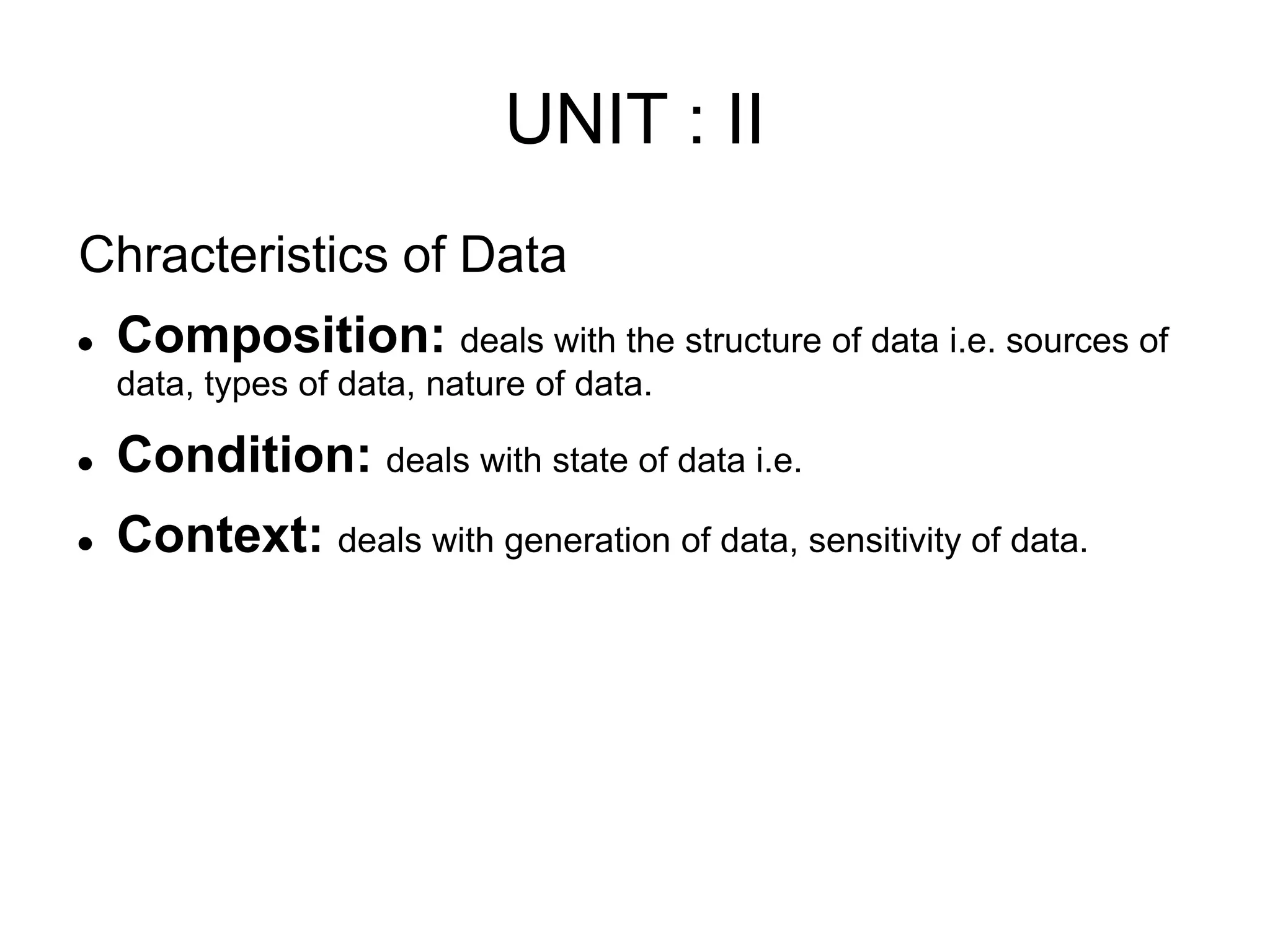
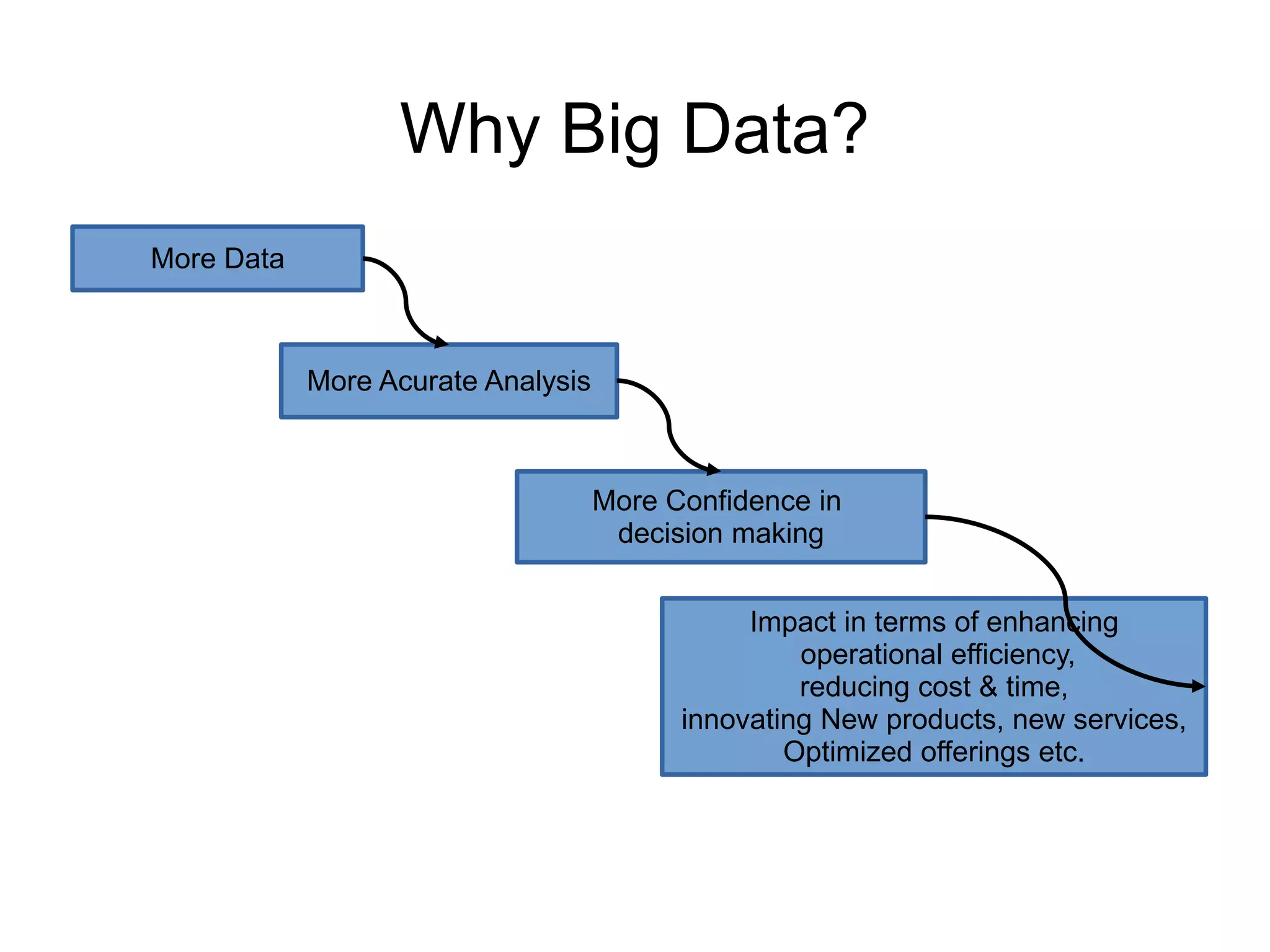
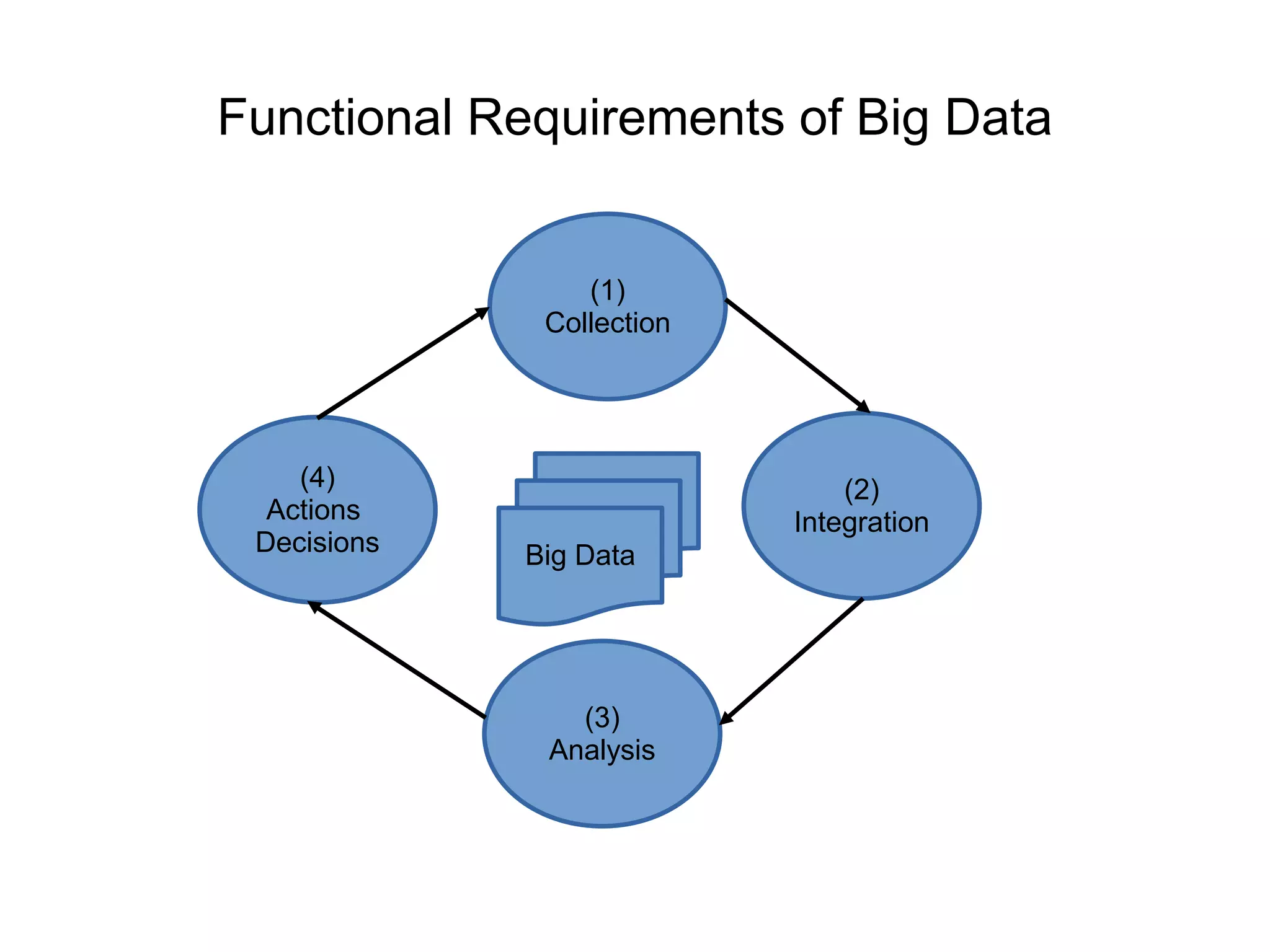
This document discusses characteristics of big data and the big data stack. It describes the evolution of data from the 1970s to today's large volumes of structured, unstructured and multimedia data. Big data is defined as data that is too large and complex for traditional data processing systems to handle. The document then outlines the challenges of big data and characteristics such as volume, velocity and variety. It also discusses the typical data warehouse environment and Hadoop environment. The five layers of the big data stack are then described including the redundant physical infrastructure, security infrastructure, operational databases, organizing data services and tools, and analytical data warehouses.