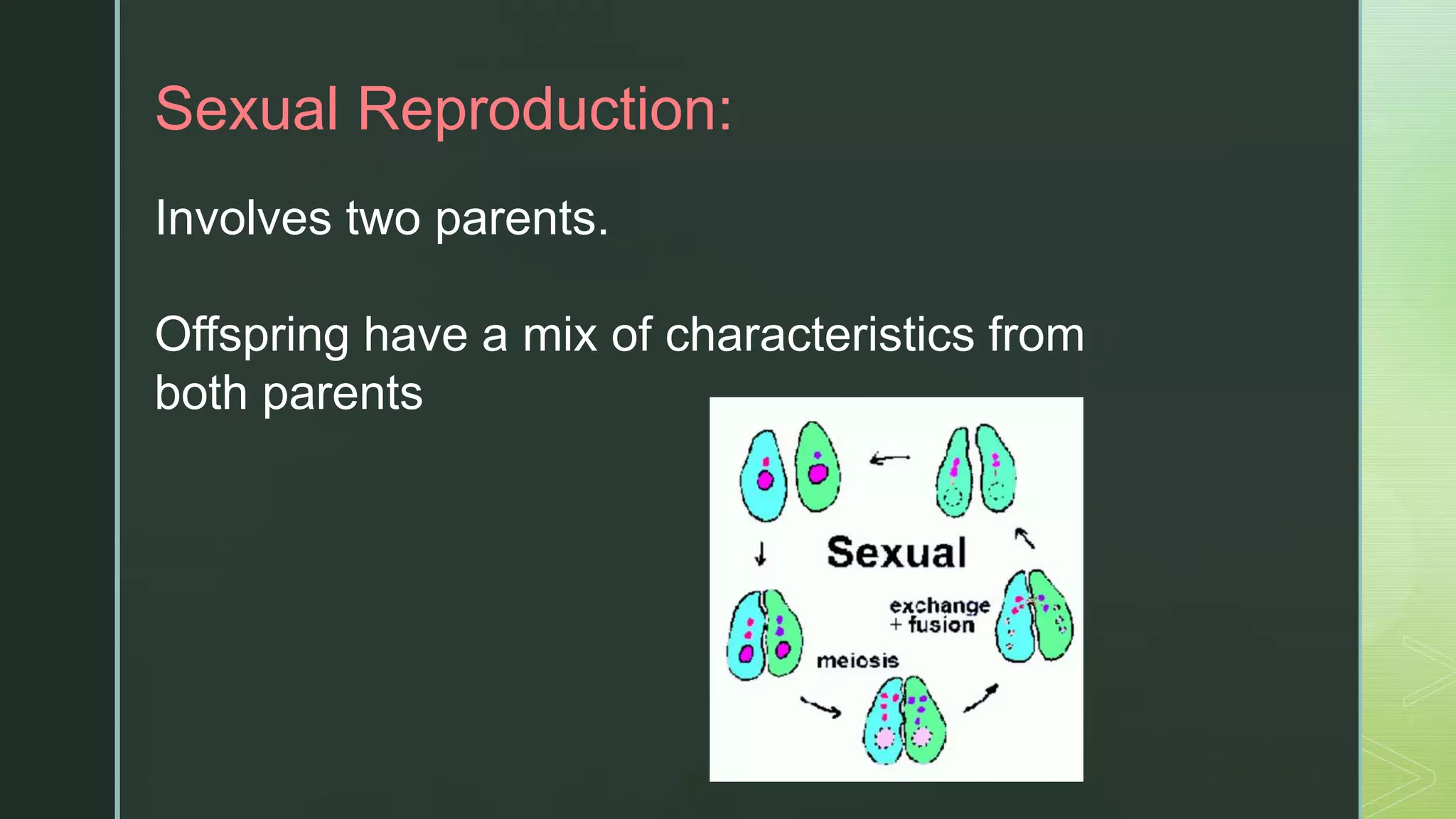
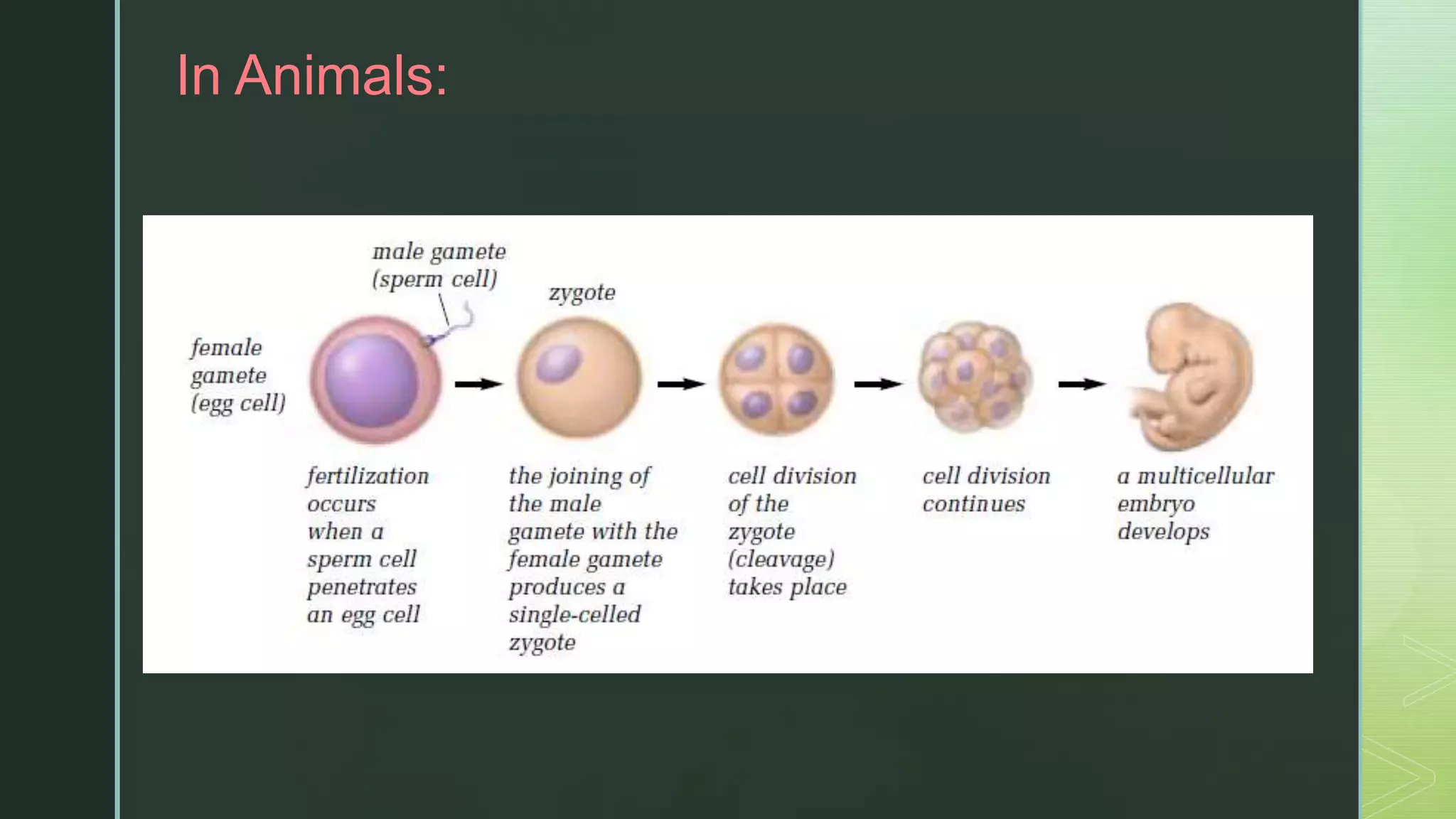
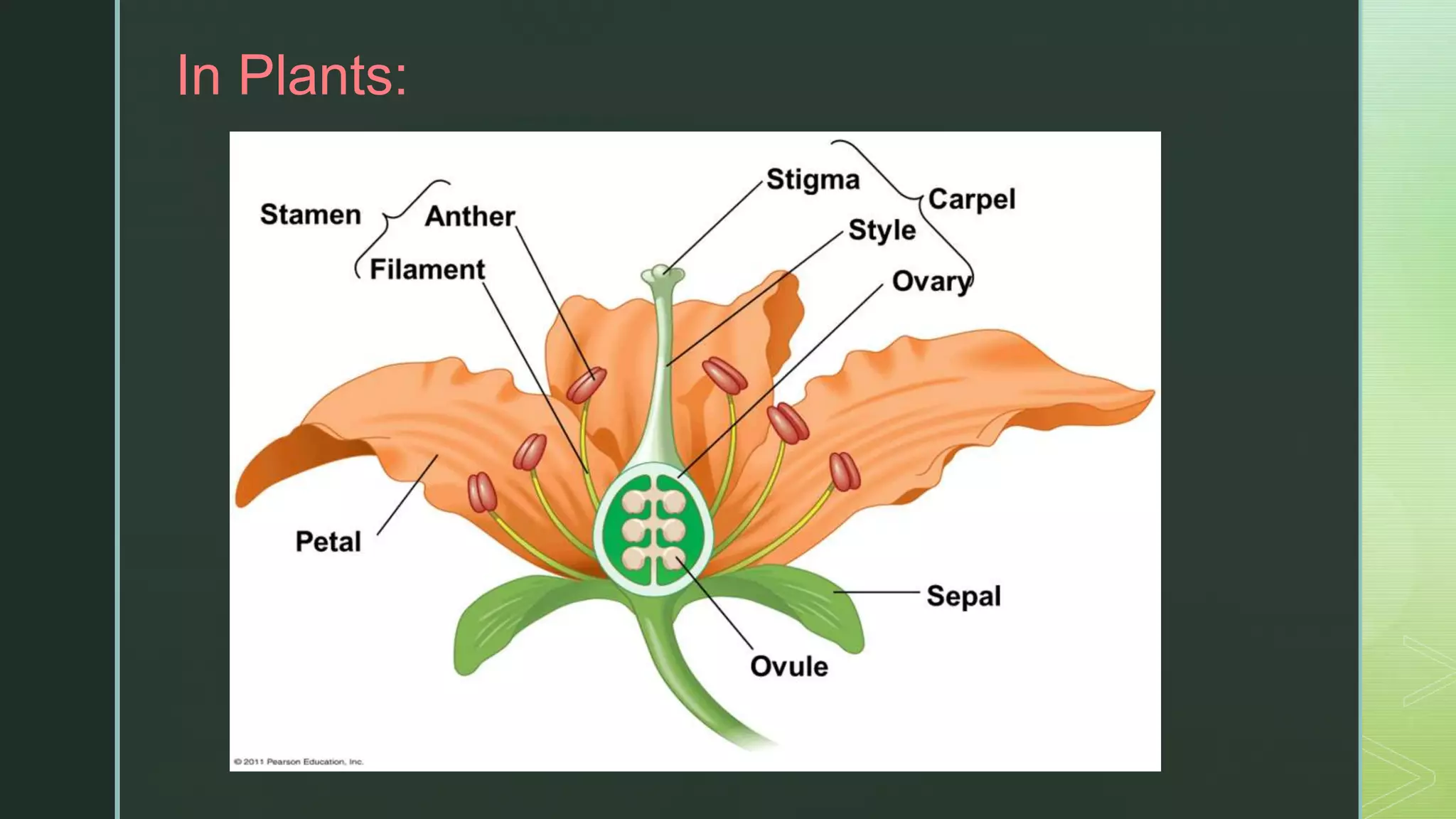
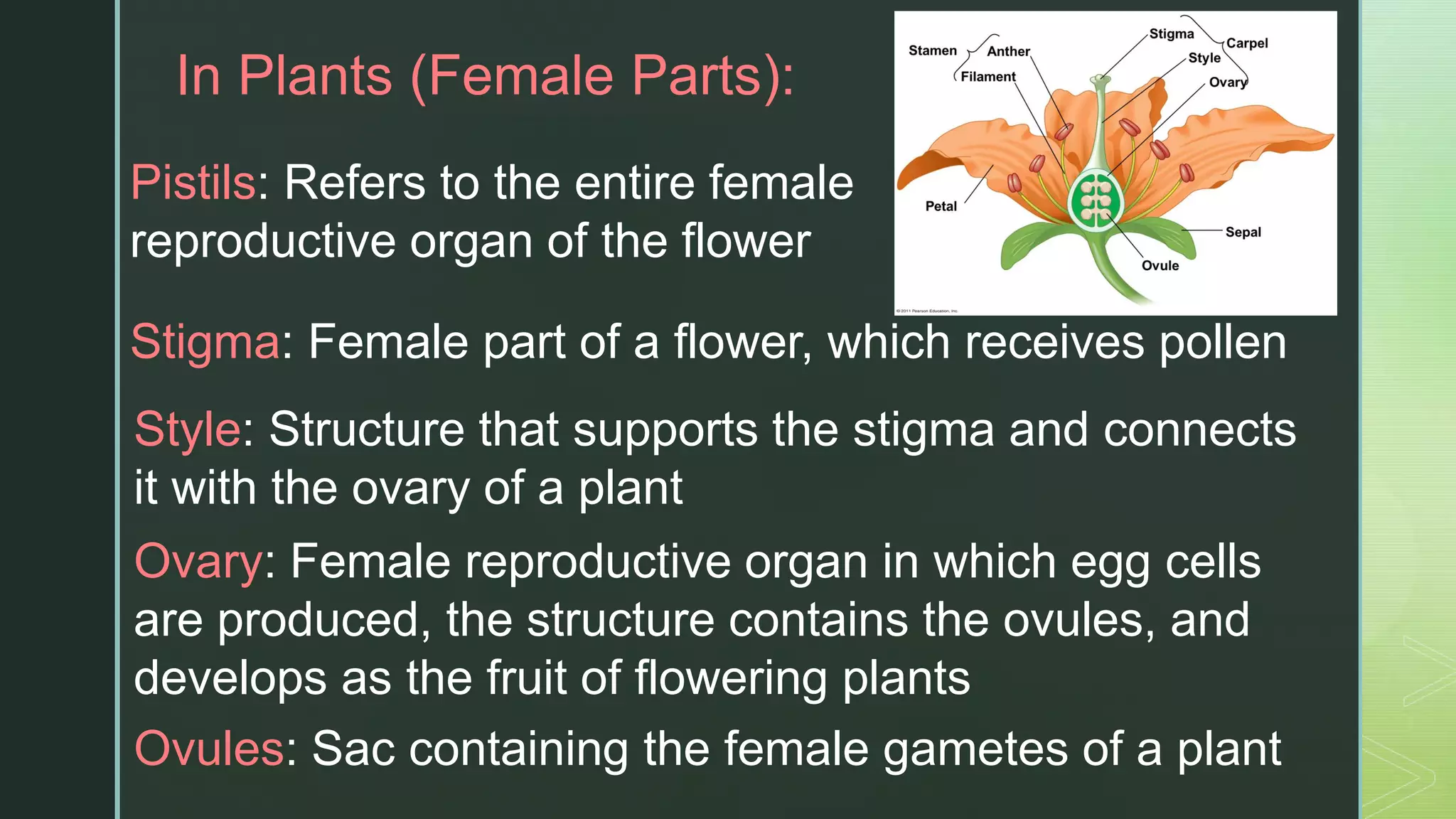
Asexual reproduction involves only one parent and produces offspring that are identical to the parent. There are four main types of asexual reproduction: binary fission, budding, spore production, and vegetative reproduction. Sexual reproduction involves two parents and results in offspring with mixed characteristics. It occurs through the union of male and female gametes - sperm and egg. Both asexual and sexual reproduction have advantages and disadvantages for organism survival and adaptation. Some organisms, like aphids and corals, are capable of both asexual and sexual reproduction.