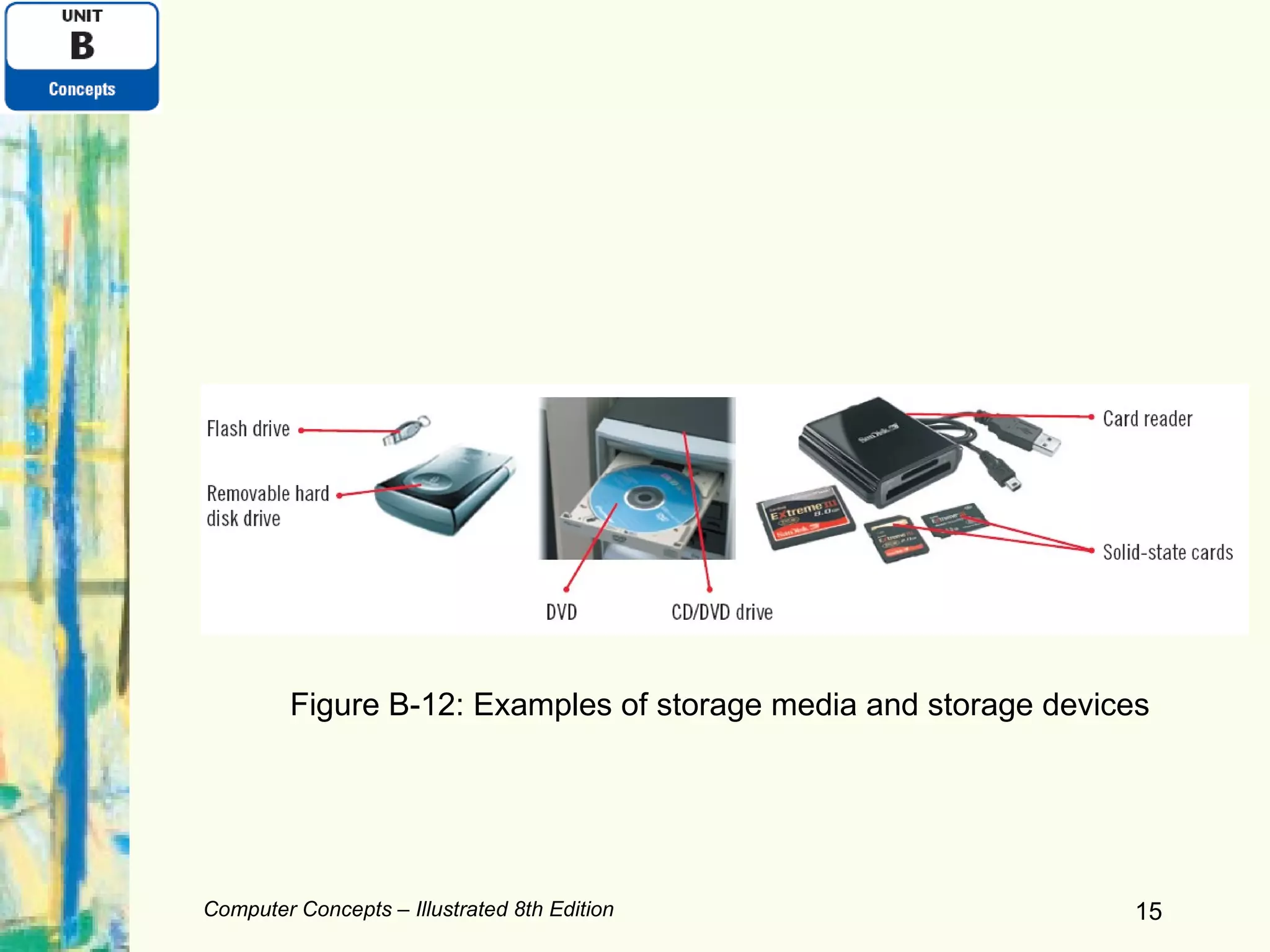
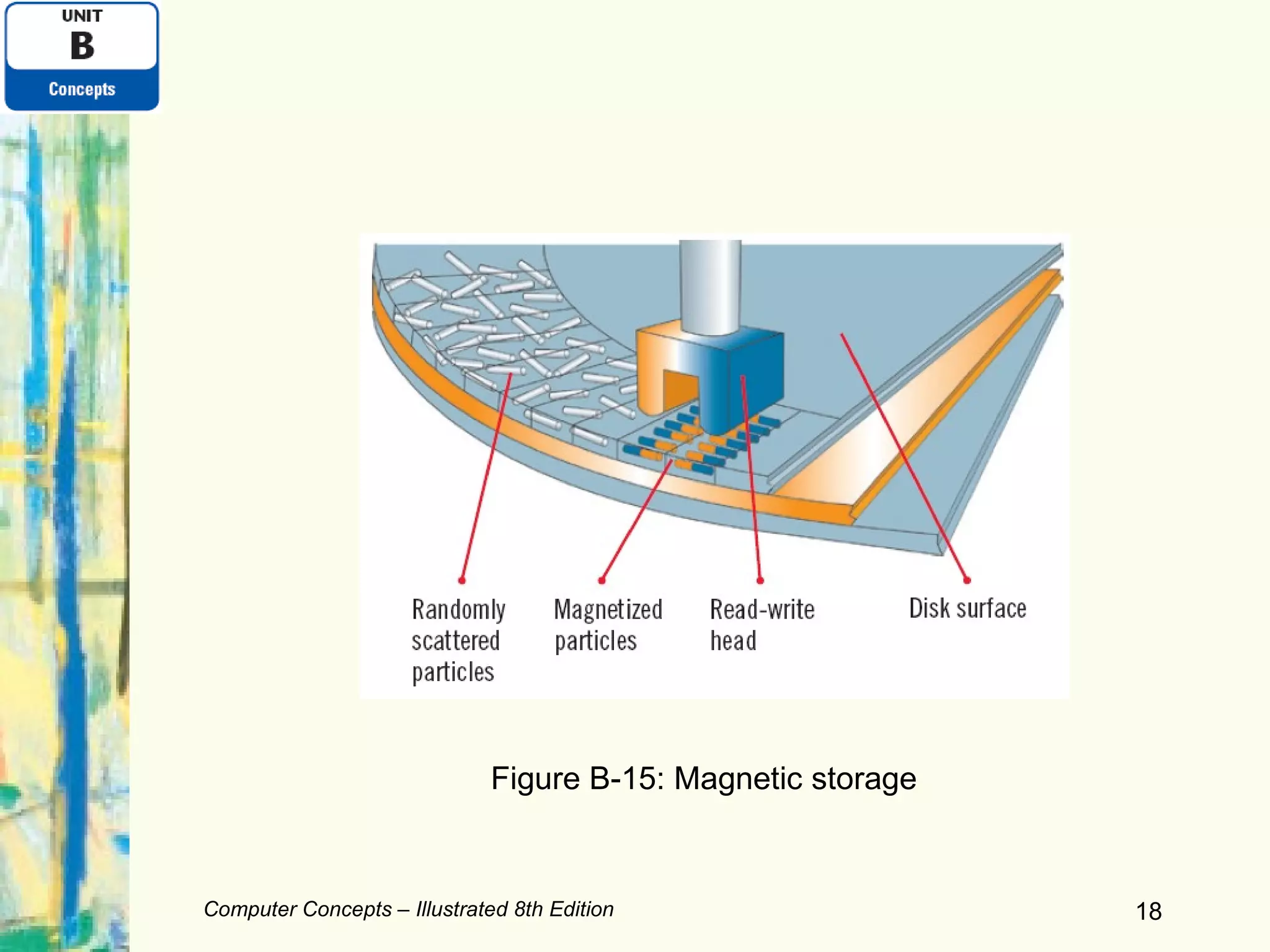
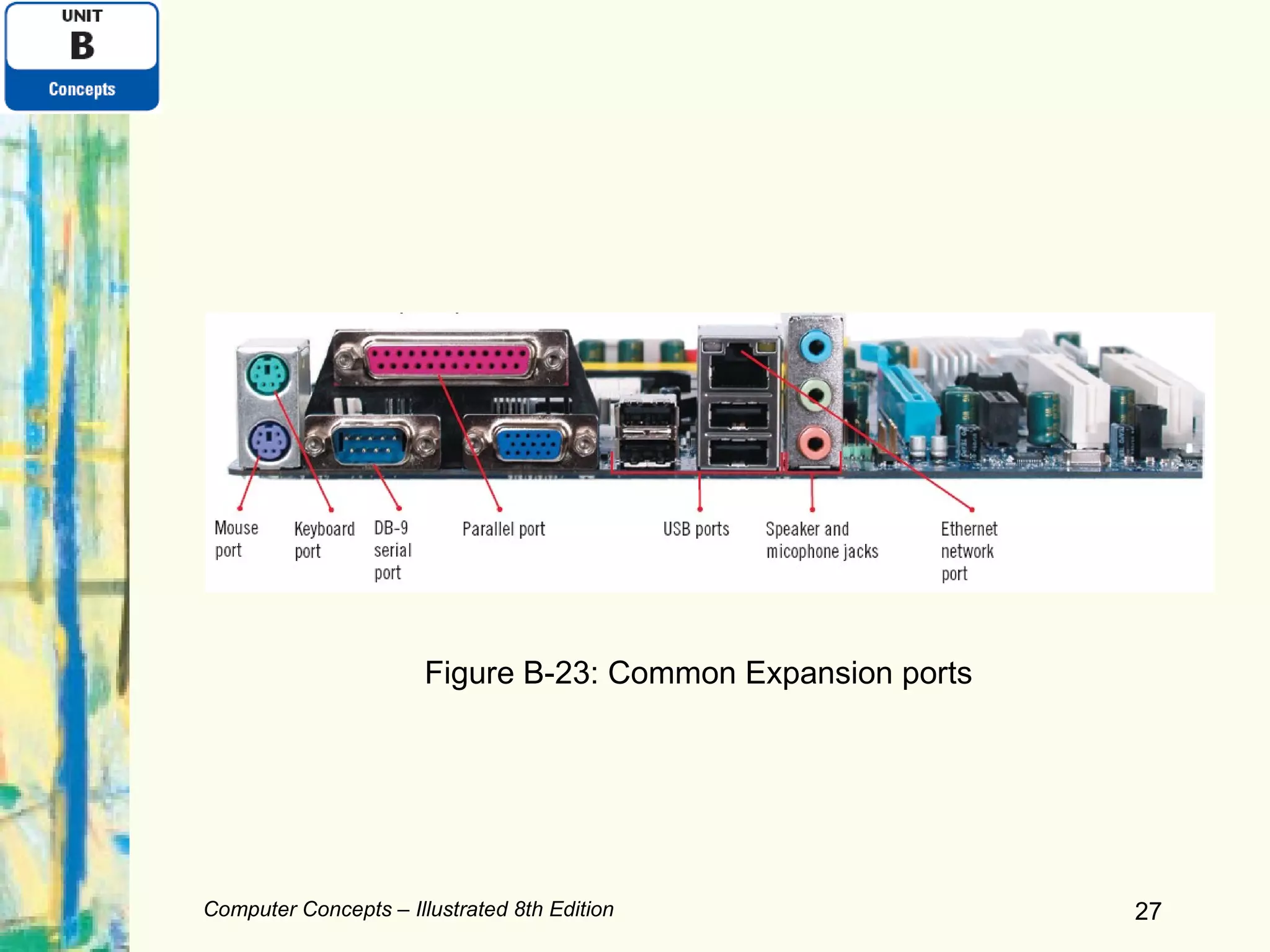
This document discusses computer hardware components including input devices, display devices, printers, and data storage systems. It examines keyboards, mice, monitors, hard drives, solid-state storage, CDs, DVDs, and expansion ports. The document also covers comparing printers and storage types as well as expanding computer systems and recycling electronics.