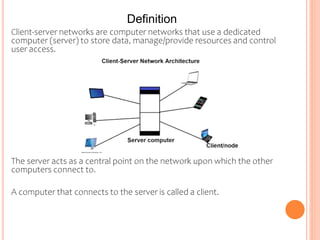
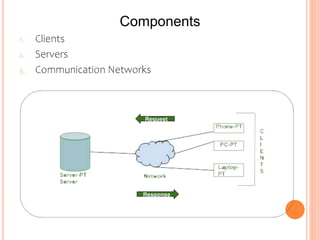
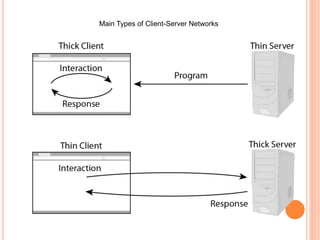
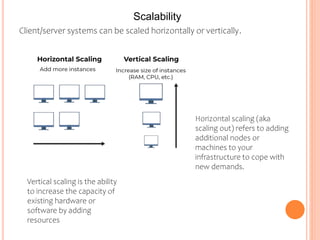
1) Client-server networks have dedicated servers that store data and resources while clients access these servers.
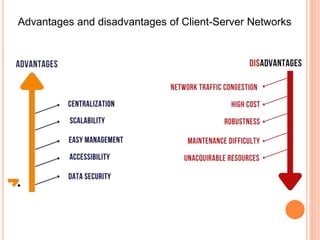
2) They enable efficient sharing of resources, scalability, security, data management, and collaboration across networks.
3) Servers manage network resources like files, devices, and processing power while clients rely on servers and run applications like email clients.