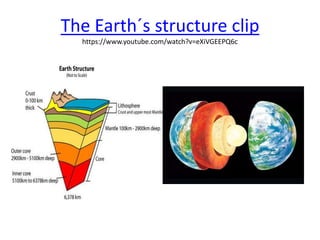
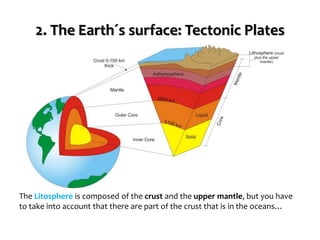
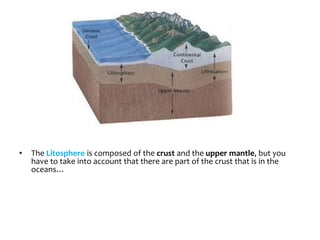
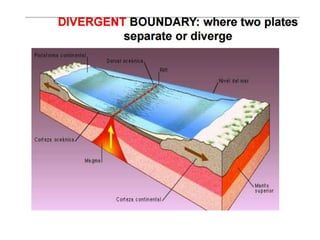
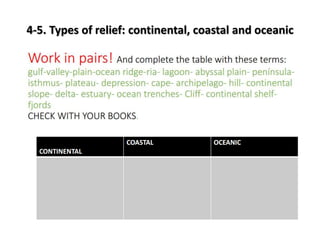
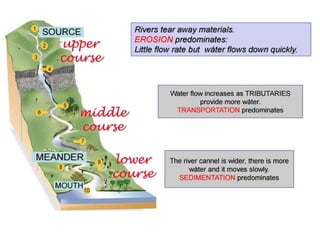
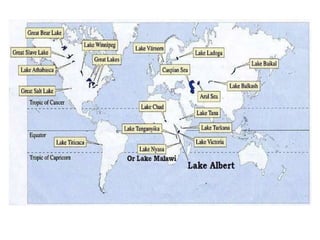
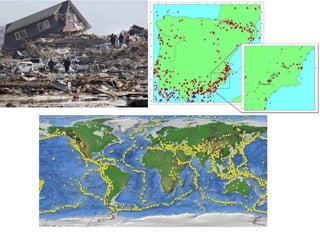
This document provides an overview of key topics related to earth's relief and water systems. It discusses the earth's structure, tectonic plates, changes in relief from internal and external forces, different types of land relief including continental, coastal and oceanic, rivers, lakes, glaciers, groundwater, and natural hazards like volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. Key terms are defined throughout and a vocabulary list is provided at the end to help students prepare for an exam on this material.