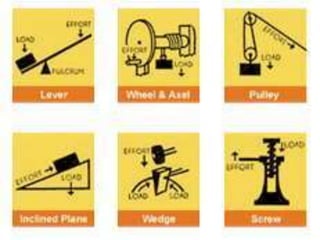
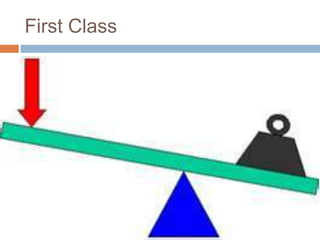
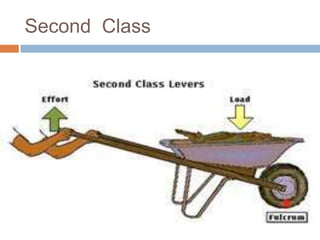
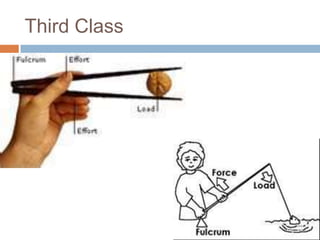
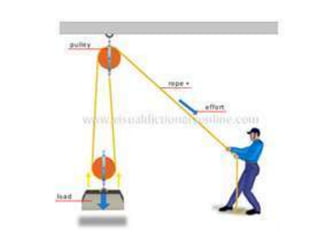
This document discusses mechanical systems and simple machines. It explores how mechanical systems have improved lives through vehicles, medicine, and resource gathering. Some key contributions discussed are the Canadarm on the International Space Station and Robonaut, the first robot astronaut. The document then covers the six main simple machines: lever, inclined plane, wedge, screw, pulley, and wheel and axle. Each machine is defined and an example of its use is provided.