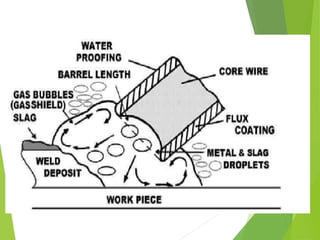
The document presents an overview of underwater welding, including its necessity, methods (wet and dry welding), advantages, and risks involved in the process. Wet welding is characterized by its direct exposure to water with minimal equipment, while dry welding involves a gas-filled chamber for improved safety and quality. The document also discusses future advancements in underwater welding technology, such as automation.