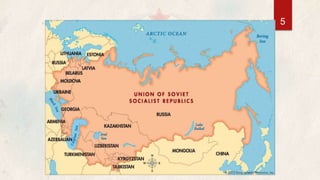
The USSR was a socialist state that existed from 1922 to 1991, comprising 15 Soviet republics. It was established following the Russian Revolution and adopted a centrally planned economy and one-party rule under the Communist Party. In the late 1980s, Mikhail Gorbachev introduced policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) that contributed to nationalist movements in the republics seeking independence. This led to the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, with Russia and 14 other republics becoming independent states.