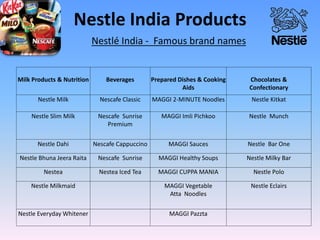
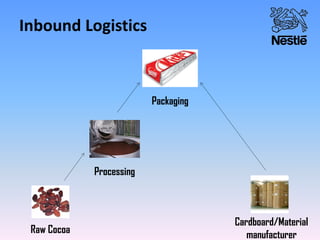
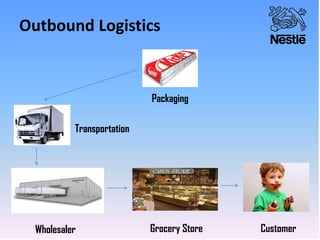
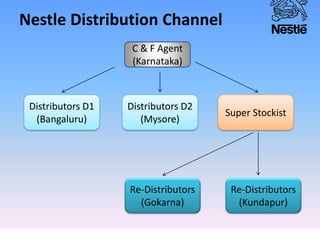
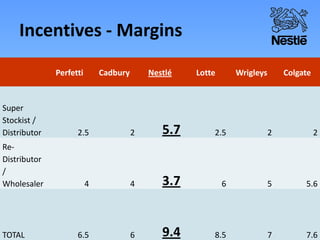
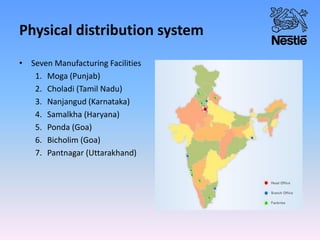
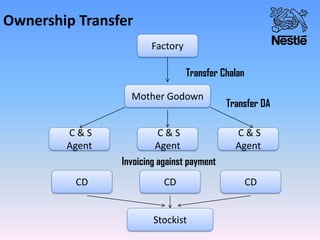
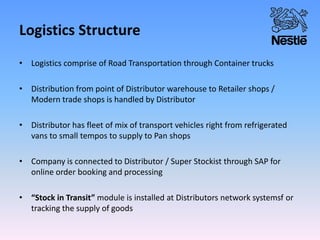
Nestle is the world's largest food and beverage company founded in 1867 in Switzerland. It employs over 250,000 people globally and has operations in almost every country. Nestle operates under a decentralized model where each country manages its own business. In India, Nestle sells a wide range of products from milk and nutrition to chocolate and coffee. It uses a multi-layered distribution network of distributors, super stockists, wholesalers and retailers to supply its products across India from its 7 manufacturing plants. Nestle provides training and incentives to motivate its channel partners.