Embed presentation
Download to read offline


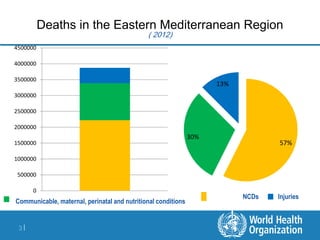
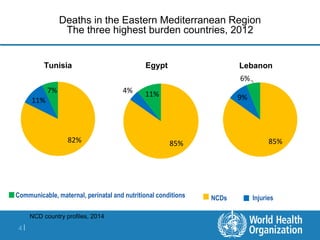
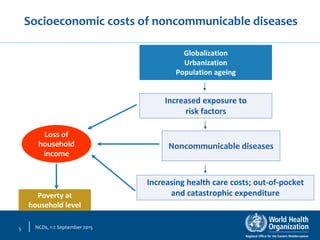






This document discusses non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and NCD alliances. It notes that 57% of deaths in the Eastern Mediterranean region are due to NCDs like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Risk factors for NCDs like tobacco use, unhealthy diets, and physical inactivity are on the rise globally. In 2011, the UN held its first high-level meeting on NCDs which resulted in a political declaration and commitments to address the growing NCD burden. The document then discusses the role of the NCD Alliance, a civil society network, in supporting a global response to NCDs at national and regional levels including the formation of country-level alliances.










