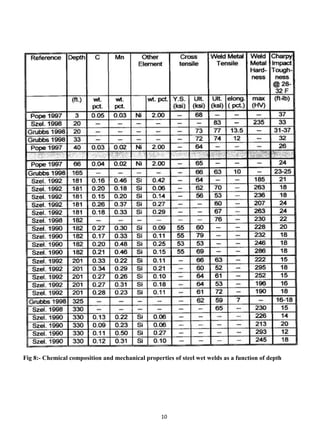
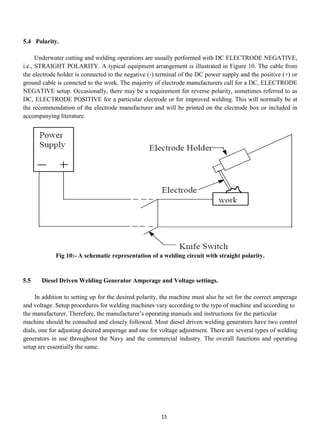
Underwater welding can be classified as dry welding, which uses sealed chambers, or wet welding, which is performed directly in water. Dry welding produces higher quality welds but requires more complex and expensive equipment. Wet welding is more economical but results in lower weld quality due to water's quenching effect. The underwater environment affects welds by introducing hydrogen that causes embrittlement and oxygen that increases porosity. Weld quality declines with increasing depth due to higher pressures. Proper welding equipment and techniques can help reduce these negative impacts.





![3.2 Effect of depth on Porosity
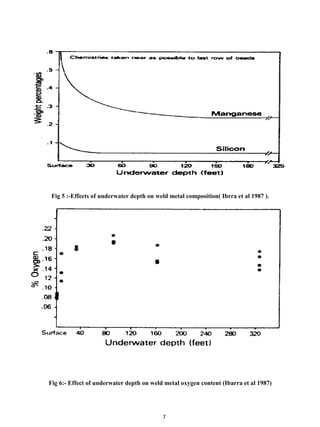
Porosity in underwater wet weld is caused by hydrogen, techniques to reduce the hydrogen content of
wet should also be effective at reducing porosity. Increasing the calcium carbonate content of a rutile-base
electrode coating has been shown to reduce porosity in wet welds. Sanchez-Osio et al [1995] increased
calcium carbonate from 9 to 12.5 pct., which decreased porosity from 2.2 to 1.0 pct at a depth of 30 ft(9m).
Carbonates decompose to form carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide in the arc, reducing the partial pressure
of hydrogen, and thus reducing the amount of hydrogen absorbed into the weld pool.
Fig 7:- Effect of underwater depth on porosity. (Suga and Hasui 1986)
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/underwaterwelding-121020023604-phpapp01/85/Underwater-welding-8-320.jpg)