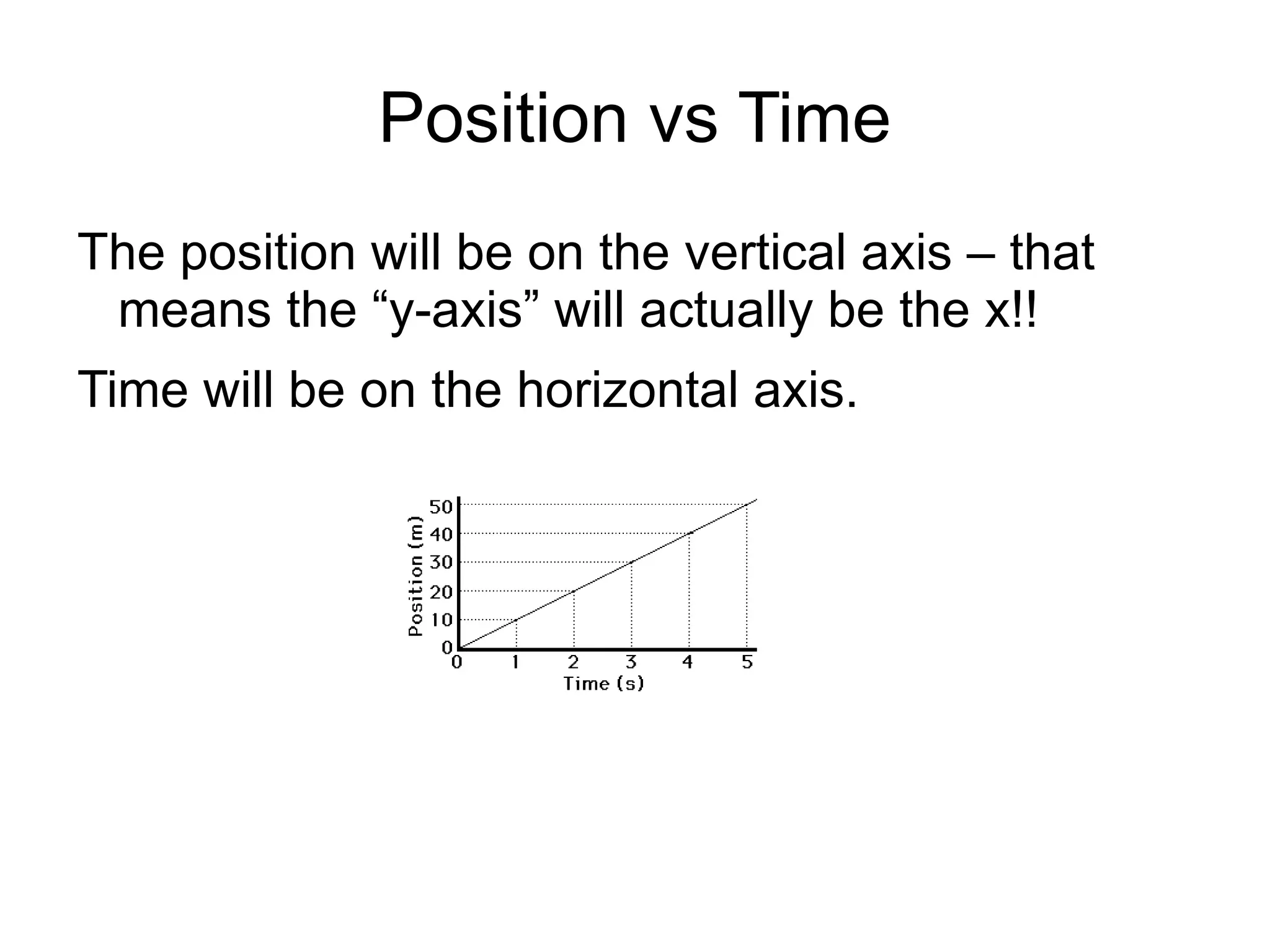
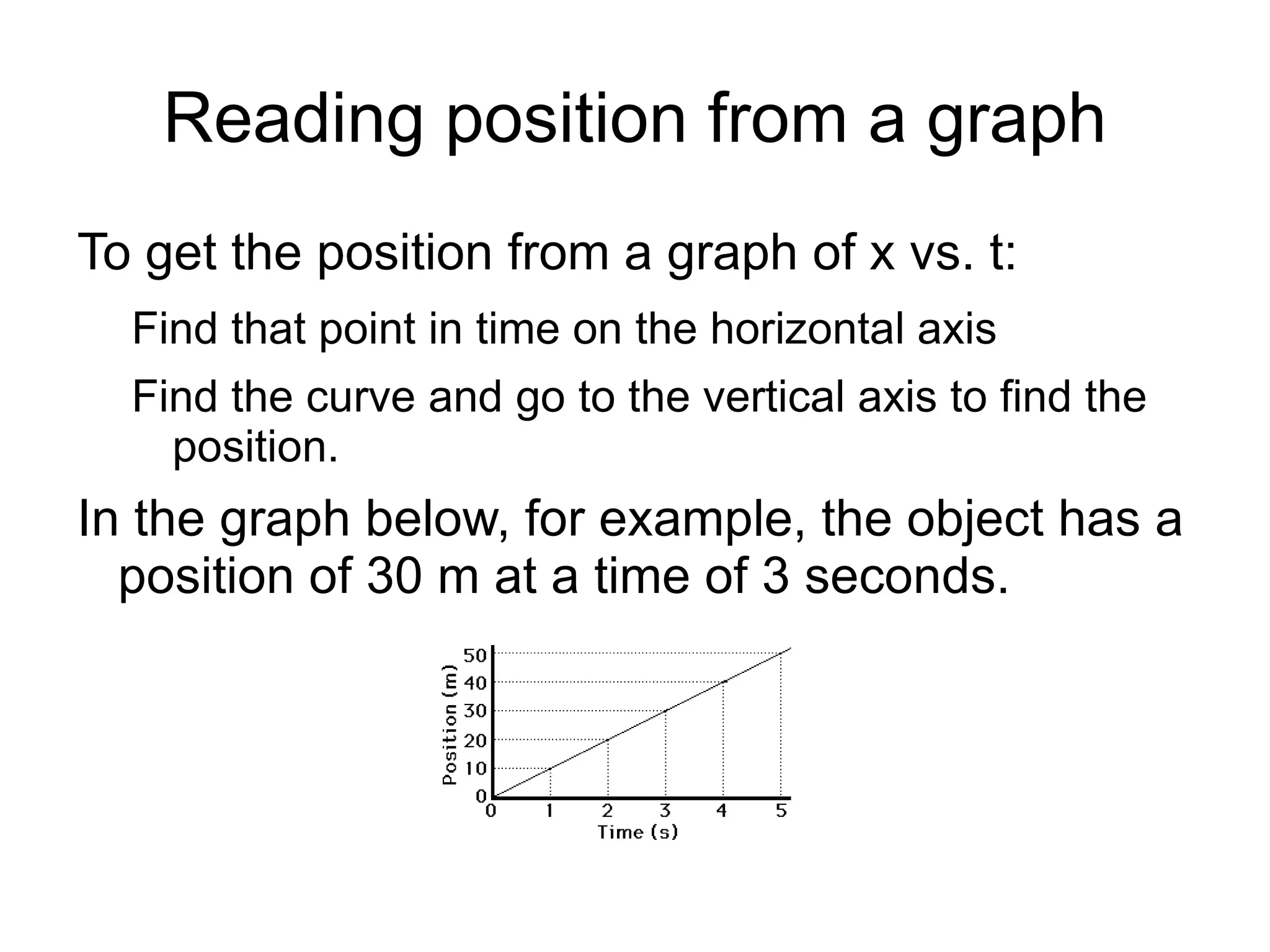
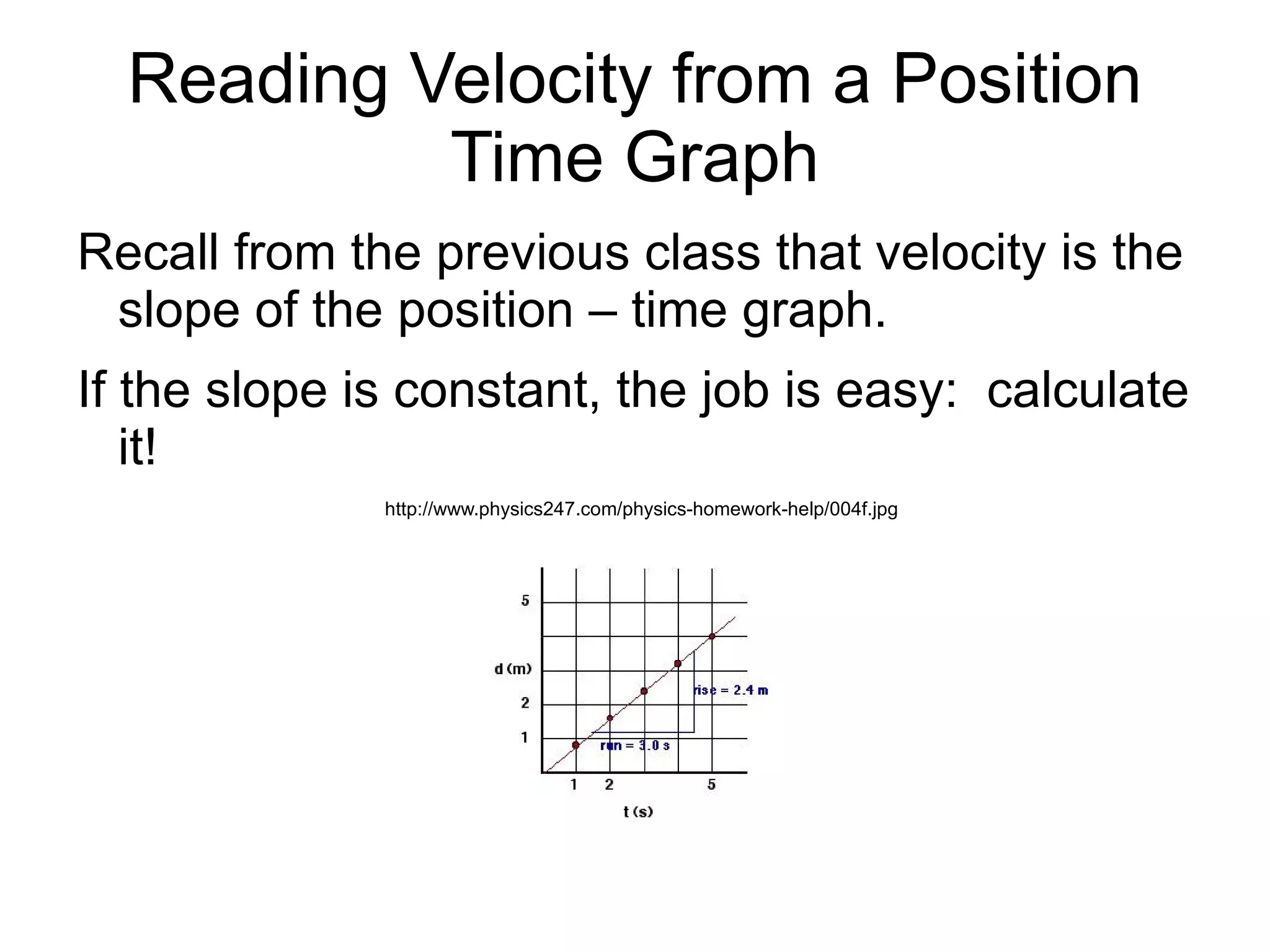
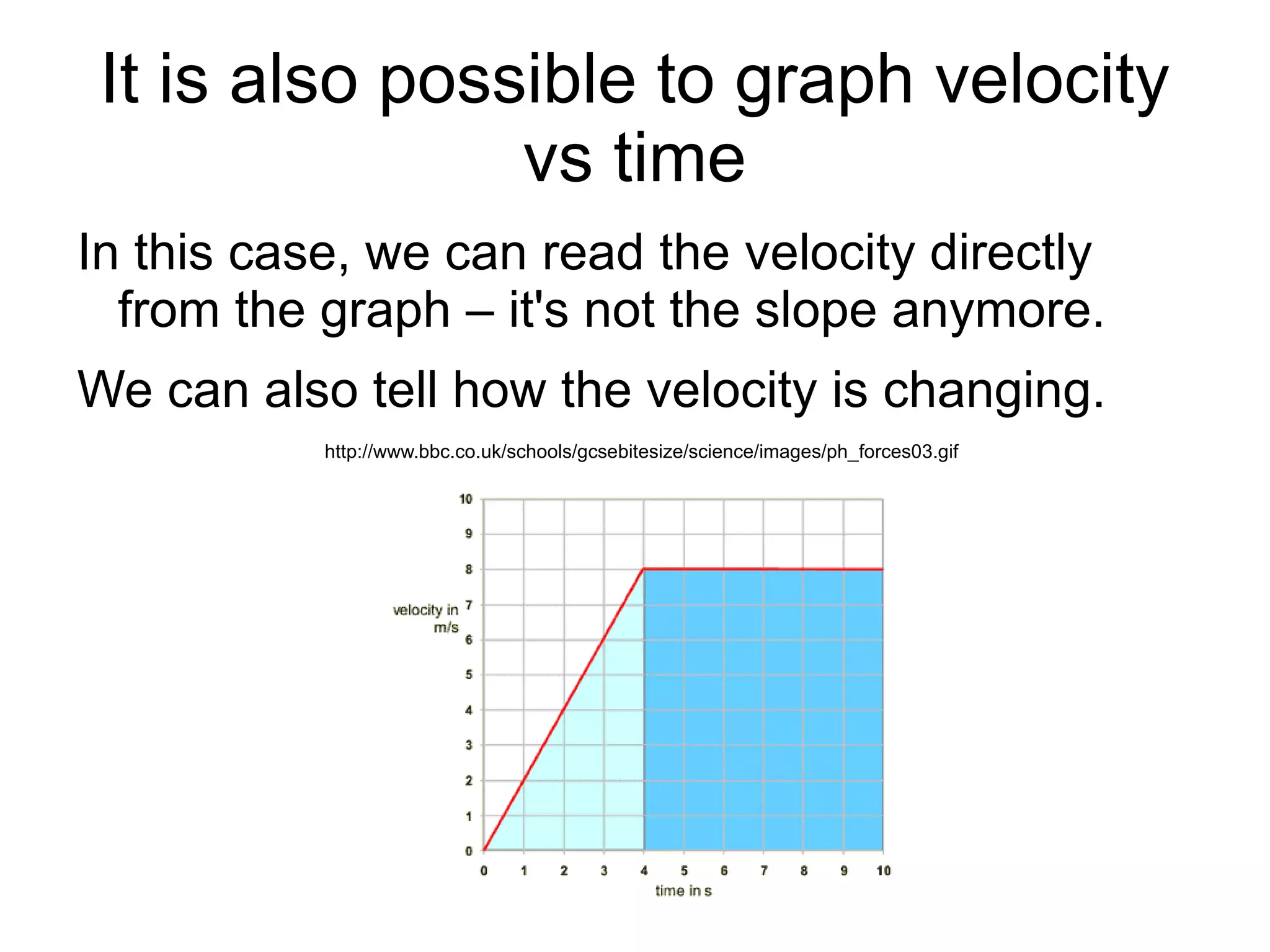
The document discusses position vs time graphs and velocity vs time graphs. It explains that position is graphed on the y-axis and time on the x-axis for position graphs. Velocity can be determined from the slope of the position graph. Velocity graphs show velocity directly on the y-axis rather than as a slope. Both graph types can provide information about an object's speed and whether it is slowing down, speeding up or stopping.