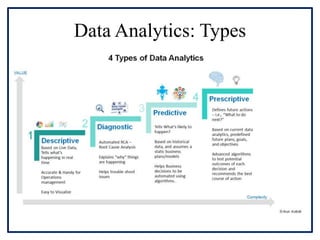
This document provides an overview of recent trends in marketing, including the importance of data analytics, customer relationship marketing, digital marketing, sustainable marketing, rural marketing, and global marketing. It discusses how data analytics is used to make better marketing decisions and analyze customer data. Customer relationship marketing focuses on developing long-term customer relationships through good customer service and communication. Digital and global marketing are growing in popularity due to factors like increased internet access. Sustainable marketing promotes environmentally-friendly products. Rural marketing addresses the specific needs and challenges of marketing to rural communities. The document also introduces incoterms, which are international commercial terms that define responsibilities in transporting goods internationally.




![What kind of data is used by data
analytics?
• Data can be related with:
Production [manufacturing] data
Sales data
Advertisement expenditure data
Customers data
Market data regarding demand etc](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-5-320.jpg)


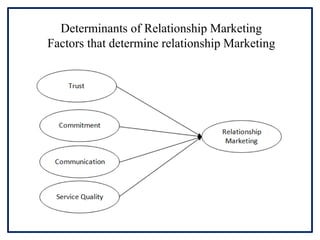
![Customer Relationship
Marketing
[CRM]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-9-320.jpg)





![Reasons for popularity of Digital
Marketing
• The following reasons can be noted:
Increasing Internet penetration
Improvement in mobile phone technology
[smart phones]
Reduction in internet usage prices
Increase in internet data speed
Development in area of E-Commerce](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-16-320.jpg)
![Types of Digital Marketing
• The following types can be noted:
Website marketing [SEO]
Search Engine Marketing [Google Ads]
Mobile Marketing through ‘Apps’
Social Media Marketing through various
platforms [Facebook, Instagram etc]
Video Marketing [YouTube]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-17-320.jpg)
![Advantages of Digital Marketing
• The following advantages can be noted:
Wider customer reach than traditional
marketing
Relatively low cost
Can be managed easily
Fetches high returns on investment [ROI]
Becoming highly popular among the
consumers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-18-320.jpg)









![Rural Consumer: Characteristics
Characteristics of rural customers [in
comparison to urban consumers]
Low education level
Low income level
Less brand awareness
Limited product choices
Rigidity in traditions and customs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-28-320.jpg)


![Rural Marketing: Rural Marts
Setting up of Rural marts by NABARD
[left] and Reliance Foundation [above]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-31-320.jpg)




![Global Marketing: Entry Strategies
• The popular methods of entry into Global
markets are:
Exporting
Licensing
Franchising
Joint Venture
Foreign Direct Investment [FDI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-36-320.jpg)
![Global Marketing: Entry Strategies
Exporting – in this method the product is made
in the home country and exported to foreign
countries e.g. manufactured goods like shoes
Licensing – in this method, license [or permit]
is given to foreign companies to manufacture
products e.g. in case of medicines
Franchising – it is an agreement between the
franchisor and a franchisee for operating
business as per the terms of the franchisor e.g.
McDonalds operates restaurants on this model.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-37-320.jpg)
![Global Marketing: Entry Strategies
Joint Venture: In this method a company
collaborates with a foreign company to enter
into a joint venture to manufacture goods and
services. E.g. Honda of Japan and Hero motors
of India had a joint venture ‘Hero Honda’
Foreign Direct Investment [FDI] – in this
method, a company starts its business in a
foreign country from the scratch – setting up
factory, hiring people, manufacturing and
selling product etc. It is a costly method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-38-320.jpg)
![Incoterms [2020]
[International Commercial Terms]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit8part2recenttrendsinmarketing-210416150323/85/Unit-8-part_2_recent_trends_in_marketing-39-320.jpg)



