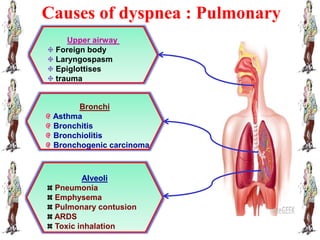
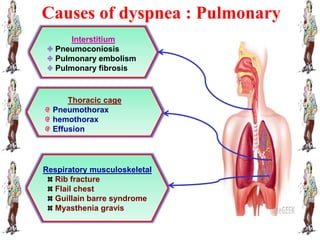
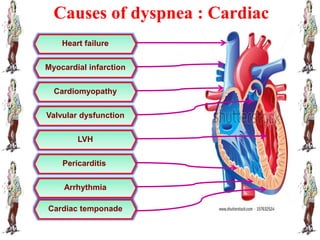
Dyspnea, meaning difficult or painful breathing, is defined as an uncomfortable need to breathe or an abnormal awareness of breathing. It can be caused by conditions affecting the upper airways, lungs, heart, chest wall, or metabolic issues. A health history and physical assessment are used to evaluate potential causes, while diagnostic tests may include chest x-rays, pulmonary function tests, echocardiograms, and blood gas analysis. Treatment focuses on the underlying cause, while nursing management includes positioning, oxygen therapy, breathing exercises, and addressing anxiety.