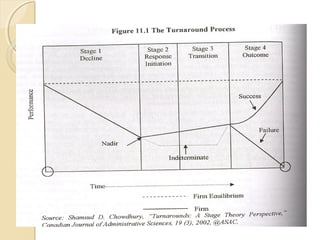
This document outlines Shamsud Chowdhury's stage theory model of the turnaround process. It identifies four stages: decline, response initiation, transition, and outcome. In the decline stage, performance deteriorates to a low point. In response initiation, strategic or operating responses are implemented to address the cause of decline. The transition stage involves time for results to manifest. In the outcome stage, performance is measured against the same metrics as decline to determine if the turnaround was successful in recovering sustainable performance. The model provides a framework for understanding the process of reversing organizational decline.