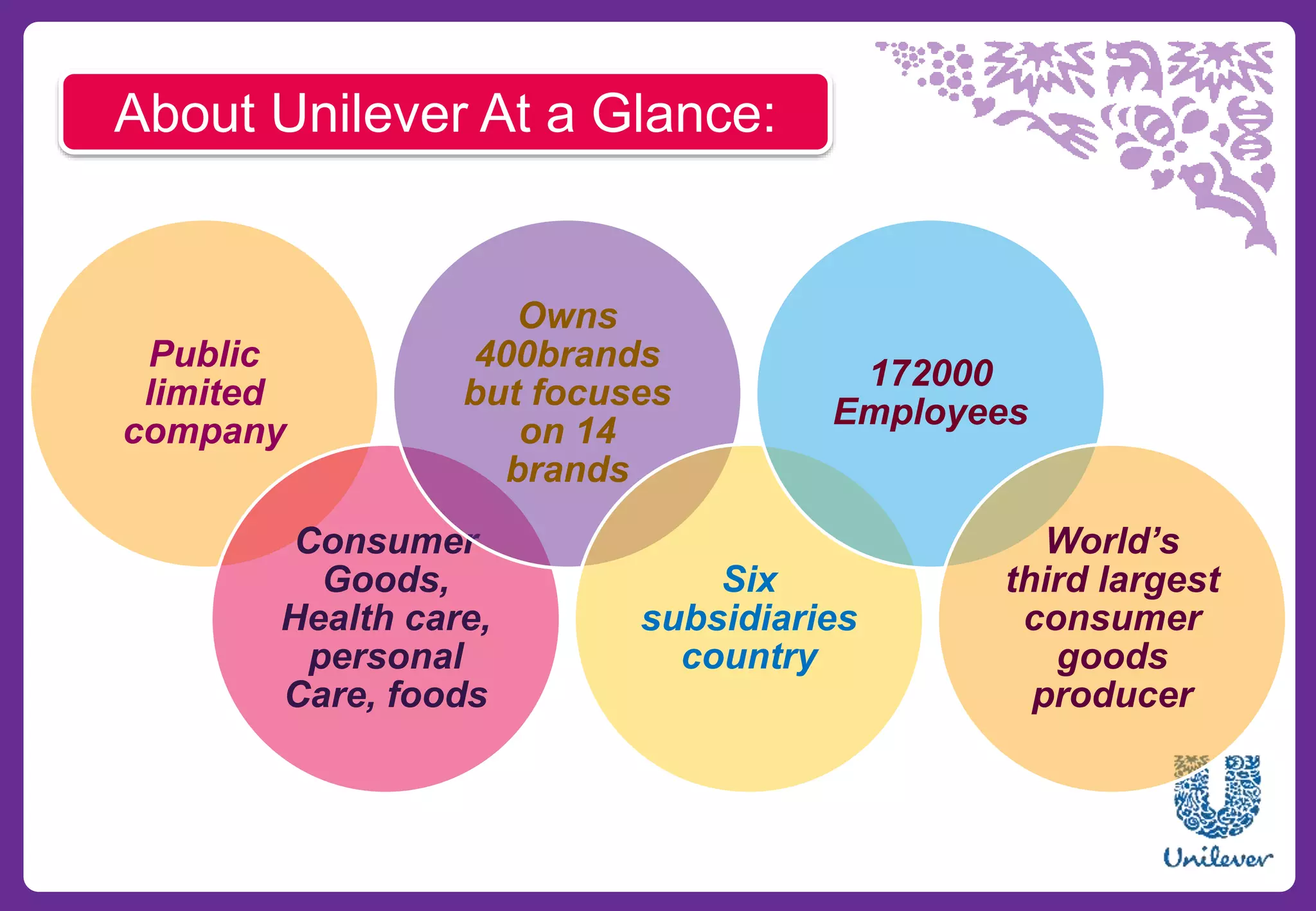
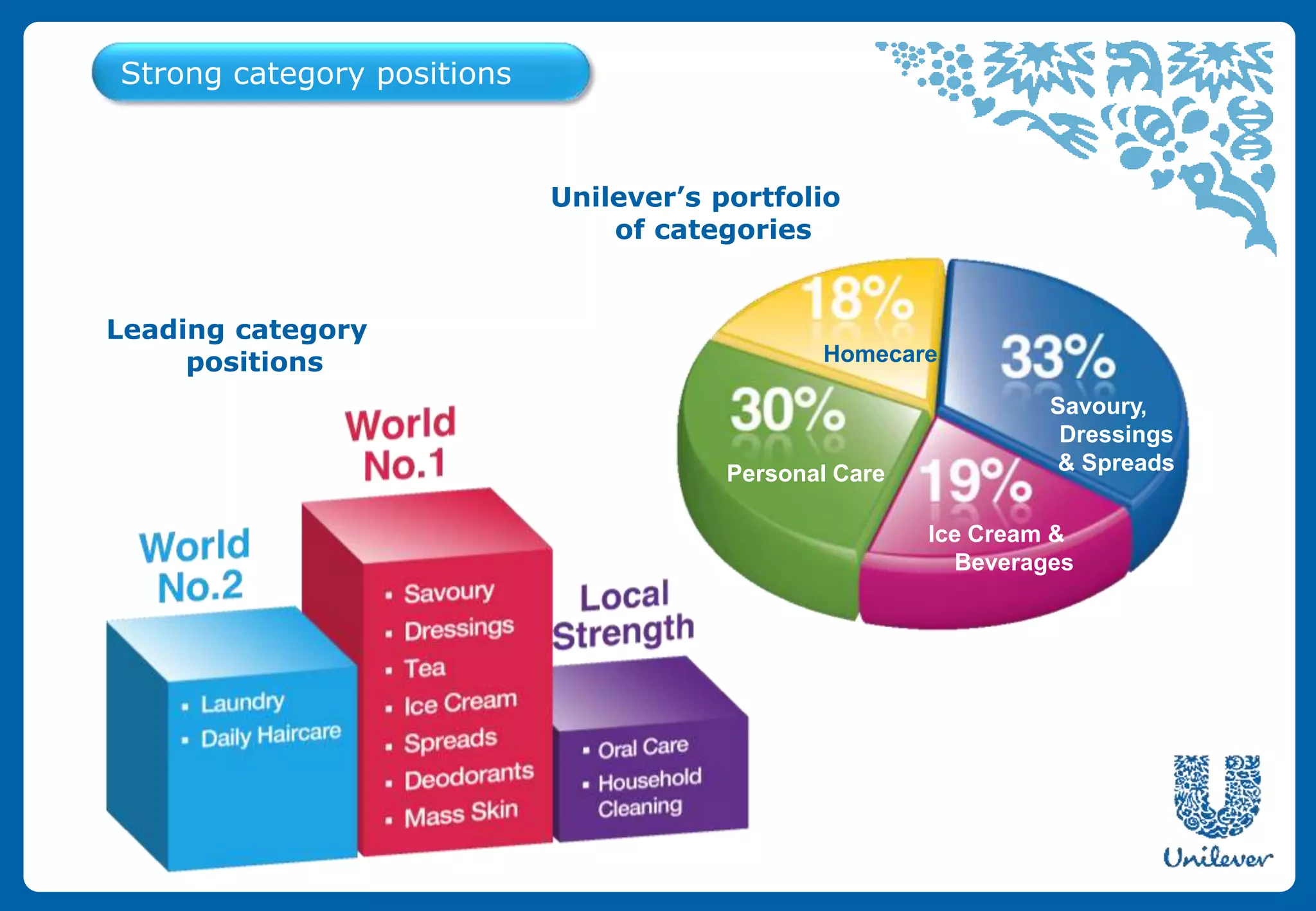
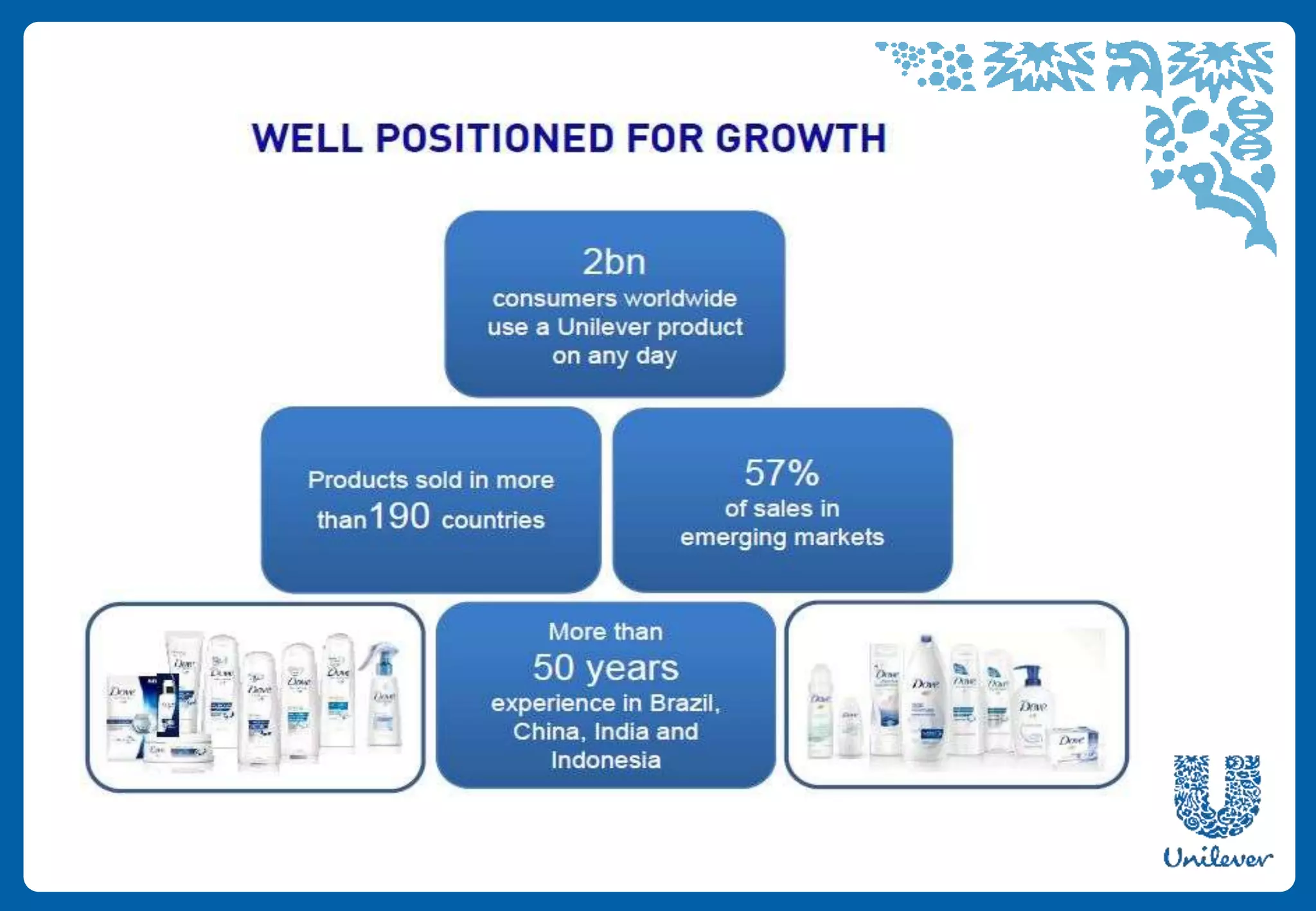
Unilever is a multinational consumer goods company formed in 1930 from the merger of Margarine Unie and Lever Brothers. It has over 400 brands and focuses on 14 core brands. Unilever employs 172,000 people worldwide and is the world's third largest consumer goods company. Its portfolio includes home care, personal care, food, and refreshment brands. Unilever has a presence in over 190 countries and reaches 2 billion consumers globally each day with its products.