This document defines and provides examples of different types of tooth structures and replacement patterns in animals:
- Monophyodont animals have one set of teeth that are not replaced, like beluga whales.
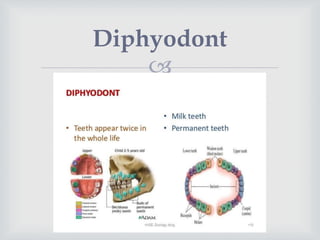
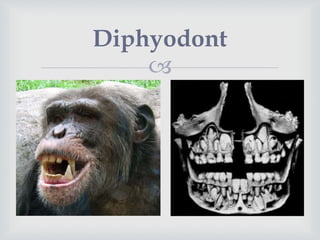
- Diphyodont animals have two sets of teeth - deciduous (baby) teeth that are replaced by permanent teeth, like humans.
- Polyphyodont animals have multiple successive sets of teeth throughout life, like crocodiles and geckos.
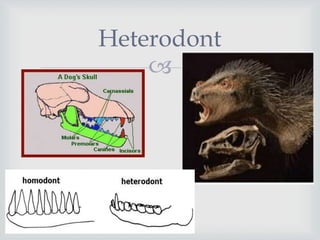
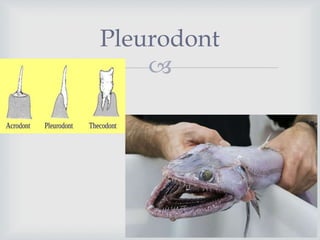
- Different tooth morphologies include homodont (similar teeth), heterodont (different teeth), and bunodont (teeth with tubercles). Tooth attachment structures also vary between animals.