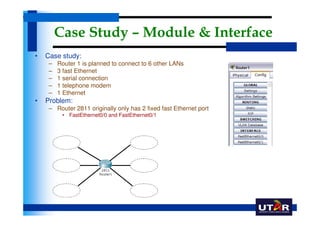
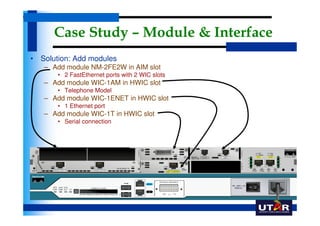
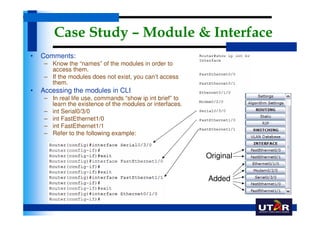
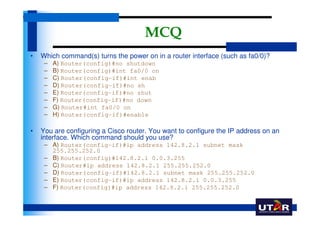
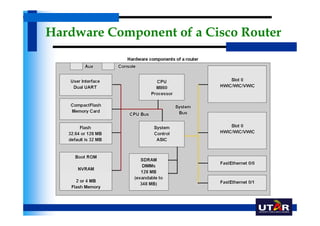
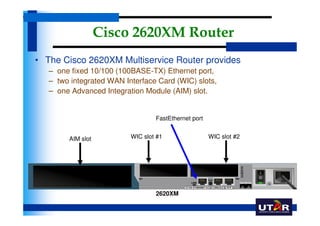
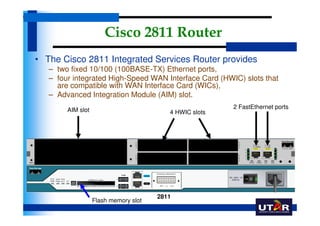
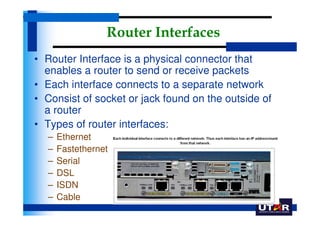
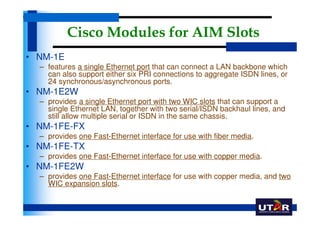
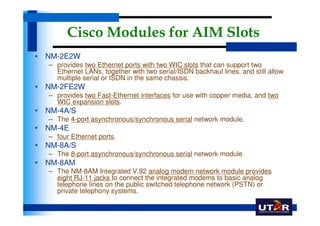
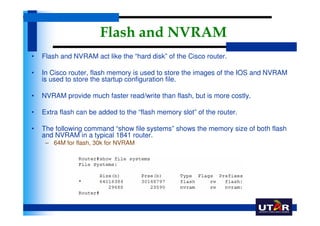
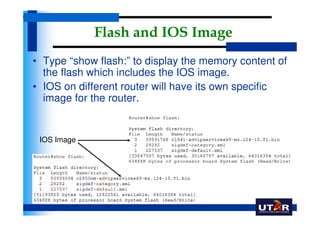
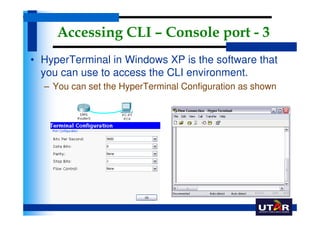
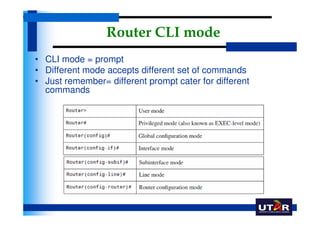
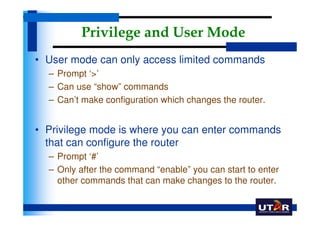
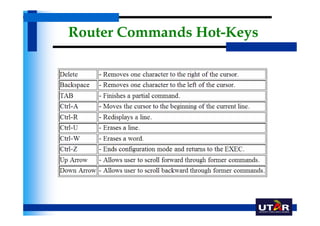
Routers are networking devices that interconnect networks by forwarding data packets between them using the best available path. The basic components of a Cisco router include a CPU, RAM, ROM, NVRAM, flash memory, and physical interfaces. The Cisco IOS operating system runs on routers and provides routing functions and network services via the command line interface. Different Cisco router models have varying numbers and types of slots to add communication modules.



















![Startup-configuration
• Stored in NVRAM. Choo#show start
startup-config is not present
• Load in as running-config during Choo#copy run start
Destination filename [startup-config]?
the router startup. Building configuration...
[OK]
• Command for viewing the Choo#show start
Using 508 bytes
startup-config: “show start” !
version 12.4
• Backing up running-config in !
hostname Choo
startup-config: “copy run start” !
enable password uccn1003
– Note, when you turn off switches or !
interface FastEthernet0/0
routers and then turn them back on, ip address 192.168.1.254
they will load their startup 255.255.255.0
!
configuration files. interface FastEthernet0/1
no ip address
– If you do not backup the running shutdown
configuration, it will be lost. !
end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uccn1003-may10-lect03b-introtociscorouter-101212021719-phpapp02/85/Uccn1003-may10_-_lect03b_-_intro_to_cisco_router-34-320.jpg)