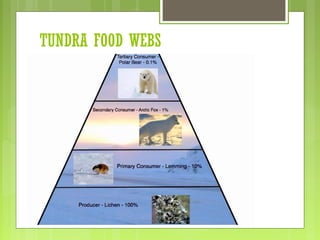
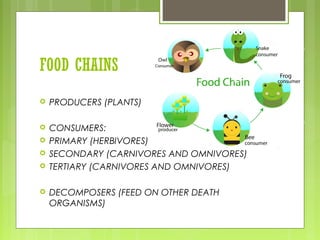
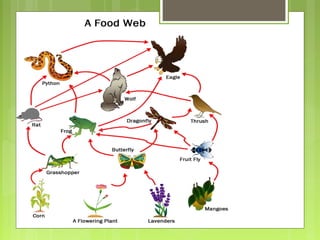
This document discusses different ecosystems and their components. It defines tropical rainforests as one of the most diverse ecosystems, containing emergent, canopy, understory and forest floor layers. Tundra ecosystems are described as having low temperatures, permafrost and short summer seasons. They are home to lichens, mosses, arctic willows and foxes. The document also explains that ecosystems are made up of biotic and abiotic elements like climate and populations. Food chains and webs show how species interact and transfer energy between trophic levels as producers, primary consumers, and decomposers.