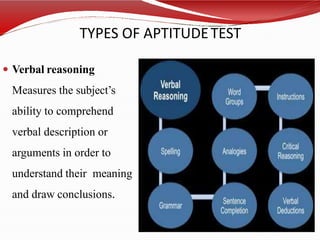
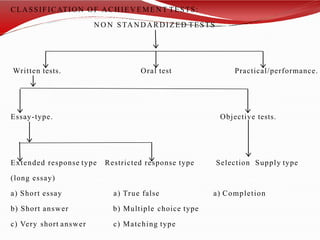
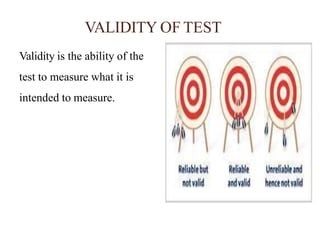
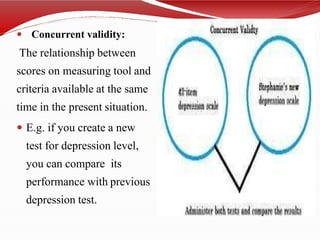
The document discusses standardized and non-standardized tests. It defines standardized tests as those with uniform administration and scoring to allow comparison between test takers. Examples include achievement, IQ, and aptitude tests. Non-standardized tests are constructed by teachers and vary in their administration. The document outlines the key characteristics, uses, and types of both standardized and non-standardized tests. It also discusses test validity, reliability, objectivity, and construction.




![STANDARDIZED TESTS:
Standardized test are those test stated the uniformity and
equality in the scoring and administrating and interpreting
the result
e.g. Any examination in which the same test is given in the
same manner to all students.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/standardizednonstandardizedtests-2nd-ppt-240308083332-4d39bef8/85/Standardized-Non-Standardized-Tests-2nd-ppt-pptx-5-320.jpg)