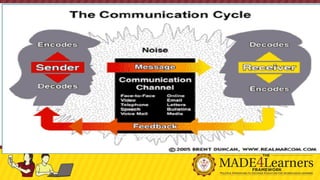
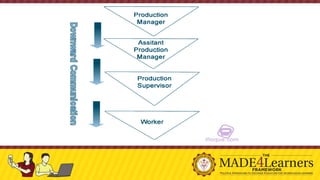
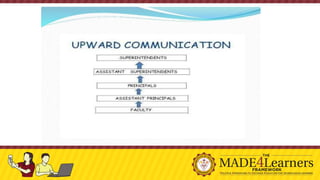
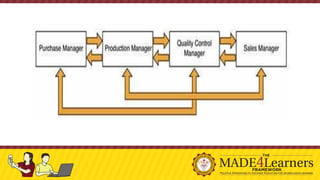
This document discusses communication in professional organizations. It defines communication and outlines its key characteristics, including that it involves a minimum of two people and is a two-way process. The document then describes the communication process, including the sender, message, encoding, channel, receiver, decoding, and feedback. It discusses different types of communication like verbal, nonverbal, and written. The document also examines formal and informal communication channels within organizations and how information flows vertically and horizontally through the organizational structure. It emphasizes the importance of professional communication for unity, professionalism, productivity, and peace/harmony within an organization.