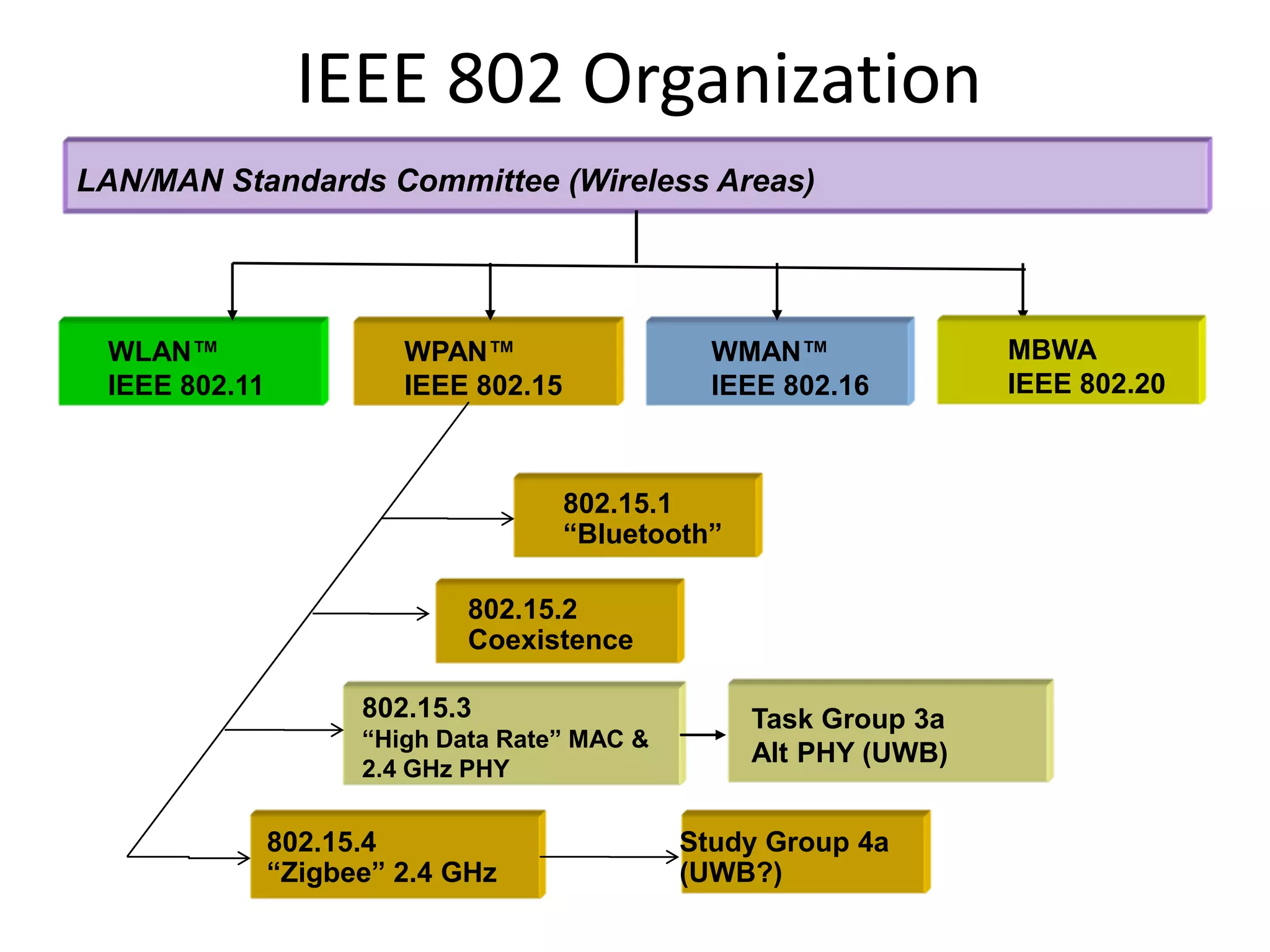
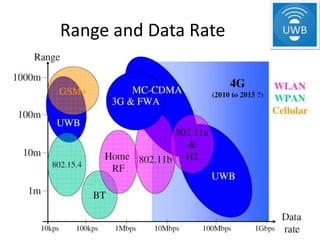
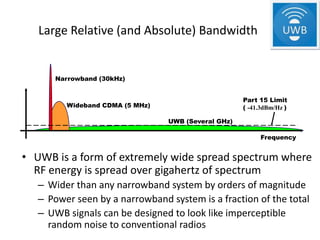
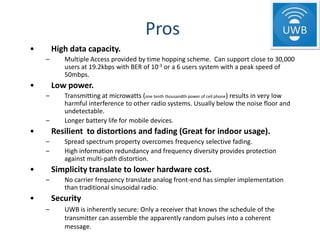
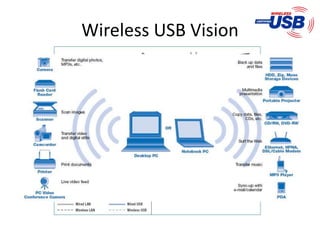
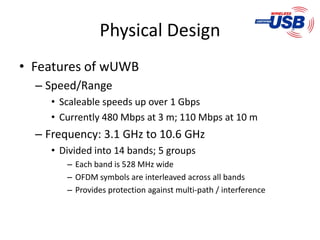
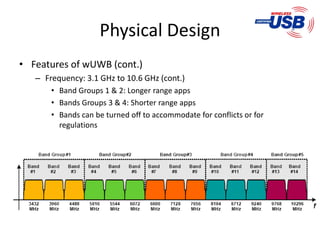
The document presents a detailed overview of various wireless communication technologies, focusing on Bluetooth and Ultra Wide Band (UWB). It highlights Bluetooth's advantages of low cost and power consumption, while discussing its limitations such as range and data rate compared to 802.11 standards. Additionally, it covers UWB's high data capacity, potential for low power applications, and challenges with GPS interference, alongside Zigbee's role in the wireless market as a low-power, cost-effective alternative for network connectivity.