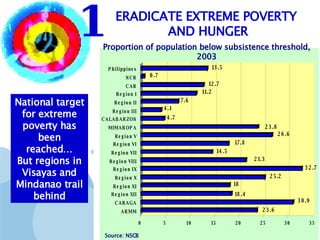
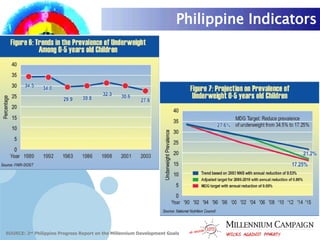
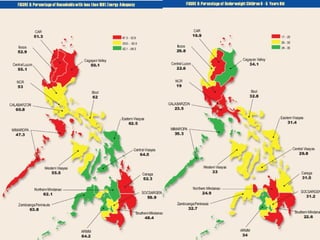
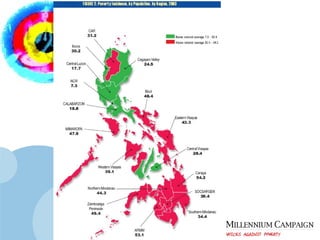
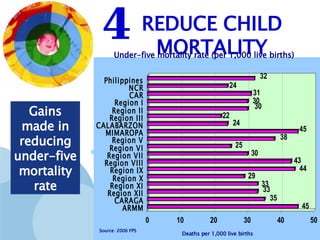
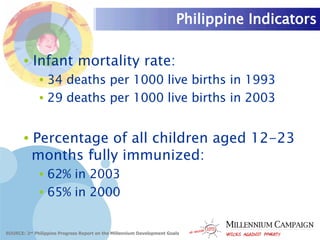
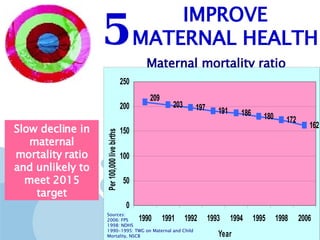
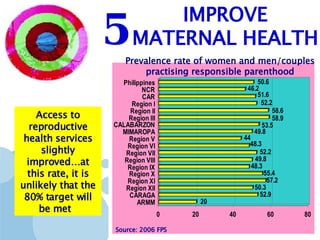
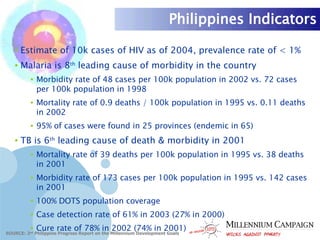
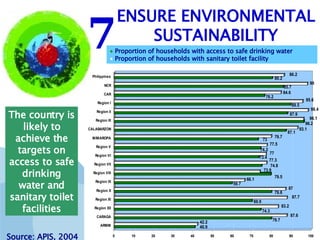
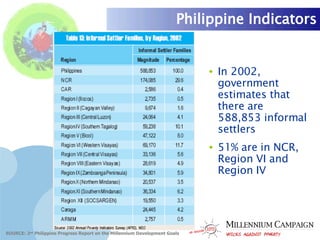
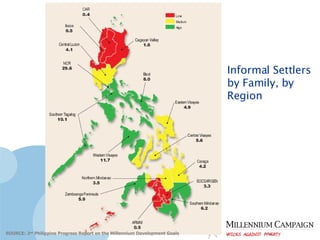
The document discusses the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), which are 8 targets established by the UN to reduce poverty by 2015. It provides an overview of the MDGs and their focus on issues like poverty, education, health, and environmental sustainability. It also analyzes the Philippines' progress and challenges in meeting targets related to reducing poverty, child mortality, maternal health, disease prevention, access to water and sanitation, and slum upgrading.