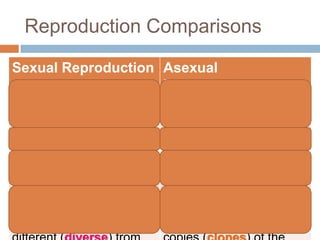
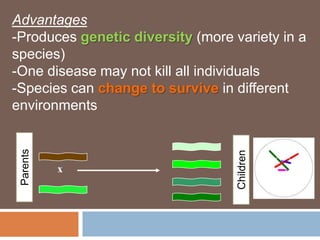
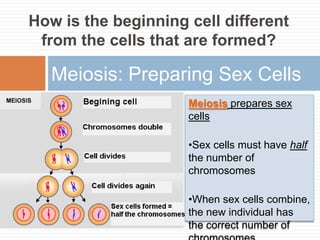
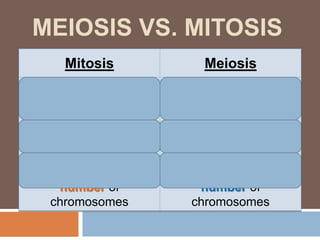
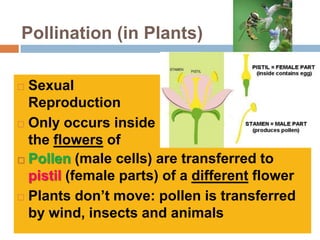
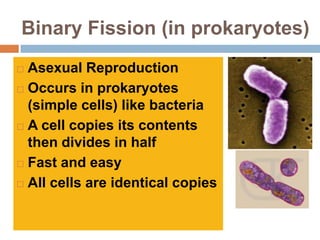
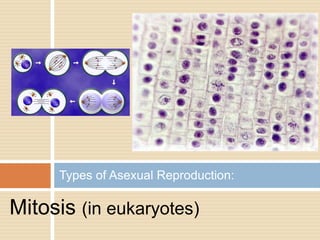
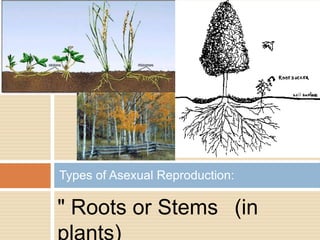
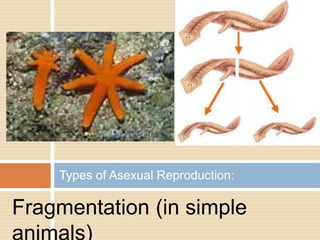
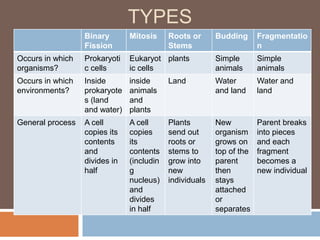
Sexual reproduction produces genetic diversity through the combining of genetic material from two parents, while asexual reproduction requires only one parent and produces offspring identical to the parent. Some key types of reproduction include binary fission in prokaryotes, mitosis in eukaryotes, budding and fragmentation in simple animals, and pollination and fertilization in seed plants. Each method occurs in different organisms and environments.