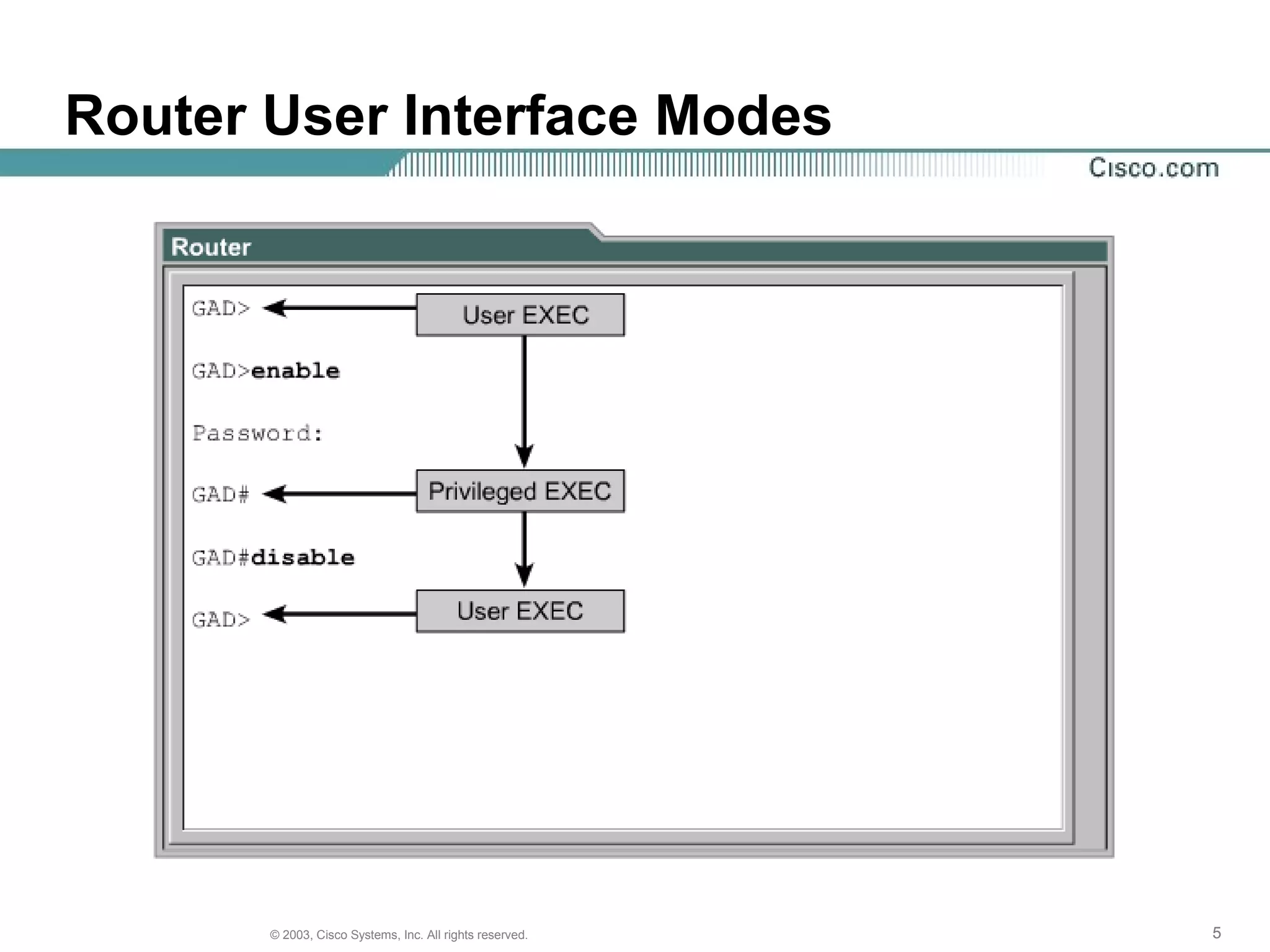
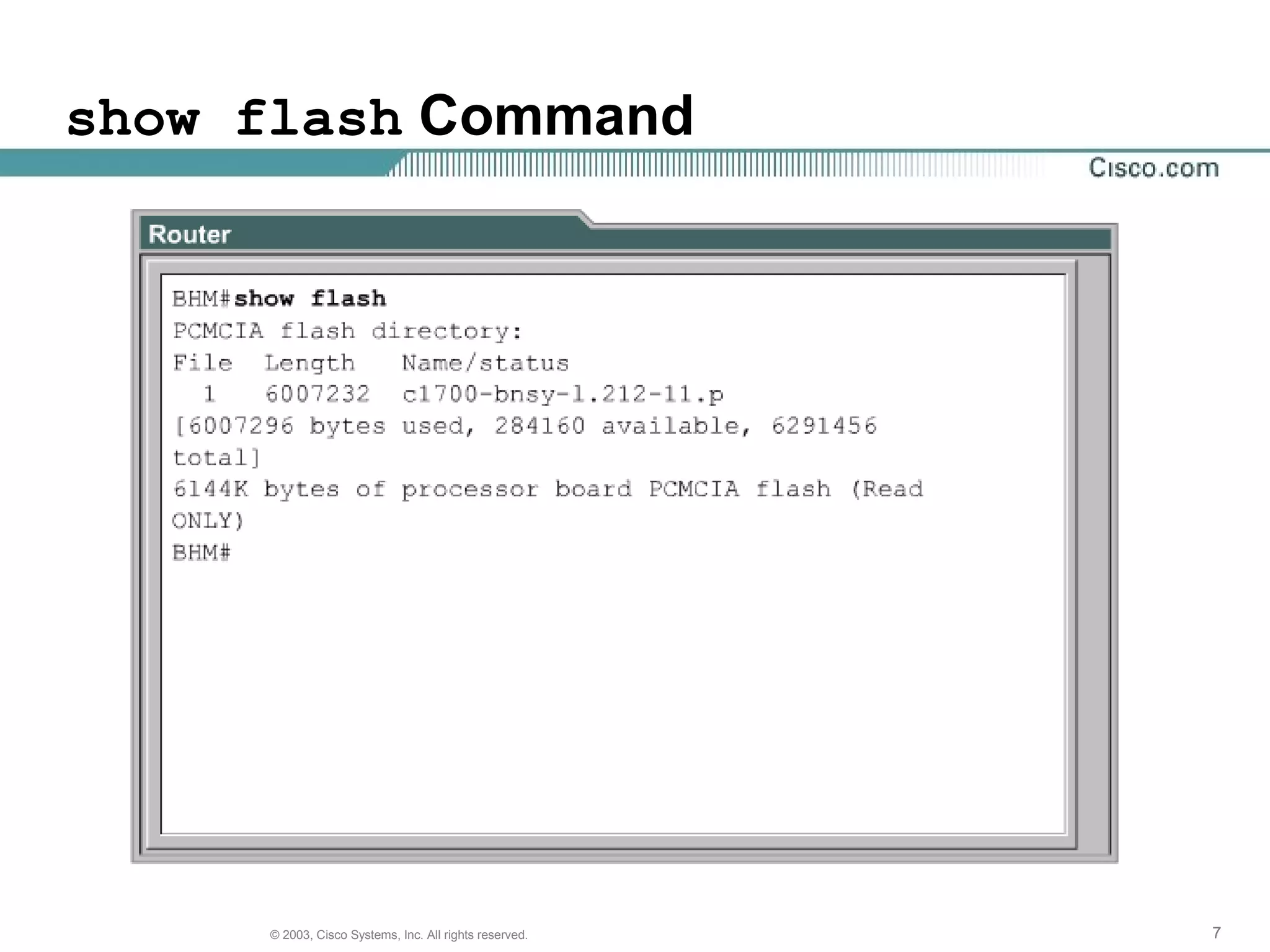
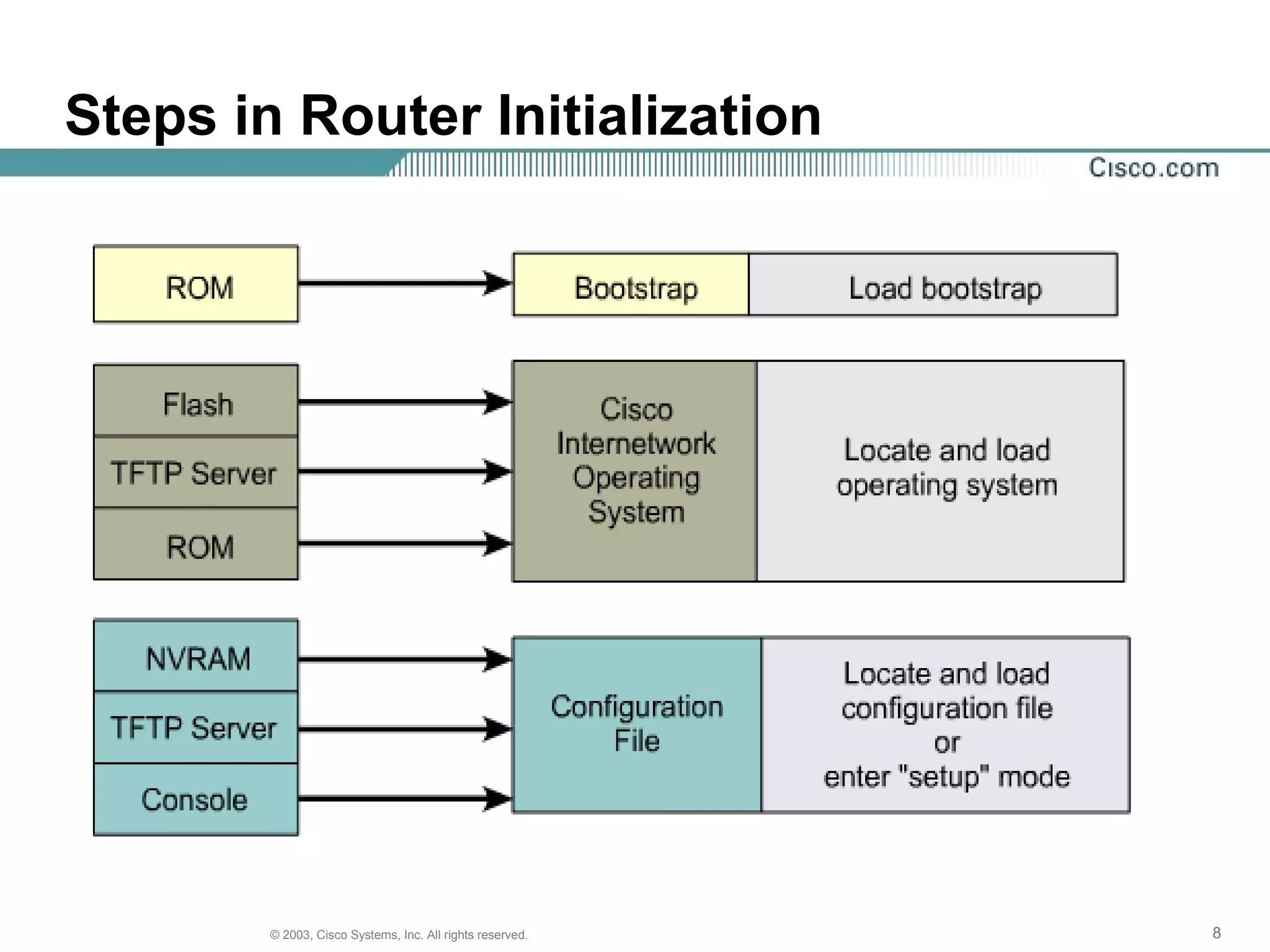
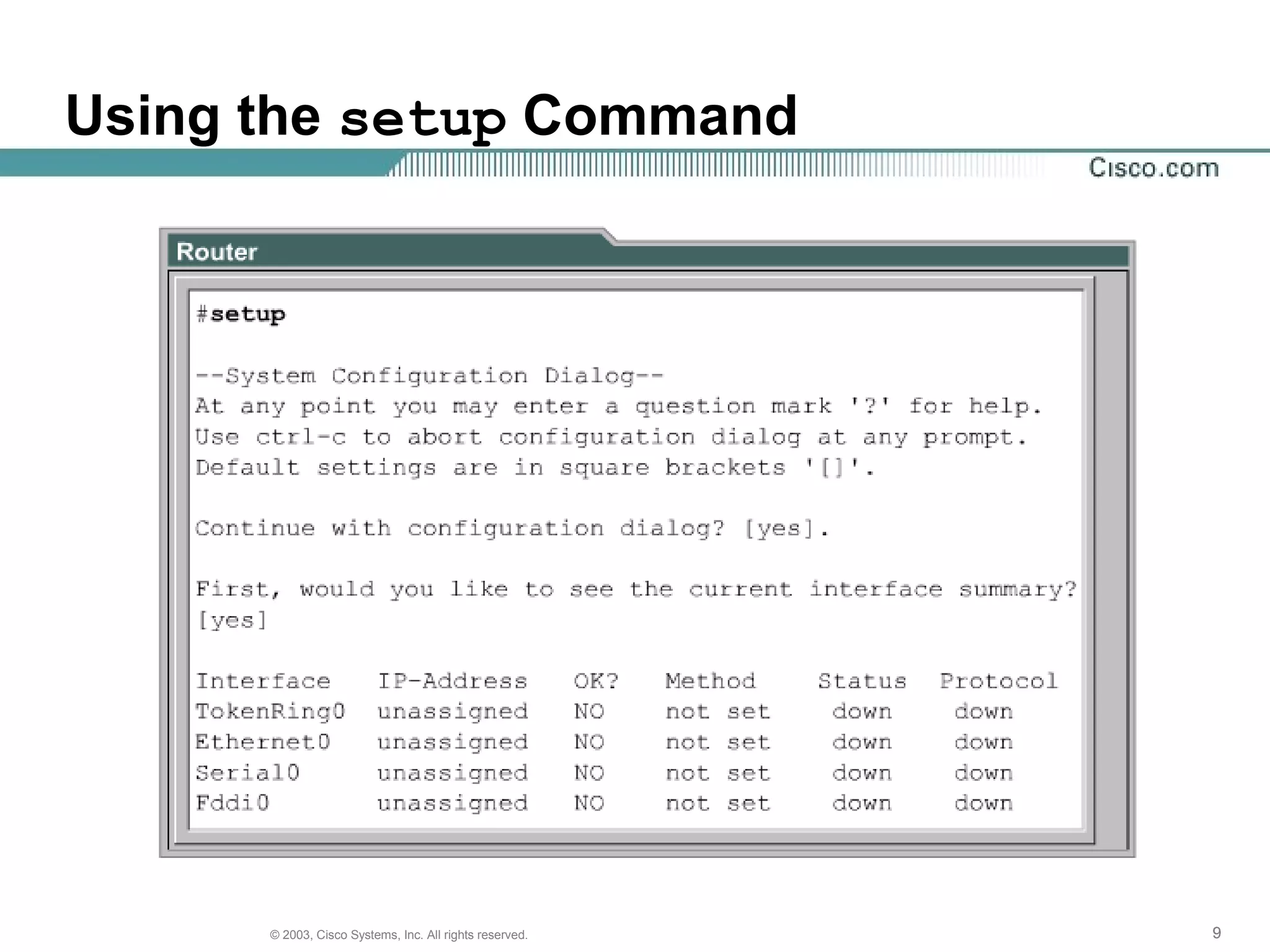
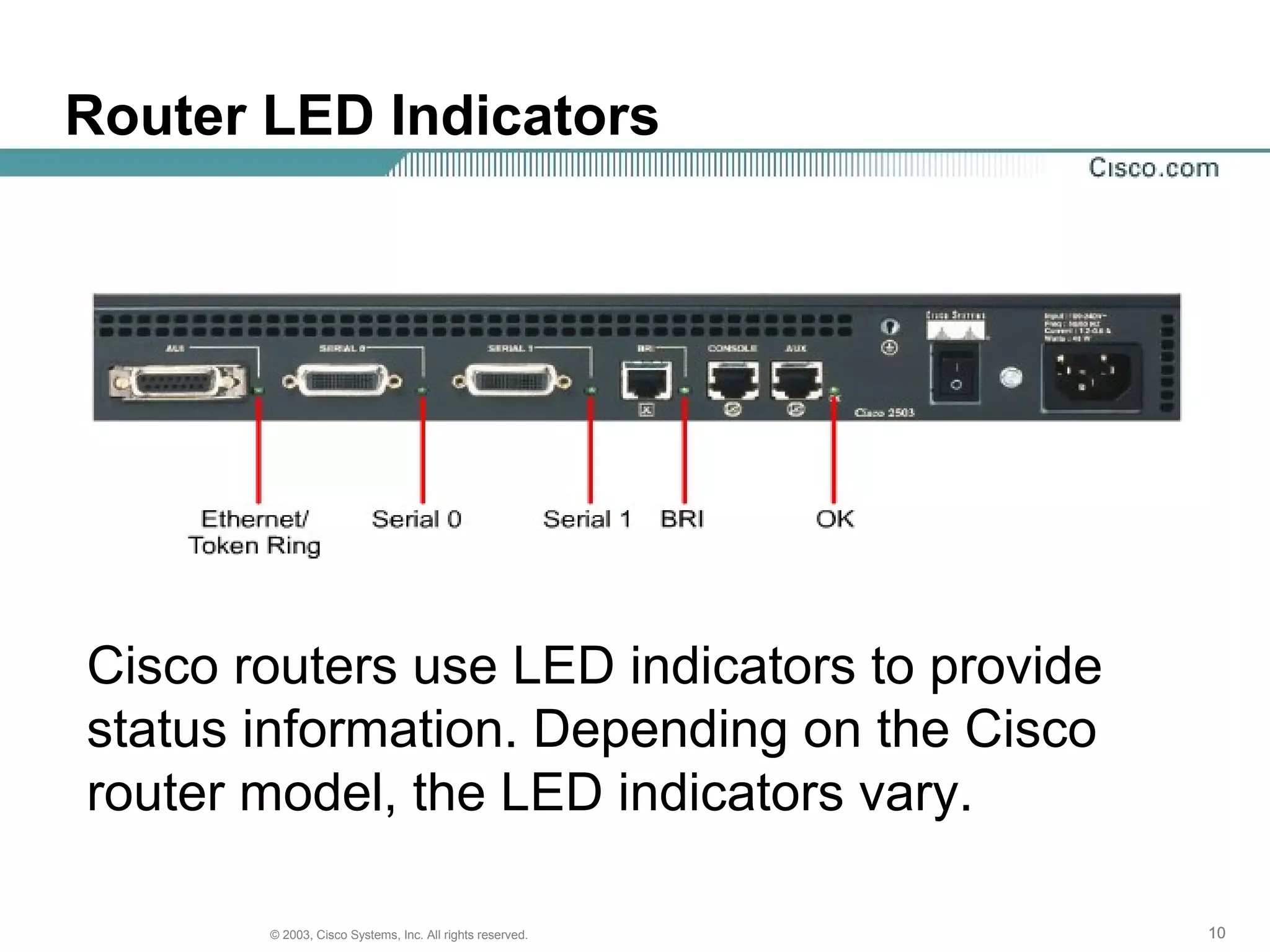
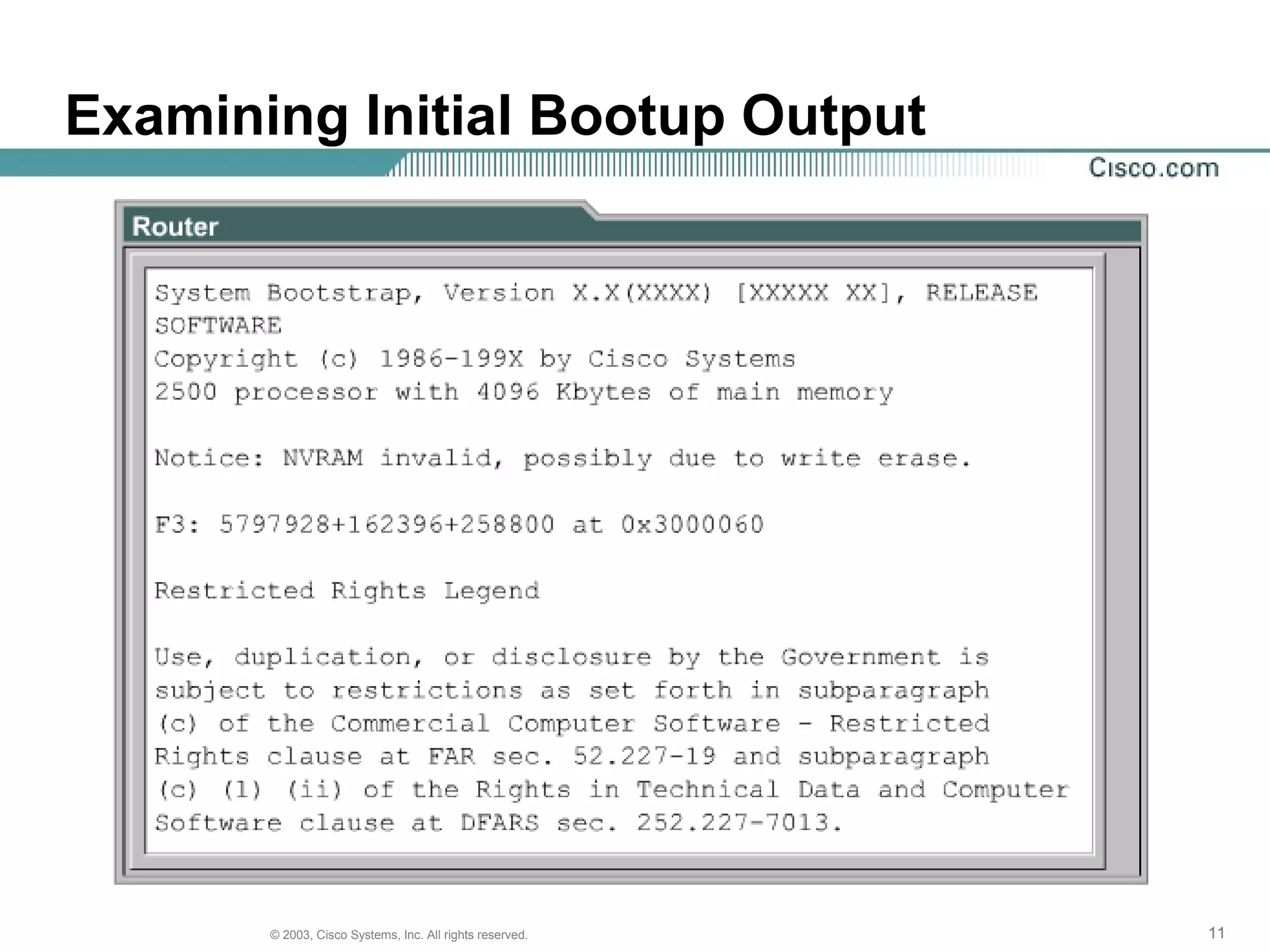
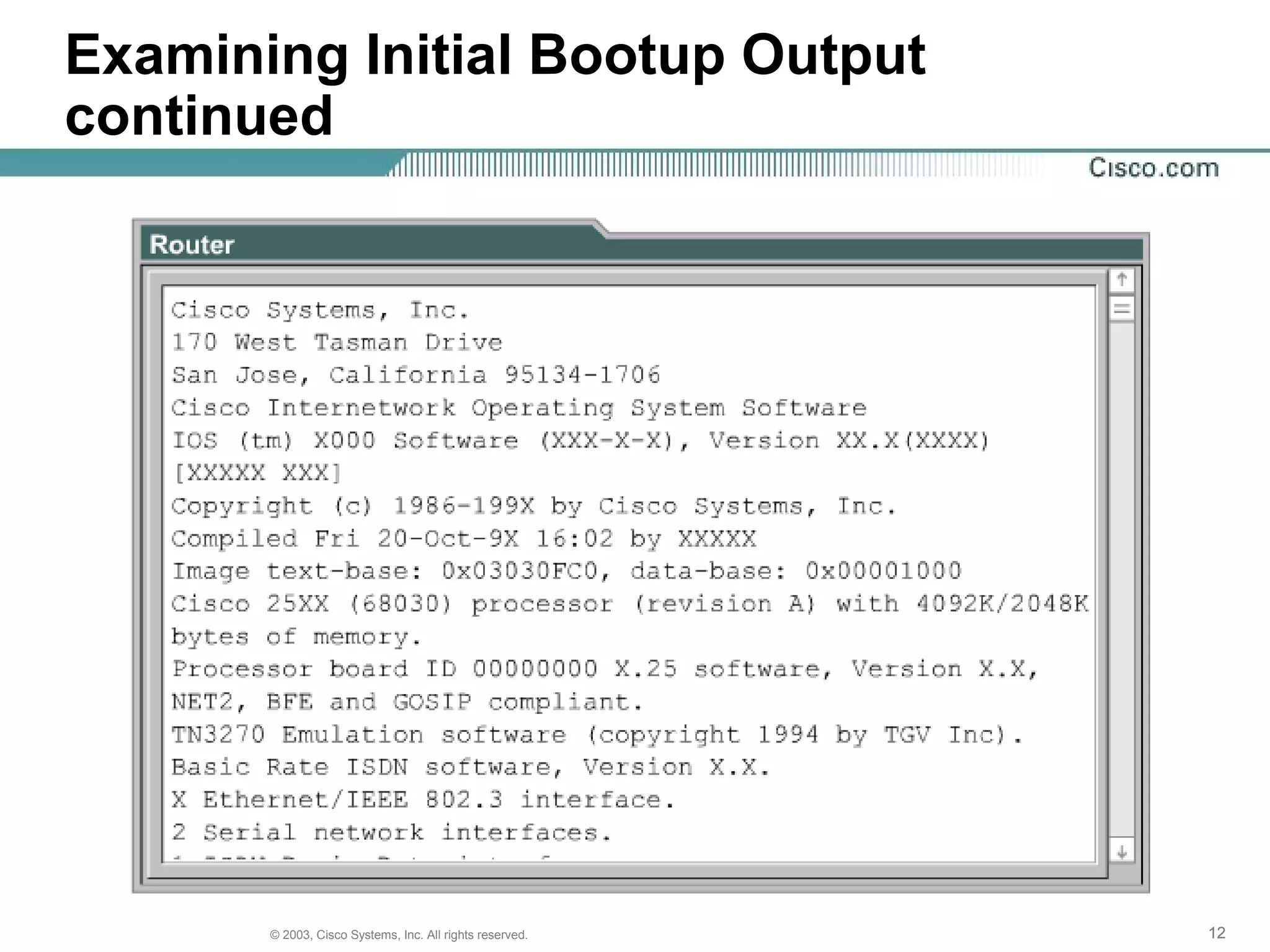
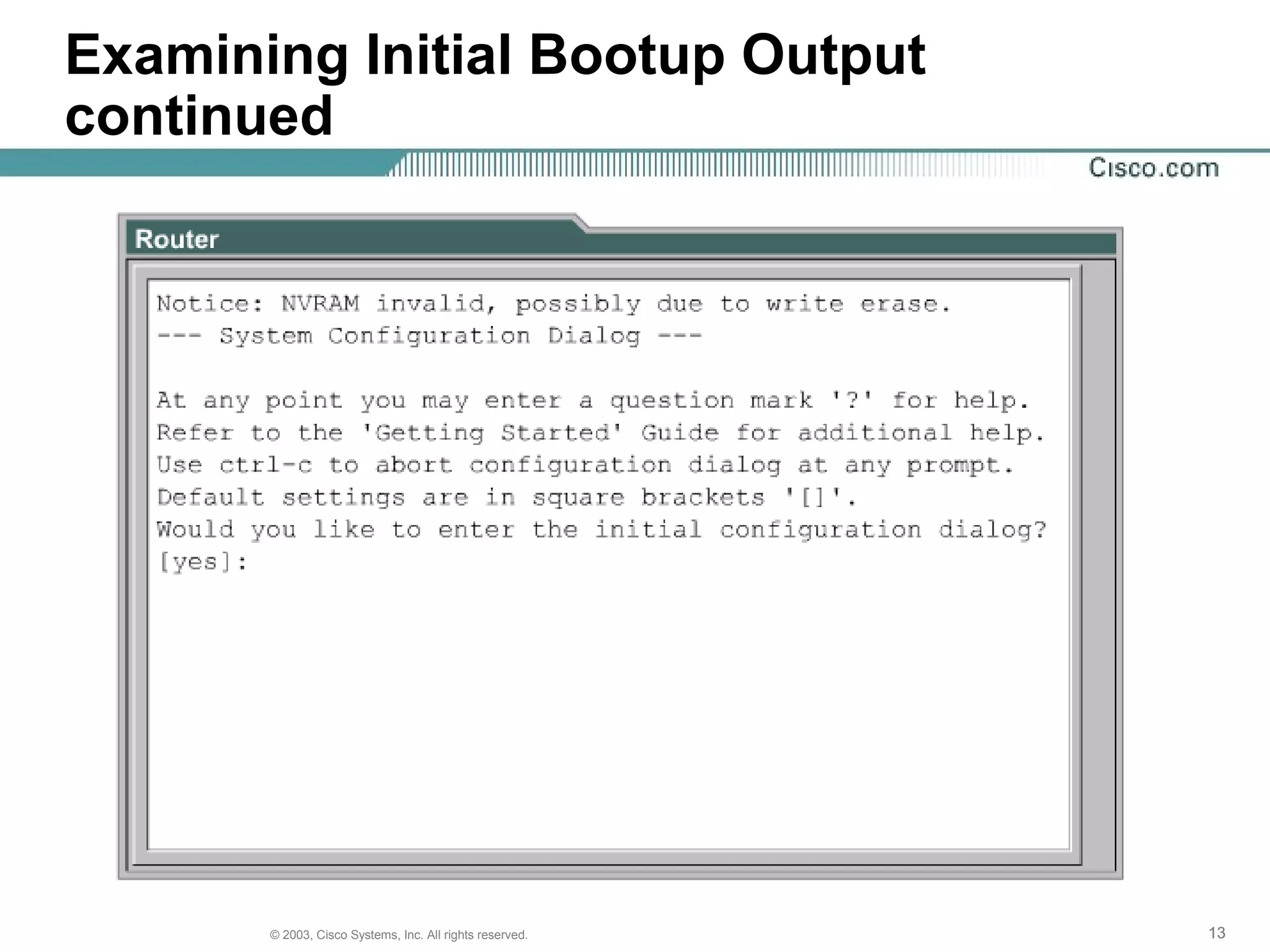
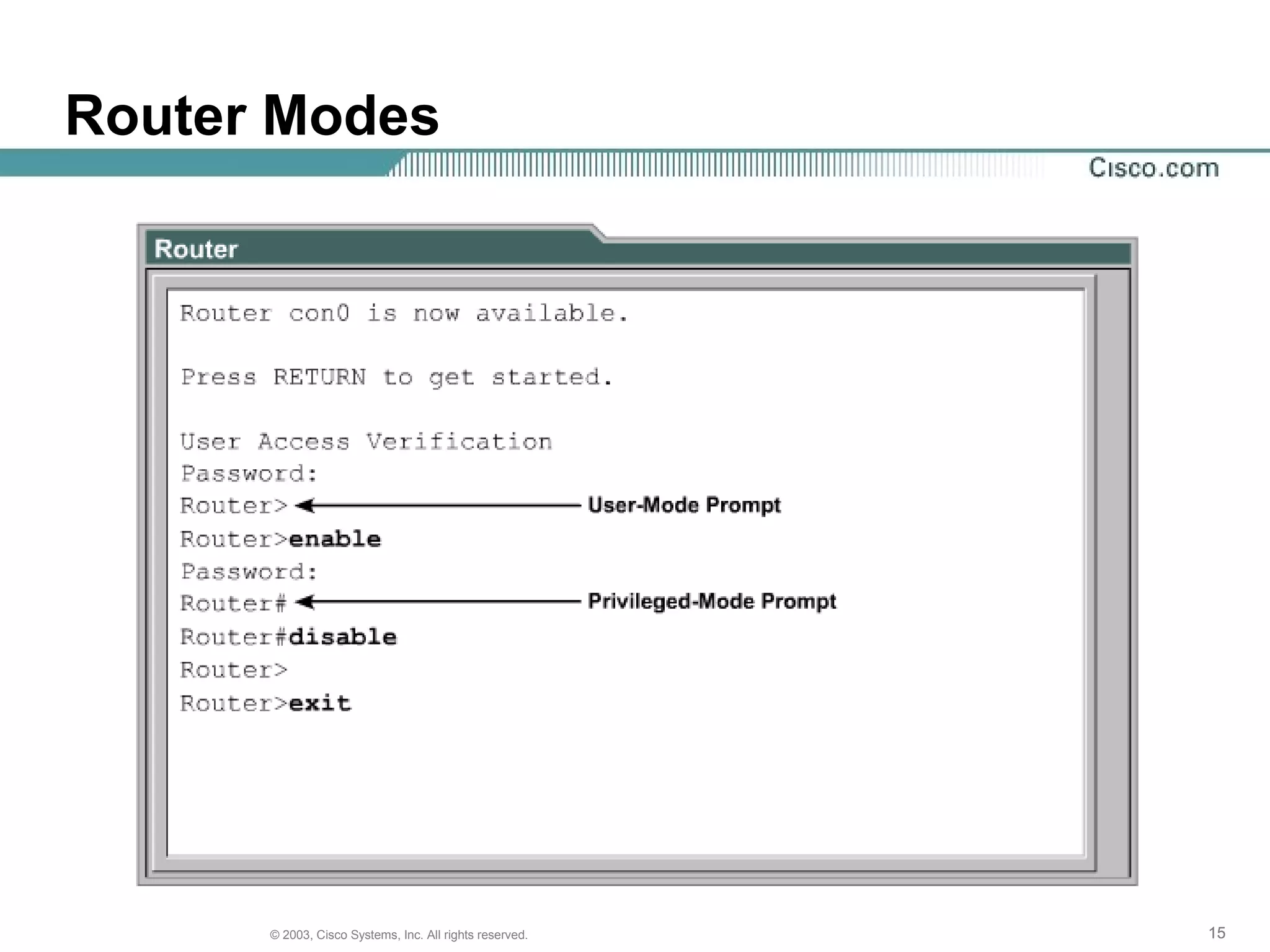
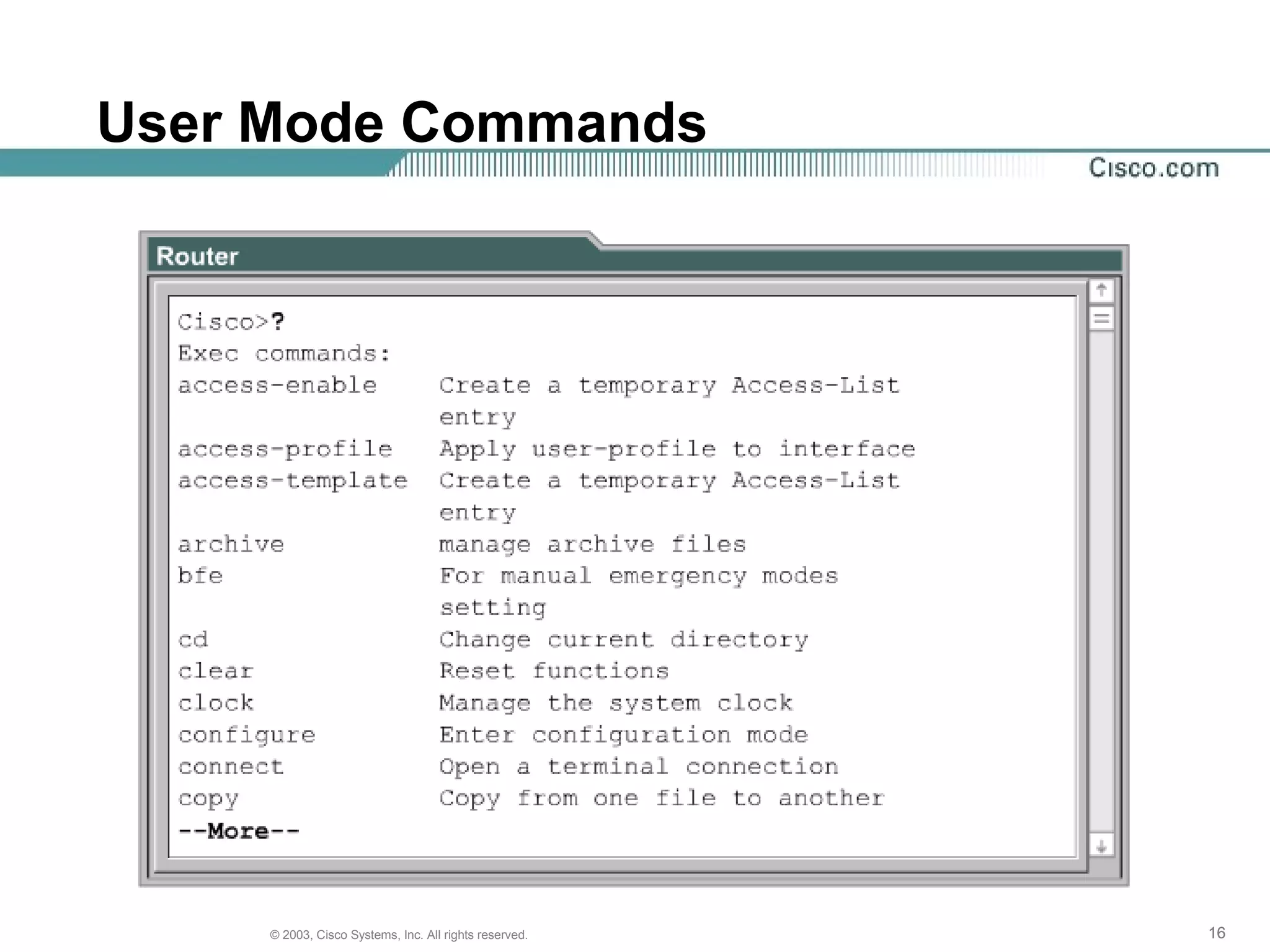
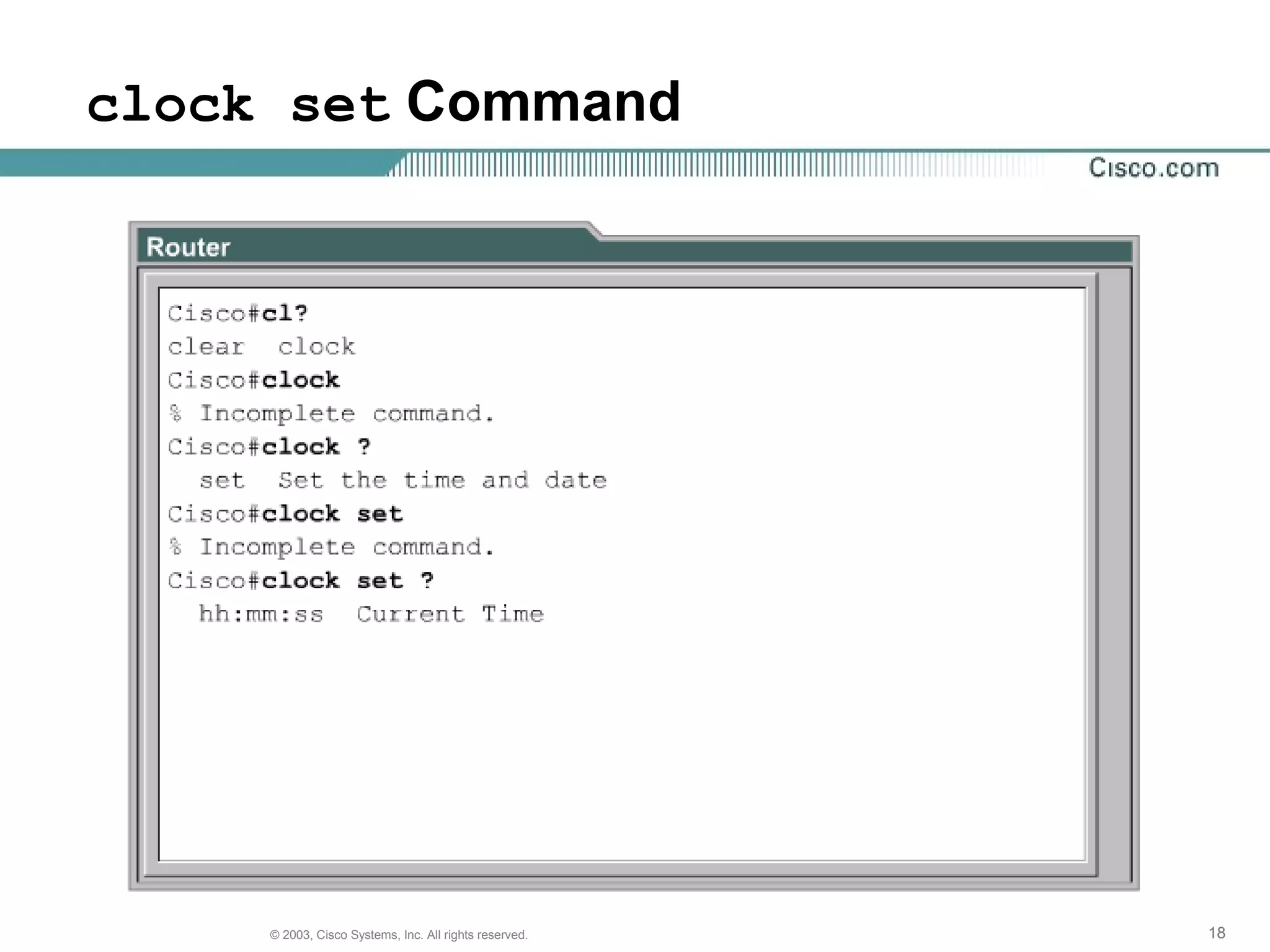
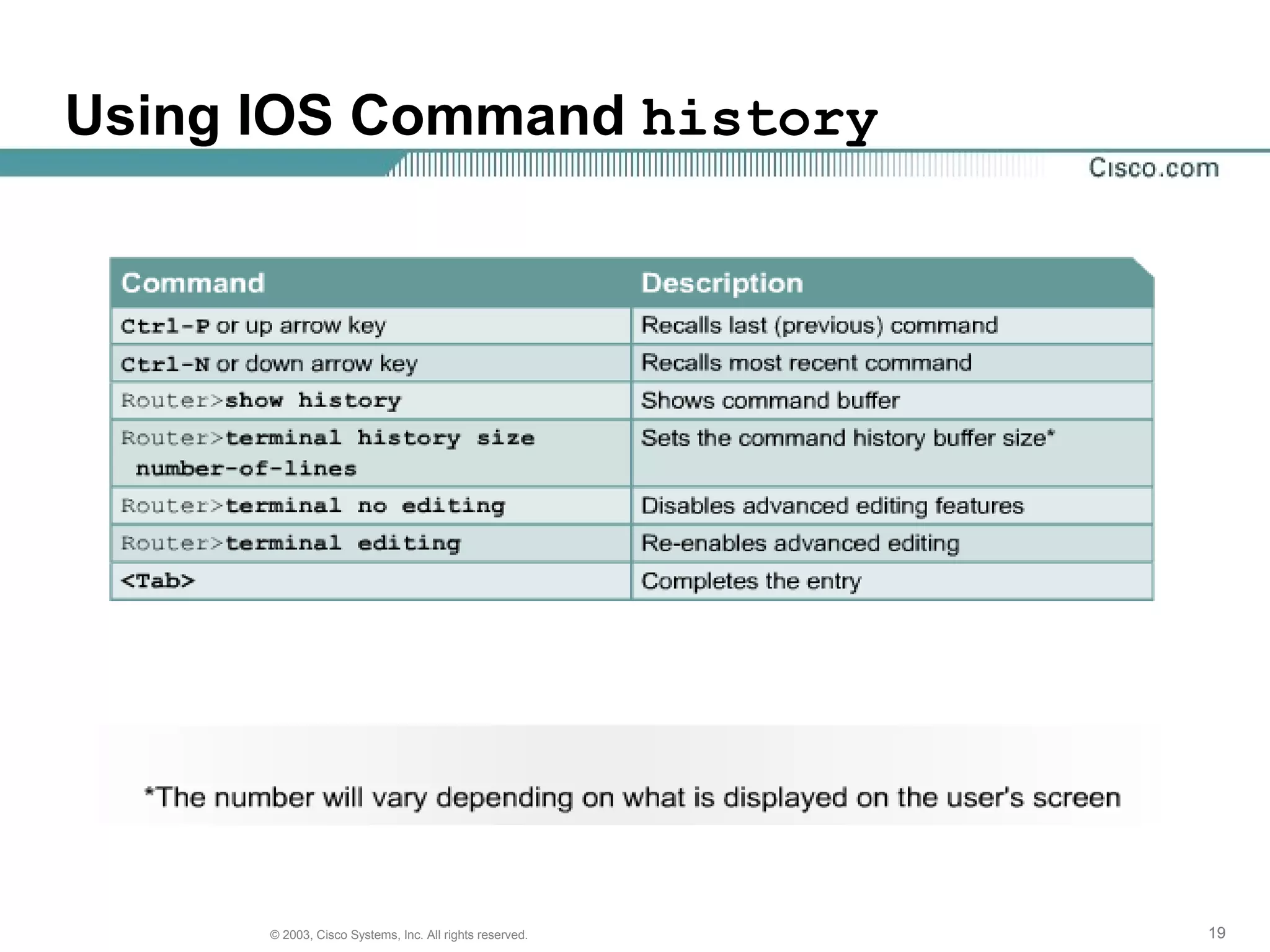
The document discusses Cisco IOS software and router initialization. It describes the purpose of Cisco IOS software as providing basic routing and switching functions, reliable access to resources, and network scalability. It explains that routers use LED indicators to provide status information and that establishing a hyperterminal session requires connecting a console terminal to the router's console port using cables and adapters. It also discusses router modes, commands, setting the clock, and using the show version command.