The document provides an overview of marketing research, defining it as a systematic search for information that connects an organization with its market to identify opportunities and solve problems. It outlines various types of marketing research, objectives, and the research process, which includes defining problems, literature review, hypothesis formulation, research design, data collection, and analysis. The text also emphasizes the importance of research design in ensuring efficient and structured research outcomes.



![What is a ‘Marketing Research’?
• Marketing research is the function that links an
organization to its market through the gathering of
information. This information allows for the
identification and definition of market-driven
opportunities and problems. The information
allows for the generation, refinement and
evaluation of marketing actions. It allows for the
monitoring of marketing performance and
improved understanding of marketing as a
business process. [American Marketing
Association]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introductiontomarketingresearch-copy-210511101801/85/Unit-1-introduction_to_marketing_research-copy-4-320.jpg)
![What are the Objectives of Marketing
Research?
• To find out the feasibility of new products and
services in the marketing [customer needs]
• To find out customers’ attitude regarding a
product of service [+ve or -ve]
• To find out the impact of a promotional campaign
on the sales of the product
• To gather customer feedback regarding a product
or service and use the information for taking
marketing decisions
• To find out the effectiveness of an advertisements
campaign](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introductiontomarketingresearch-copy-210511101801/85/Unit-1-introduction_to_marketing_research-copy-5-320.jpg)




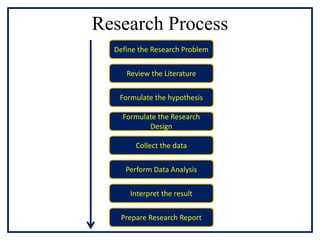

![The Research Process [Contd.]
Formulation of hypothesis: after doing the review
of the literature, a working hypothesis should be
formed, it is an assumption which has to be tested
using appropriate statistical test. The hypothesis
must be very specific and limited. [exploratory
studies do not need hypothesis]
Formulating Research Design: It is the structure
within which the research has to be conducted.
Research design makes the research more
efficient. It includes – information sources,
sample design, statistical methods that will be
used, time and cost available for research etc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introductiontomarketingresearch-copy-210511101801/85/Unit-1-introduction_to_marketing_research-copy-12-320.jpg)
![The Research Process [Contd.]
Collection of the data: data can be primary
[first hand] or secondary [published or used
data]. Depending upon several factors, a
researcher has to decide what type of data is
needed and how it must be collected.
Analysis of the data: it involves coding,
editing, tabulation, doing descriptive analysis
or applying various statistical procedures for
hypothesis testing [formulated earlier].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introductiontomarketingresearch-copy-210511101801/85/Unit-1-introduction_to_marketing_research-copy-13-320.jpg)
![The Research Process [Contd.]
Interpretation of the results: data analysis or
hypothesis testing often yields some results.
The results are generally in numerical terms.
These results have to be correctly interpreted.
Preparation of research report: Finally the
researcher has to prepare a report of the work
done by him. The report has to be prepared in
a definite format. It has three parts – the
preliminary part, main part and the conclusion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introductiontomarketingresearch-copy-210511101801/85/Unit-1-introduction_to_marketing_research-copy-14-320.jpg)

![The Research Design [Contd.]
• Research Design answers the following questions:
What is the research about?
Why is the research being made?
Where will the research be carried out?
What type of data is required for research?
What time & cost will the research take?
What sampling technique will be used in the
research?
How will the data be collected?
How will the data be analyzed?
In which format will report be prepared?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1introductiontomarketingresearch-copy-210511101801/85/Unit-1-introduction_to_marketing_research-copy-16-320.jpg)