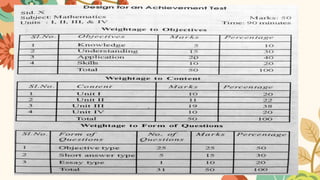
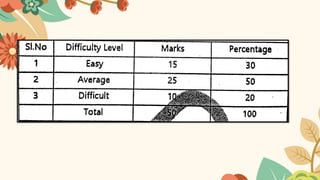
Tests are used to measure student performance and identify weaknesses. There are several types of tests, including paper/pencil tests, oral tests, aptitude tests, intelligence tests, placement tests, diagnostic tests, and achievement tests. Diagnostic tests identify specific difficulties to help teachers provide remedial instruction, while achievement tests assess student mastery of predetermined objectives. Proper test construction involves planning, blueprinting, writing questions, and analyzing results.