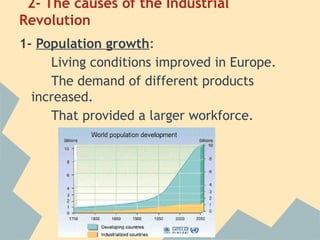
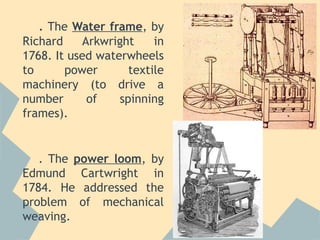
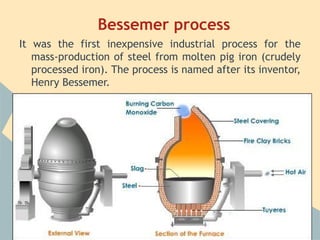
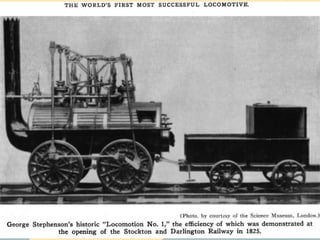
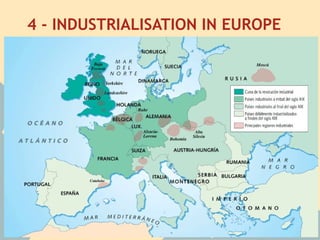
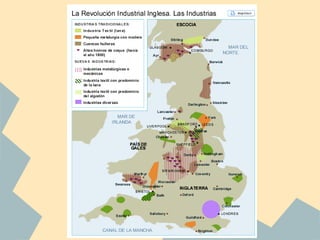
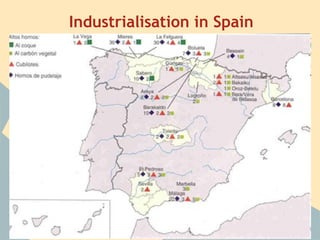
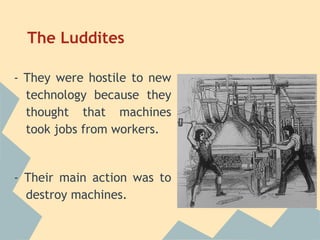
The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain and spread across Europe, transforming economies from agriculture-based to industrialized. New technologies like the steam engine powered factories where workers labored under difficult conditions. This led to the rise of organized labor movements seeking better treatment. Art styles also changed to reflect industrial and working class themes, like Realism highlighting everyday lives. Overall, the period marked massive social, economic and technological changes in Europe.