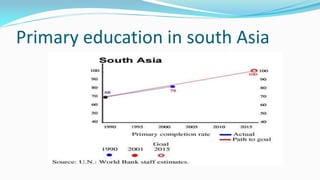
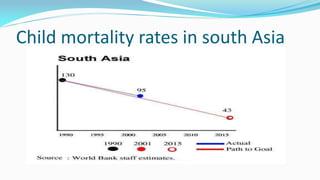
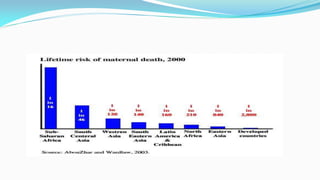
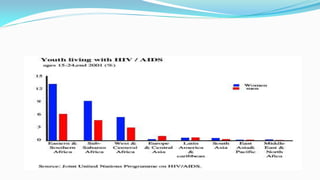
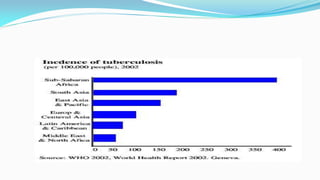
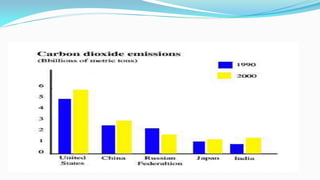
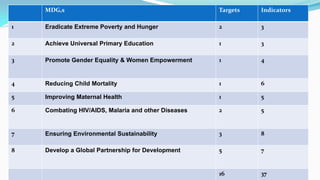
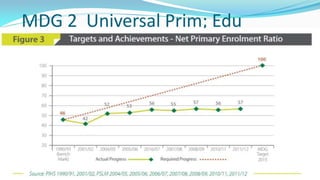
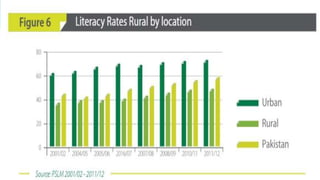
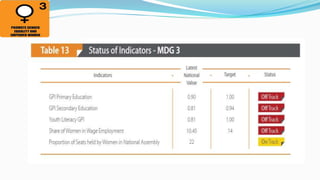
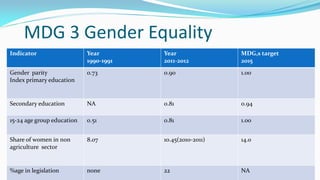
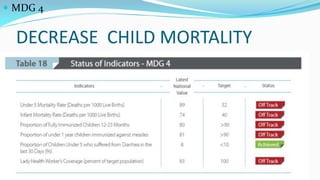
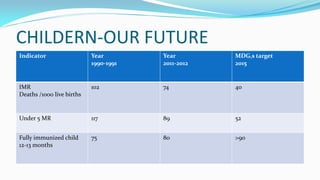
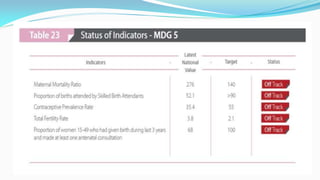
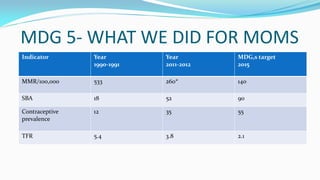
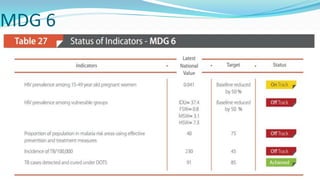
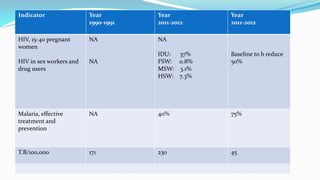
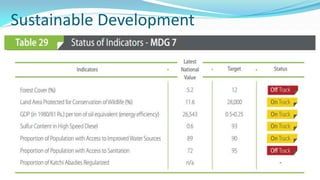
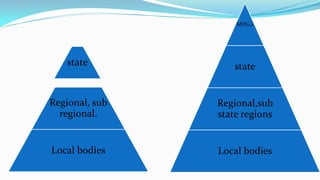
The document outlines the history and goals of the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). It discusses the 8 goals, 18 targets, and 60 indicators established by the UN. It provides an overview of progress on the MDGs in South Asia, noting achievements in reducing poverty, improving education and health. However, it also notes areas still lagging like empowering women in Afghanistan and Pakistan. For Pakistan specifically, it analyzes progress against each goal and indicators, finding that only 2 targets have been achieved so far. Barriers to progress are identified as both internal challenges like low growth, and external factors like natural disasters. Localization and community involvement are emphasized as important for accelerating progress.