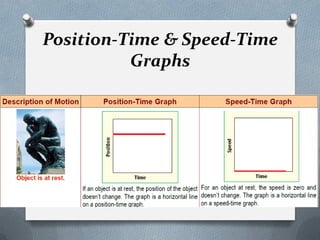
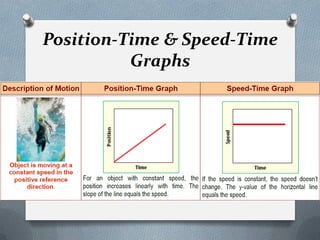
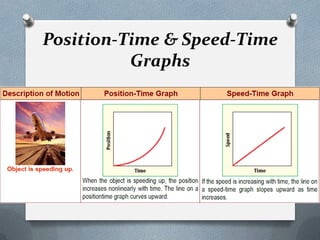
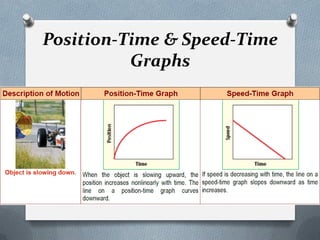
This document defines and explains key concepts related to motion and forces, including:
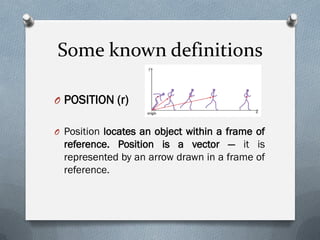
- Position locates an object within a frame of reference and is represented by a vector.
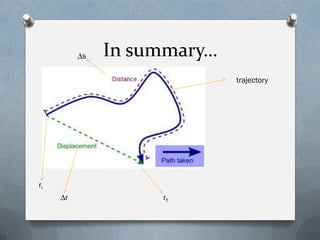
- Trajectory marks the position of an object over time within a reference frame and forms the path or line that connects each position.
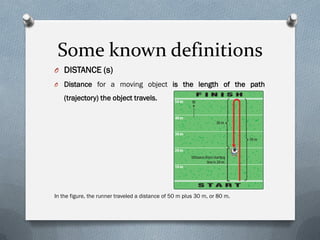
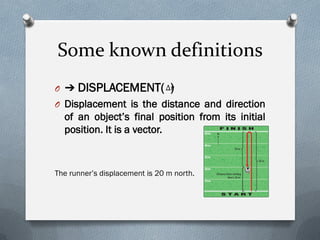
- Distance is the total length of the path or trajectory traveled by an object. Displacement is the distance and direction between an object's initial and final positions and is also represented by a vector.
- Speed describes how fast an object is moving and is calculated as the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance. In the International System of units, speed is measured in meters per second