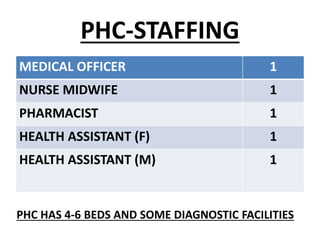
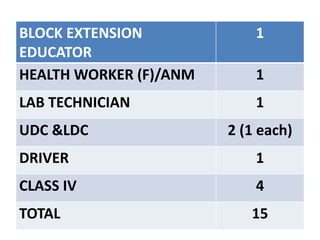
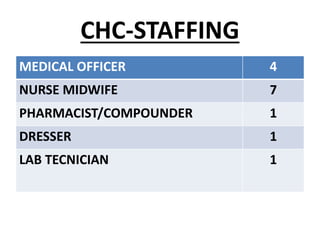
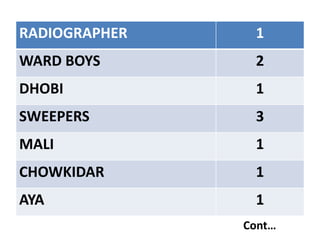
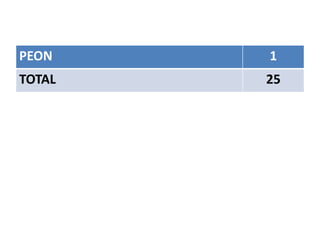
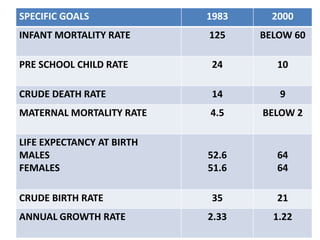
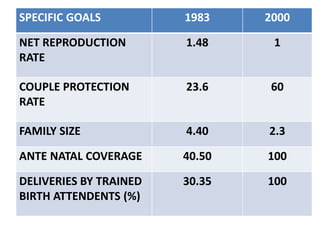
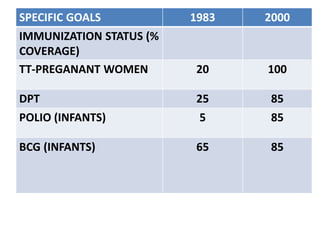
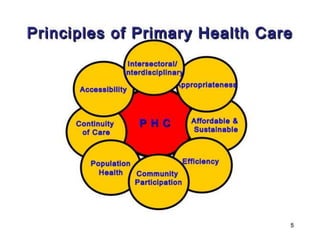
The document discusses the World Health Organization's goal of "Health for All" by the year 2000. It was established in 1977 with the aim of attaining a basic level of health that allows people to live productive lives. The strategy involved strengthening primary healthcare infrastructure at the village, sub-center, primary health center, and community health center levels. It also outlined a primary healthcare package and specific health goals for India to reduce mortality and birth rates while increasing life expectancy. The national strategy for achieving Health for All built upon the principles of primary healthcare established at Alma-Ata in 1978.