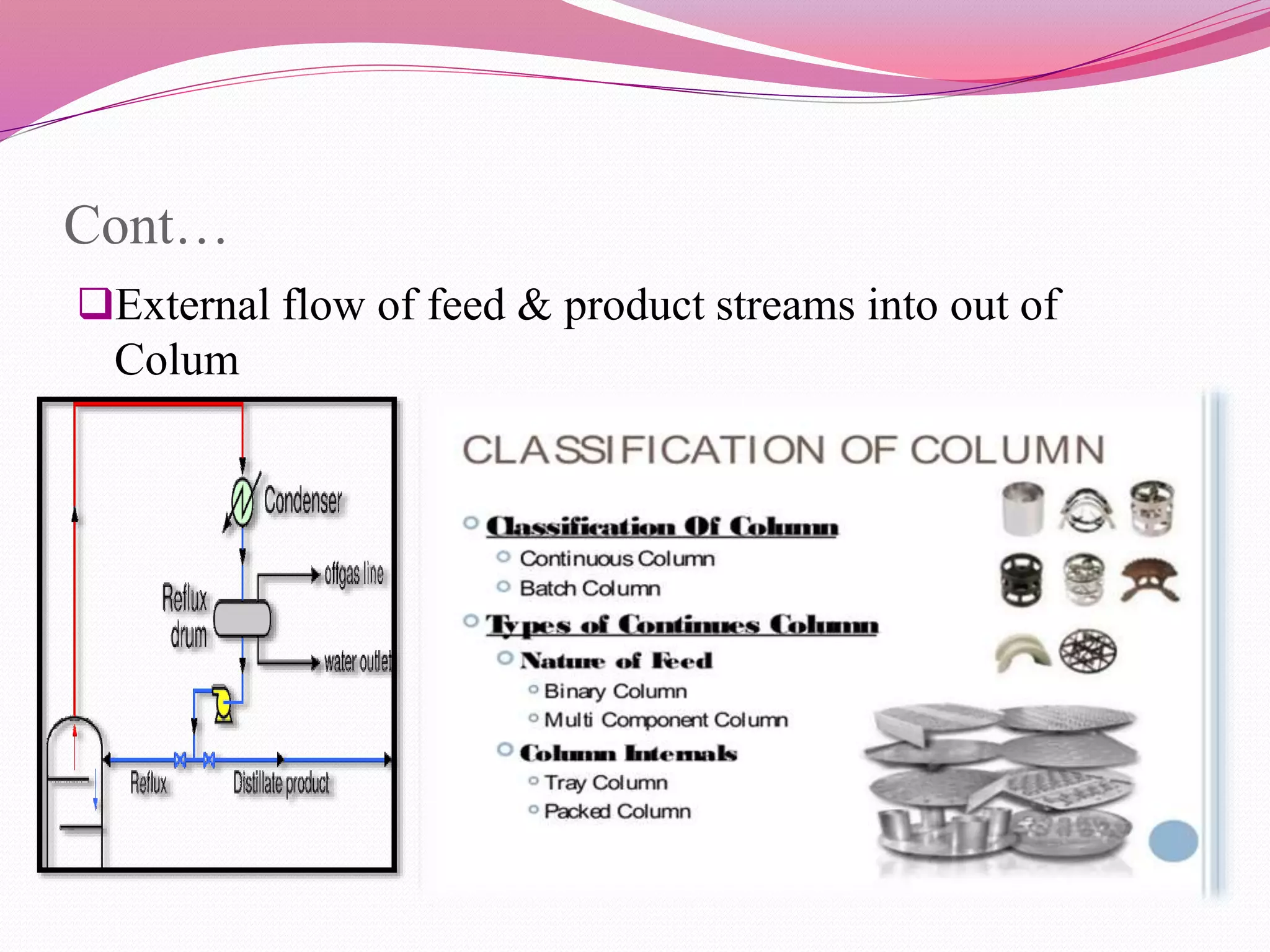
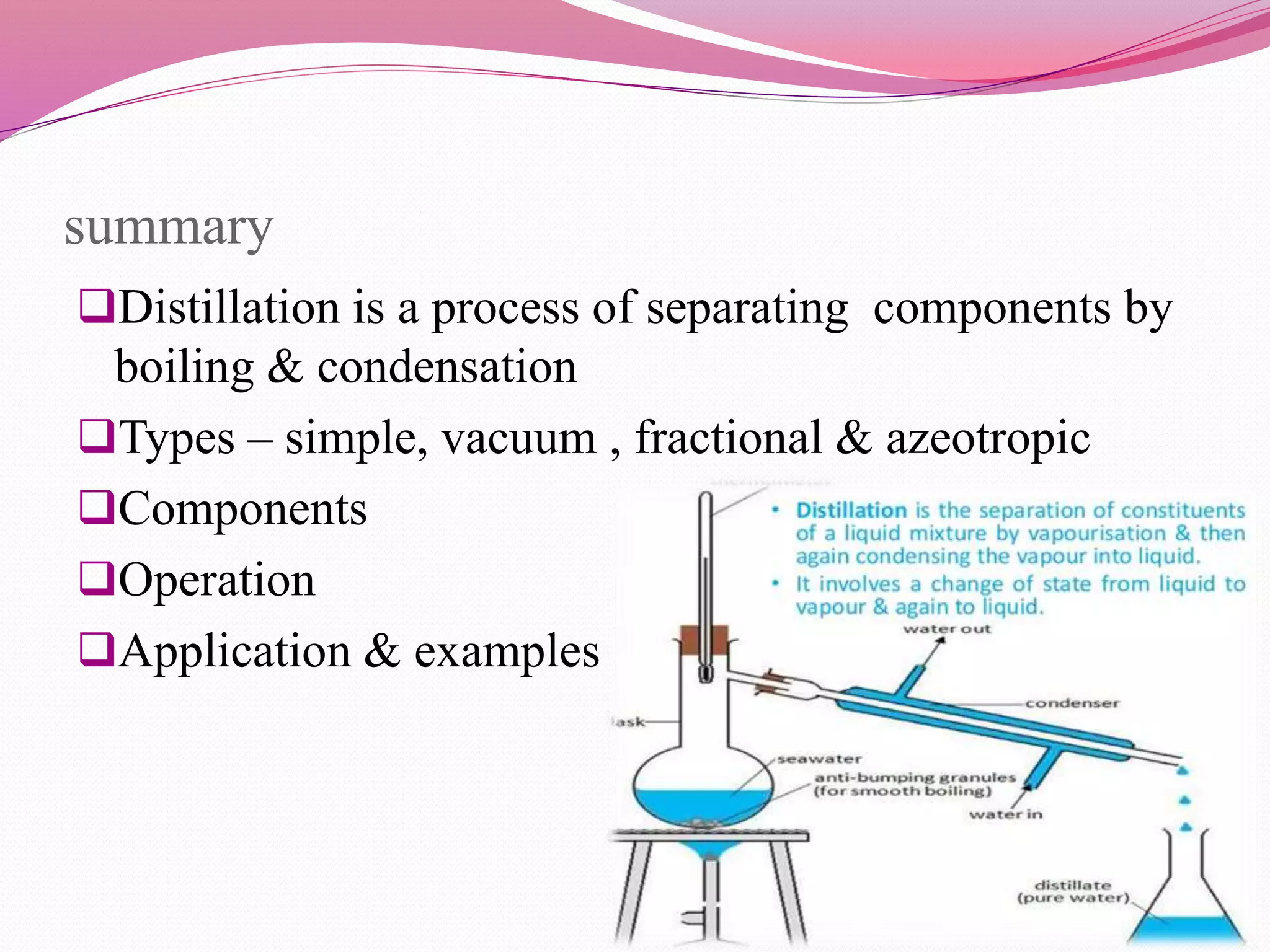
Distillation is a process that separates liquid mixtures by boiling and condensing their components with different boiling points. There are several types including simple, fractional, vacuum, and azeotropic distillation. Distillation systems generally include a heating source, distillation flask, condenser, and receiving flask. Common applications include separating crude oil fractions in industry and obtaining herbal extracts or alcoholic beverages through distillation.