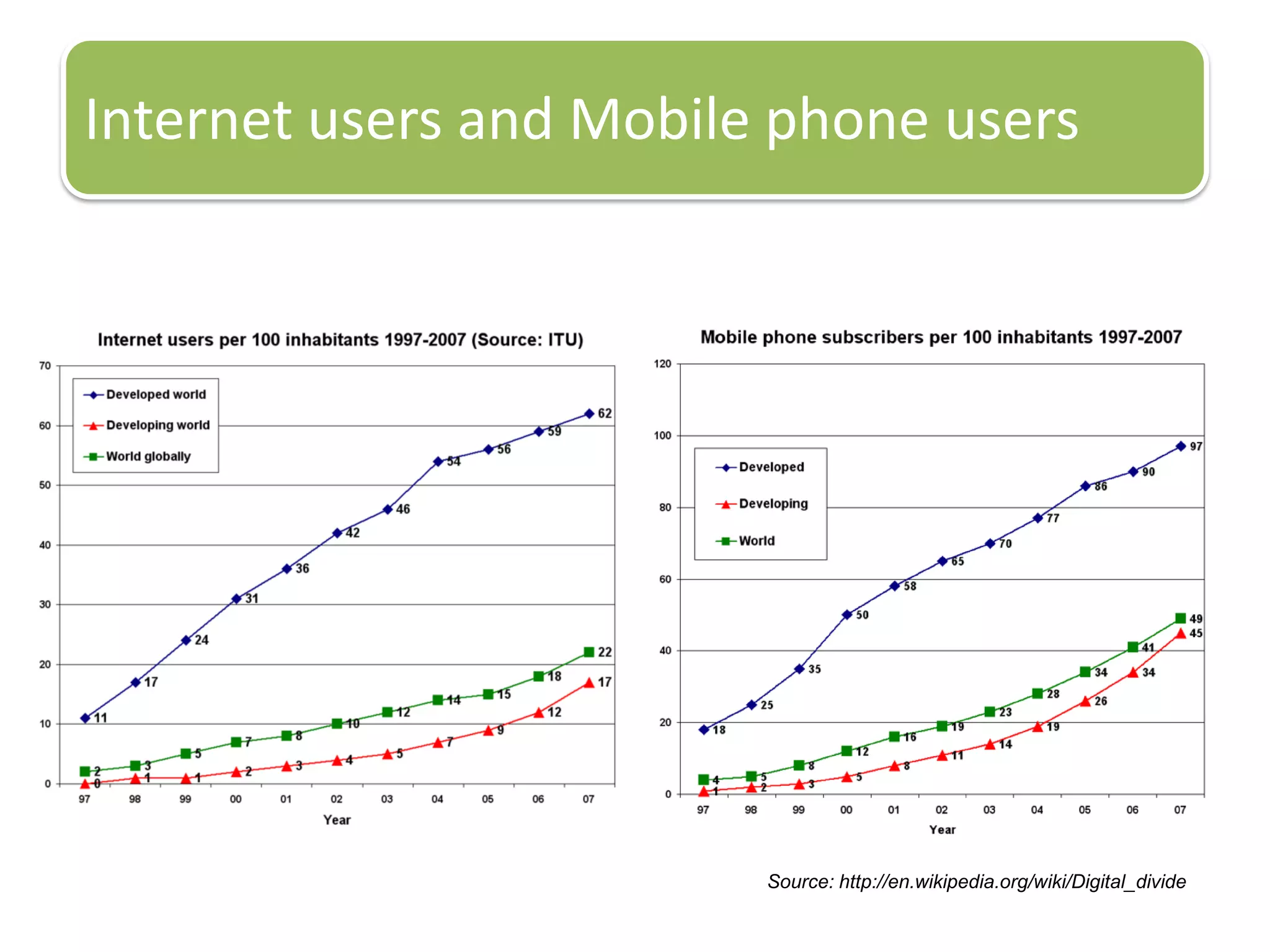
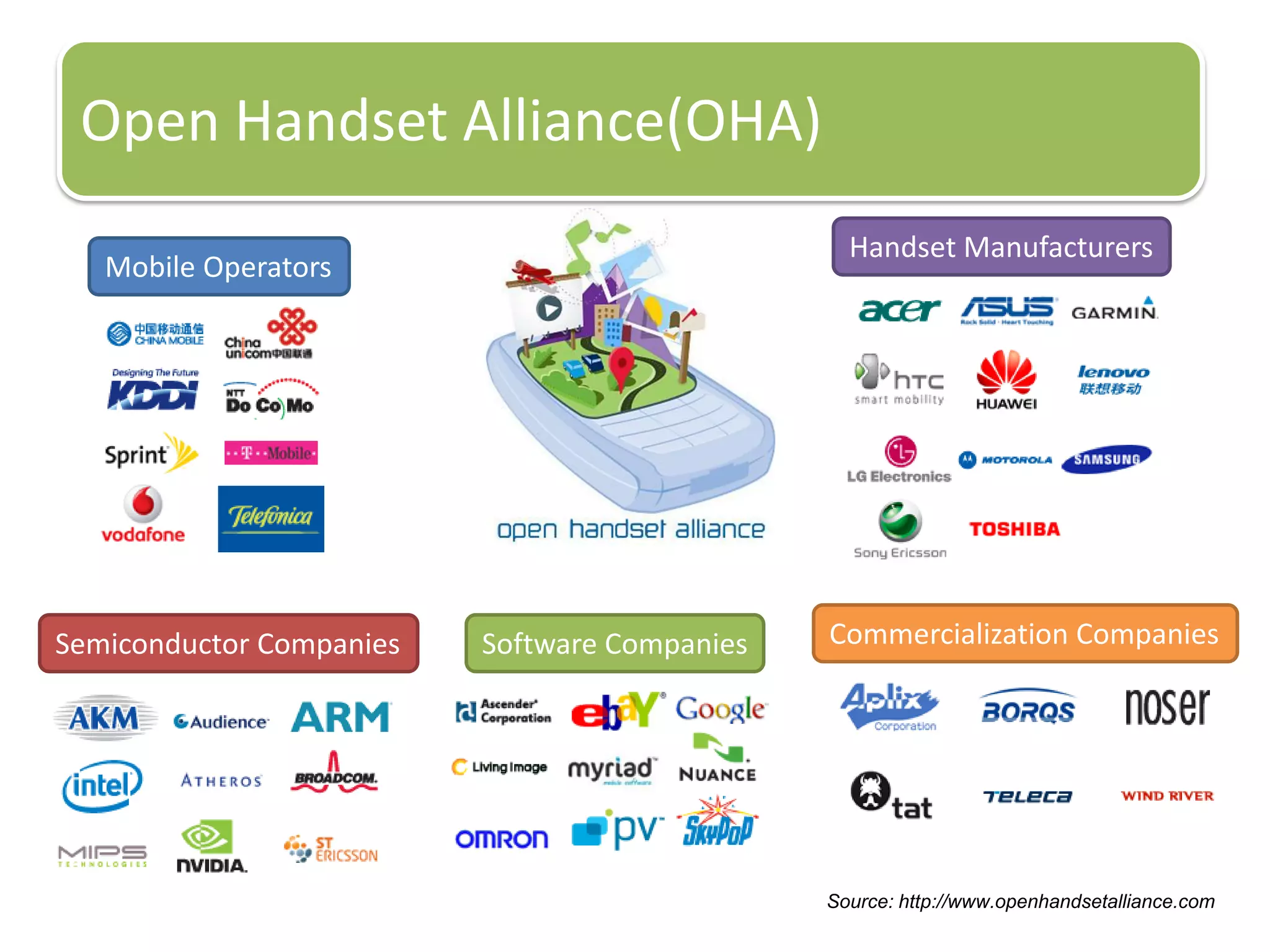
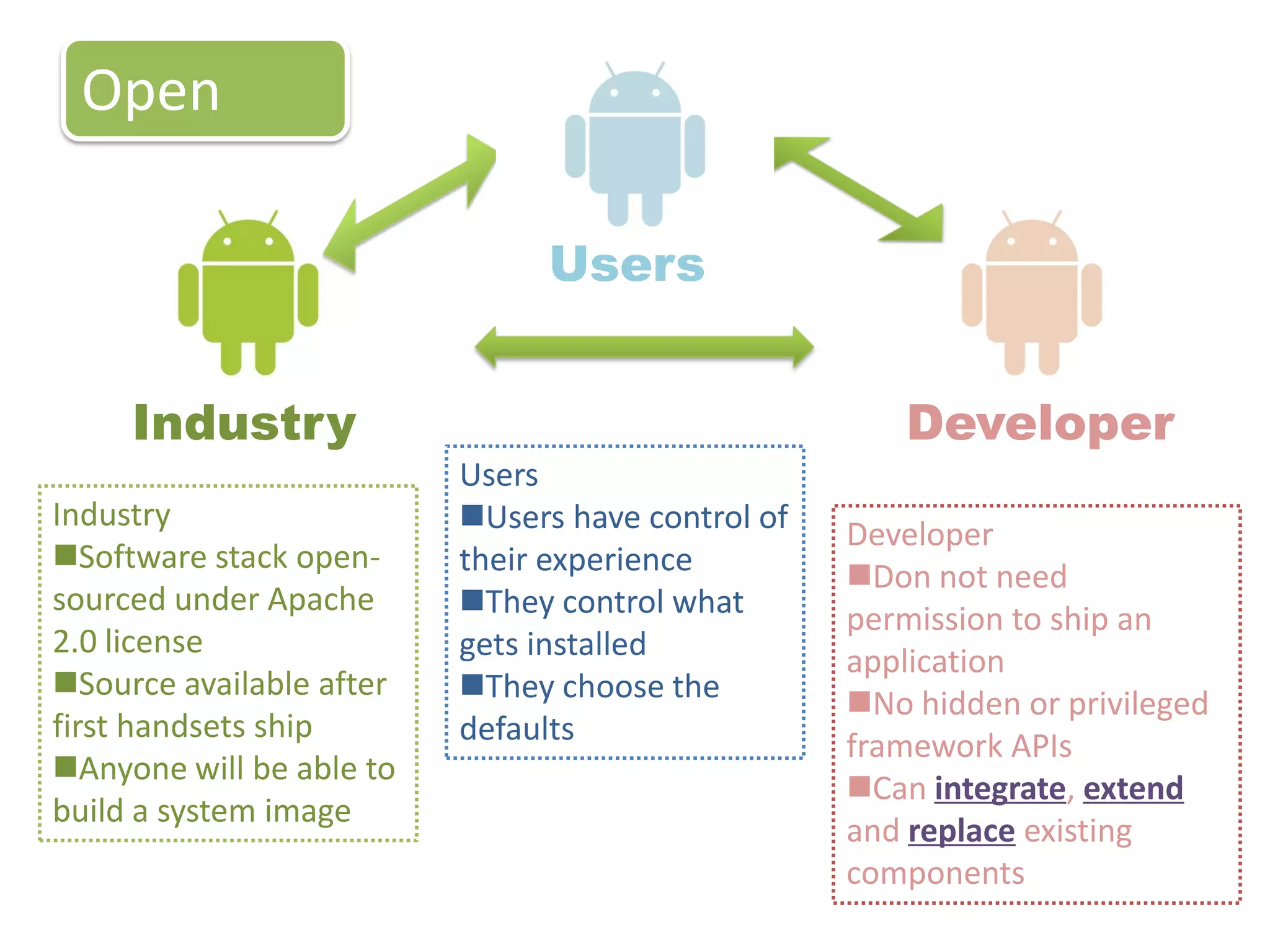
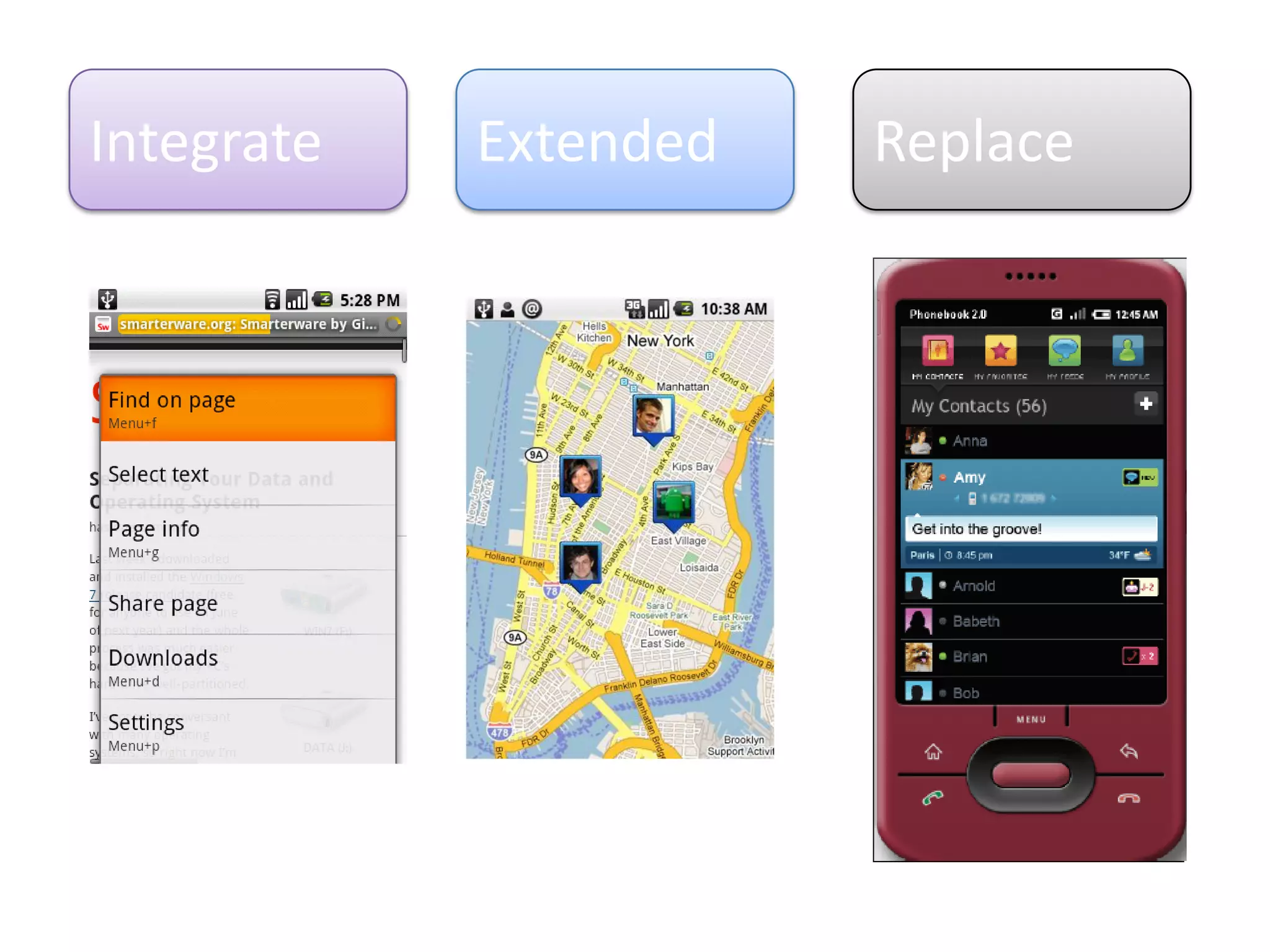
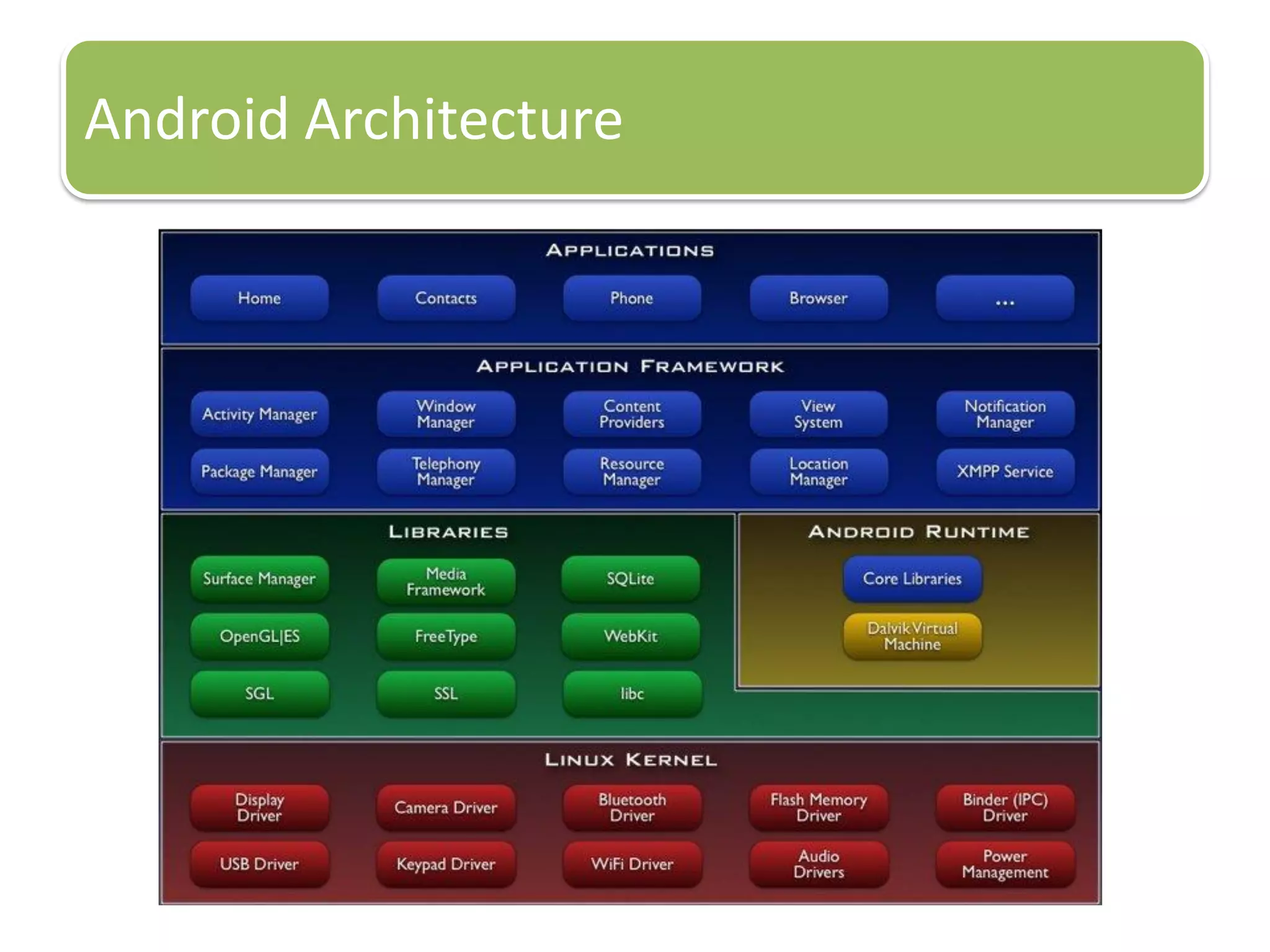
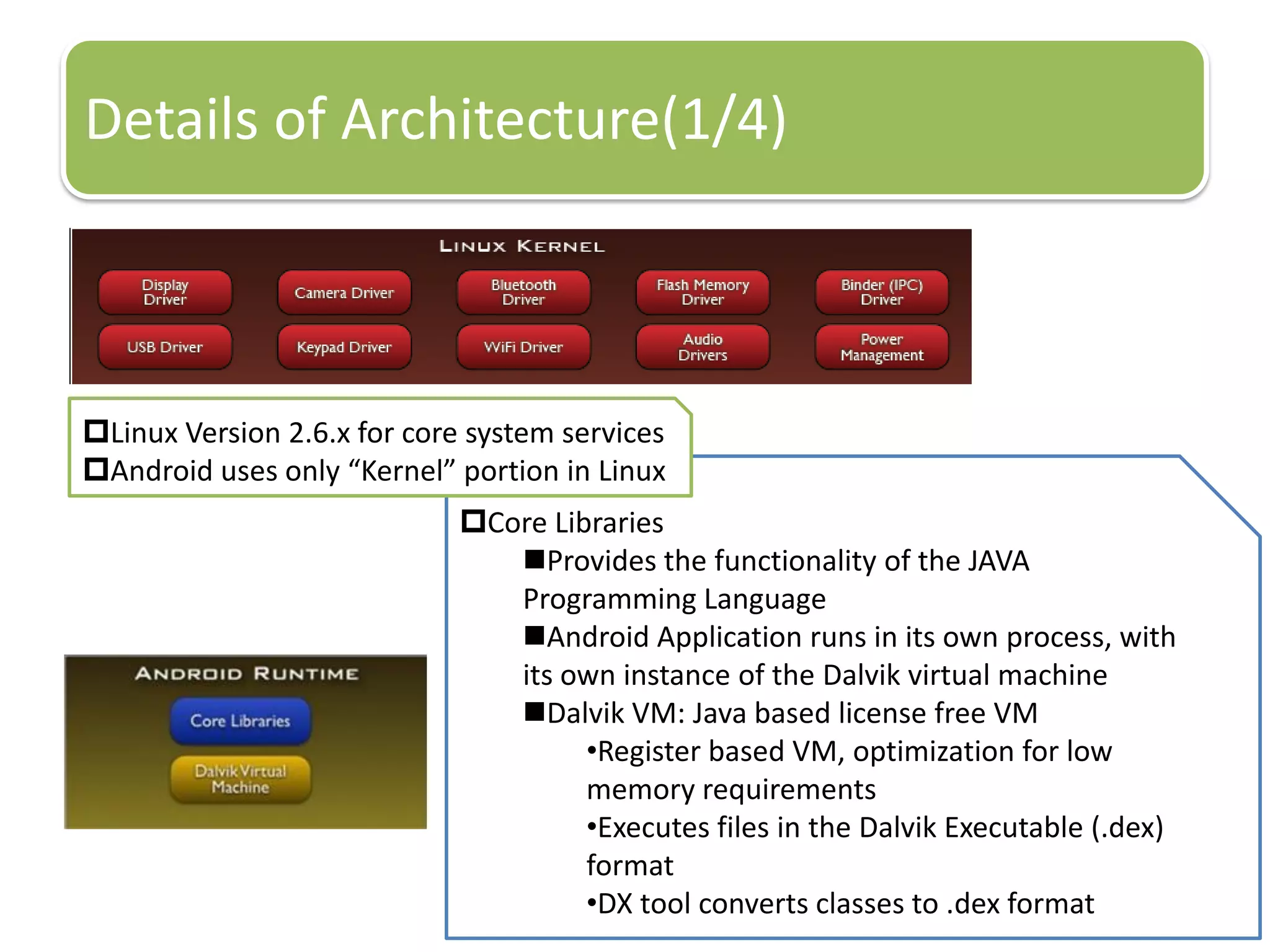
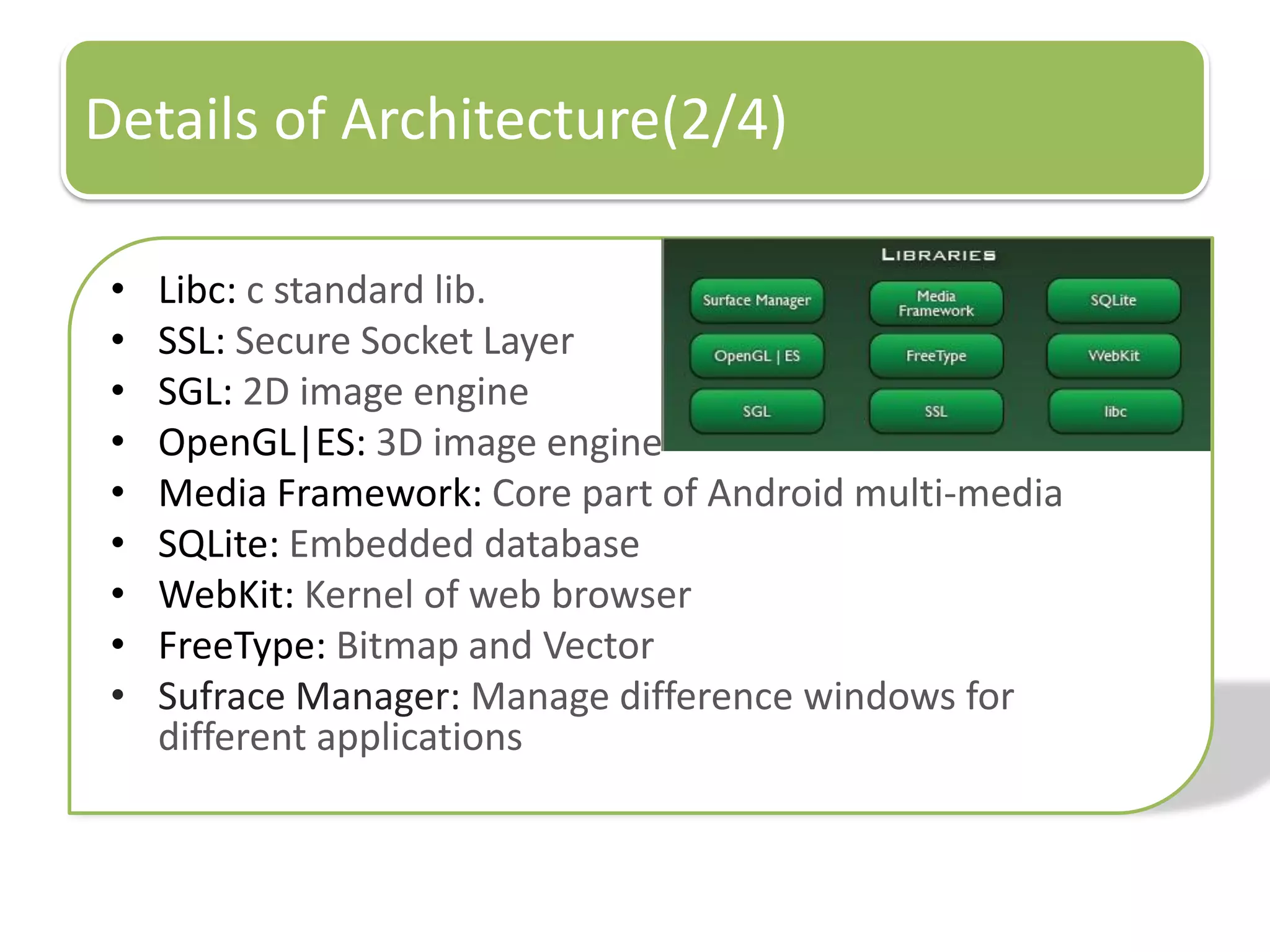
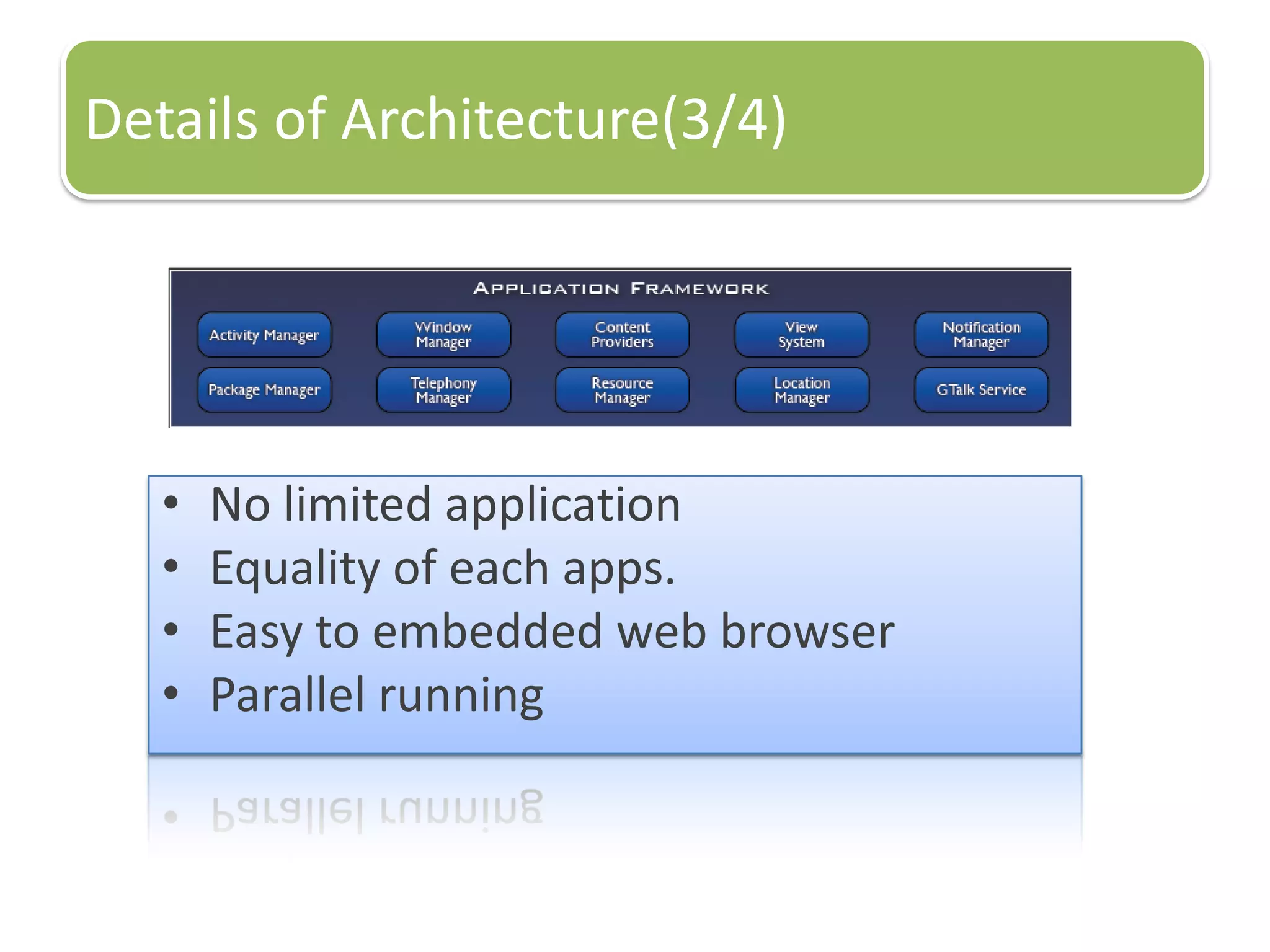
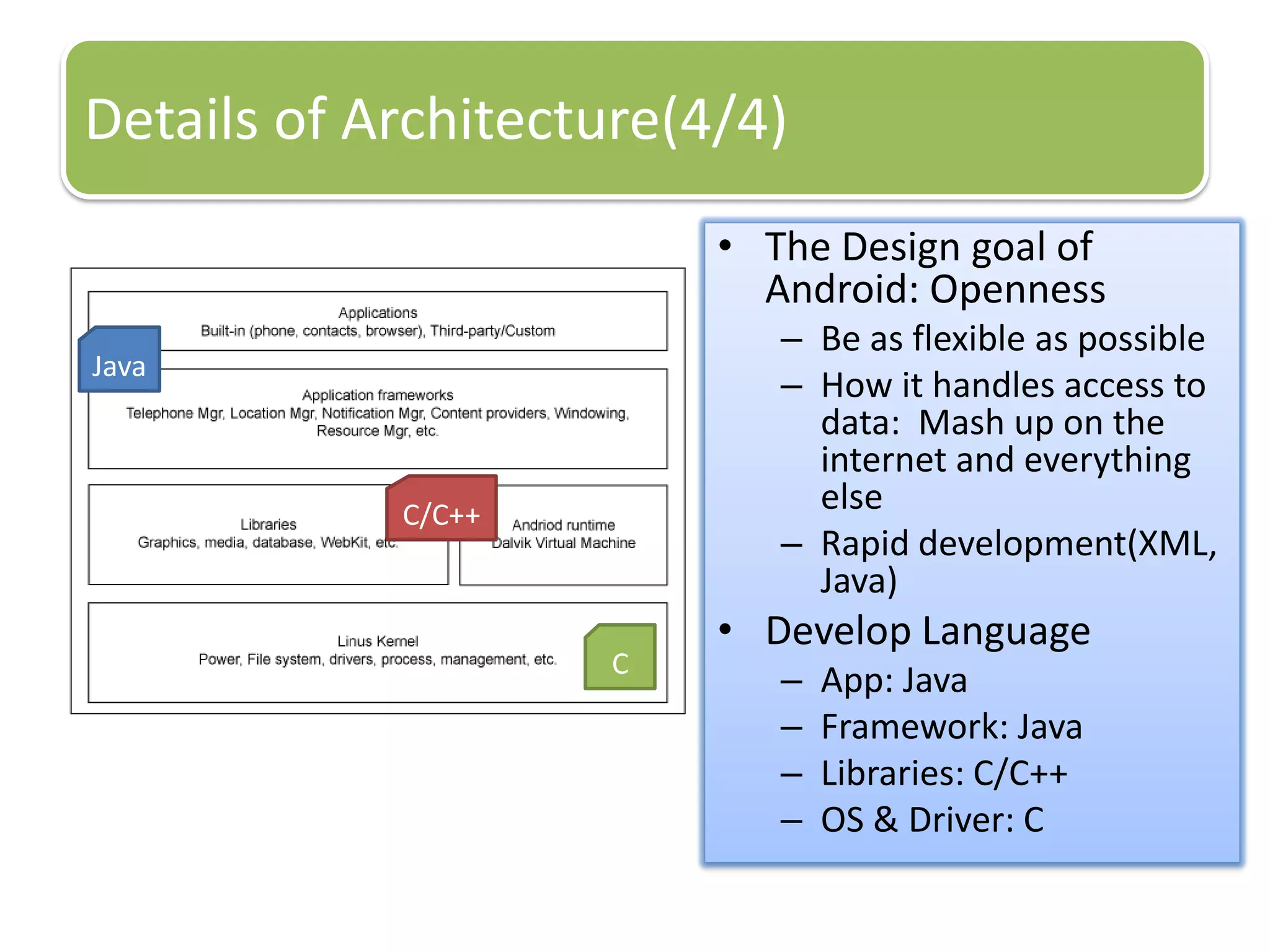
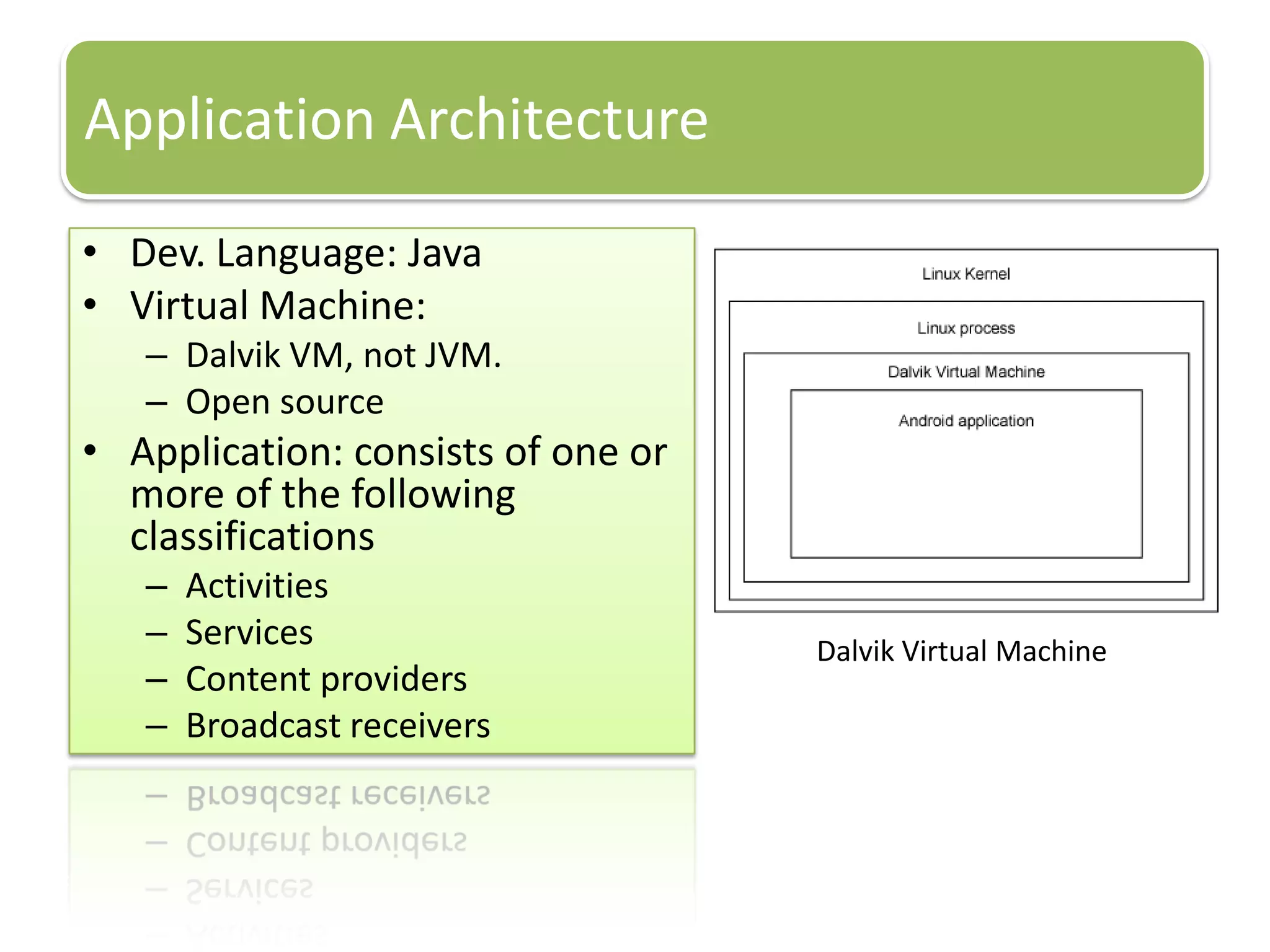
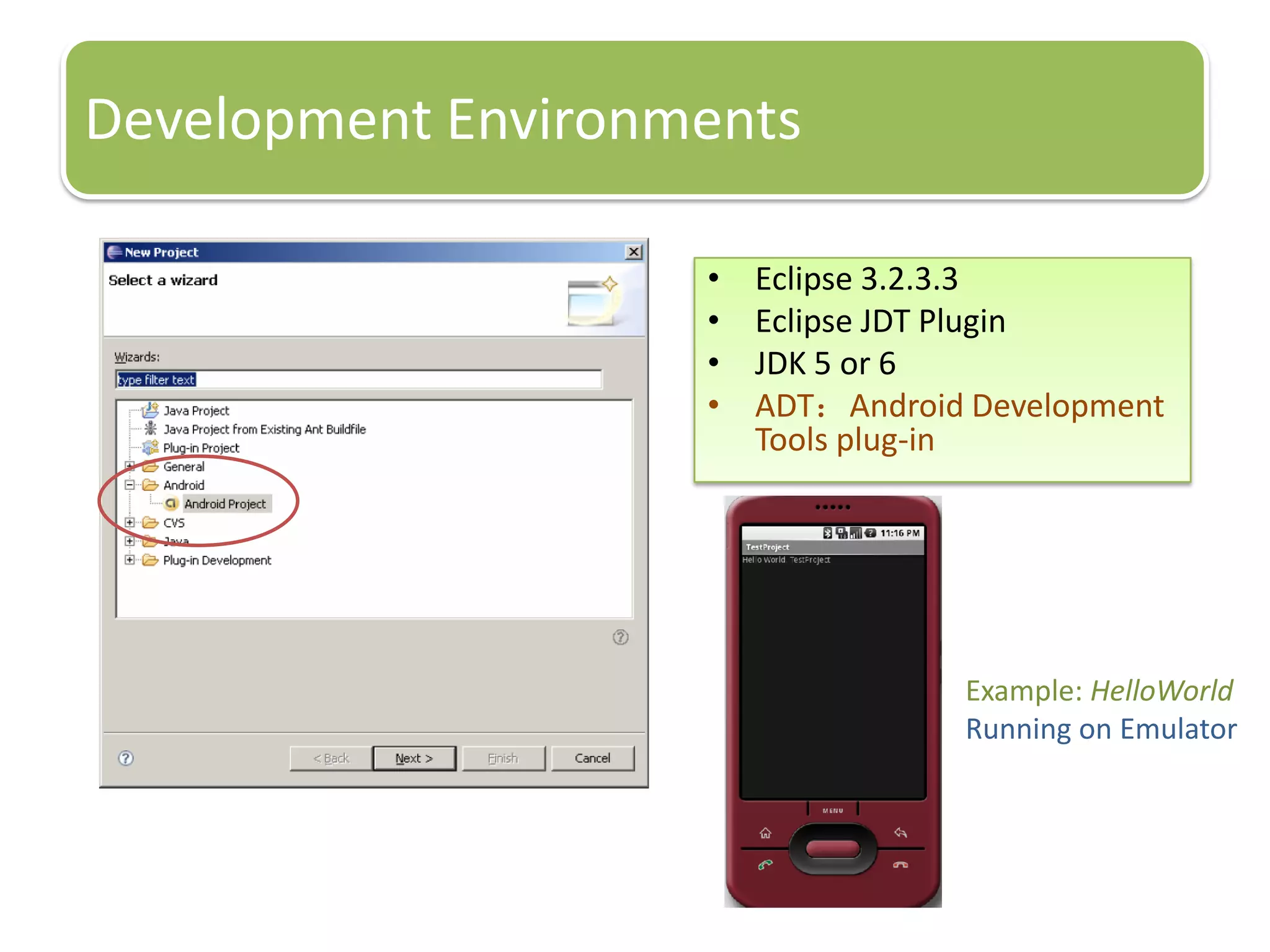
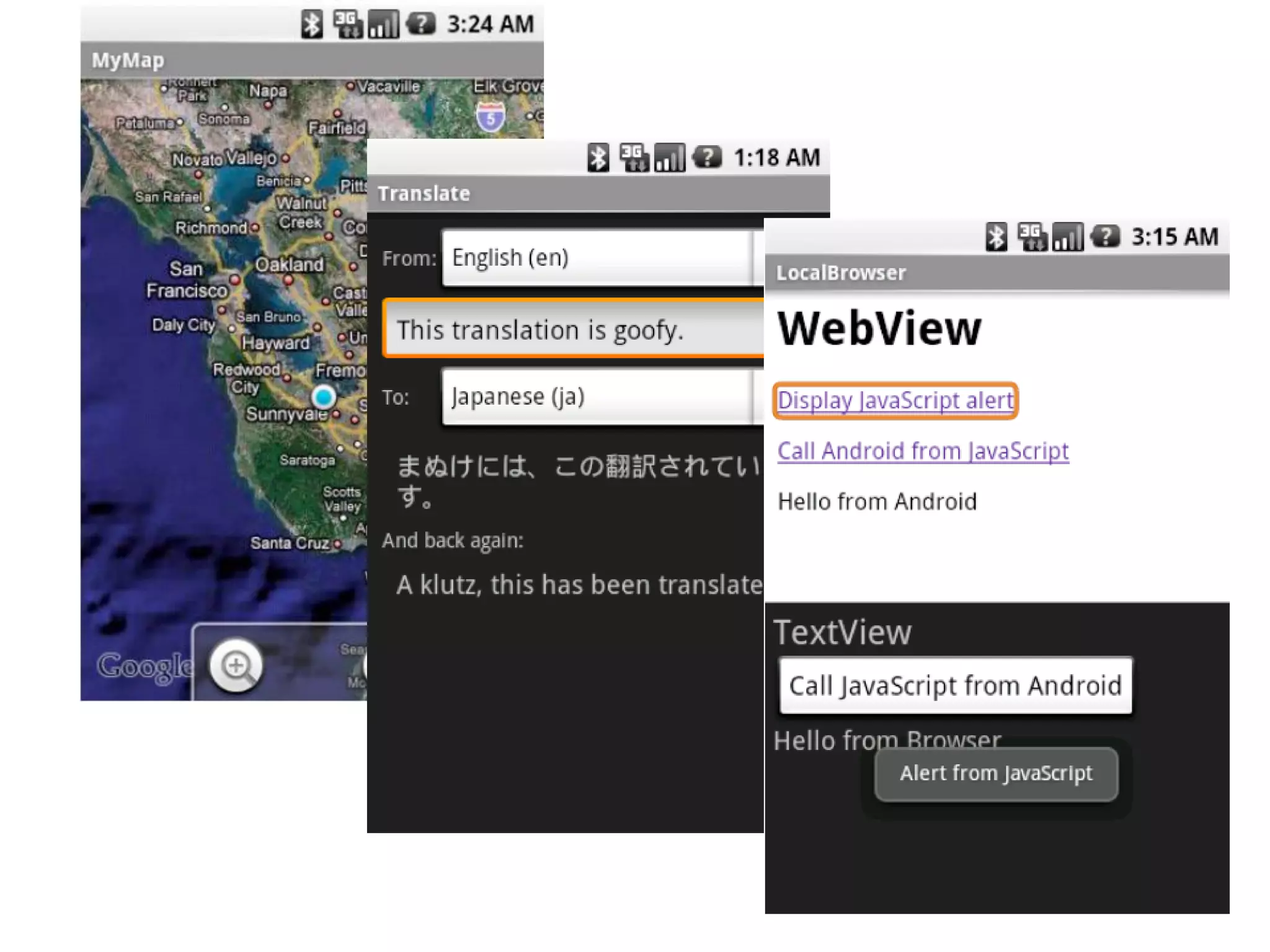
The document provides an introduction to the Android operating system. It discusses that Android is an open-source software stack for mobile devices created by the Open Handset Alliance. The architecture of Android includes components like the Linux kernel, middleware, and key applications. Developers can create Android applications using Java and tools provided in the Android SDK.