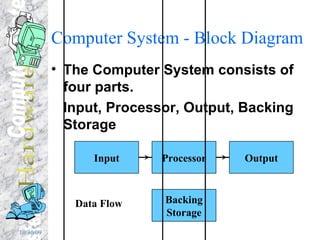
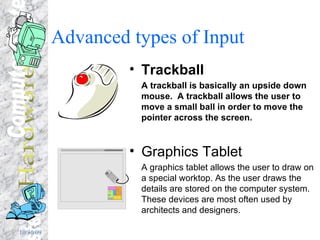
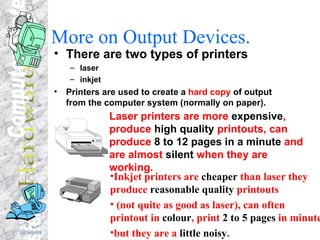
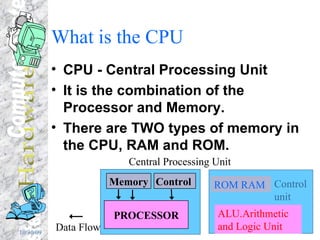
The document discusses various components of a computer system including input devices like voice recognition and handwriting recognition, output devices like printers and monitors, storage devices like hard drives and CD-ROMs, the central processing unit consisting of the processor and memory, and how data like text, numbers, graphics and programs are represented and stored in binary format in the computer's memory.